Abstract
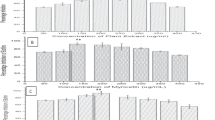
Antibiotic resistance, which has increased rapidly in recent years because of uncontrolled and unconscious antibiotic consumption, poses a major threat to public health. The inadequacy of existing antibiotics has increased the need for new, effective, and less toxic antibiotic raw materials or antibiotic derivatives. Pecan (Carya illinoinensis) and Chestnut (Castanea sativa) flowers possess abundant pollen contents and exhibit similar morphological features. The purpose of this study was to compare these two flower extracts in terms of their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Total phenolic content, total flavonoid contents, and phenolic components were also analyzed in aquatic and ethanolic extracts. Antioxidant activities were measured using ferric reducing/antioxidant capacity (FRAP) and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) methods. Antimicrobial and antifungal activities were compared by means of agar diffusion tests against bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Mycobacterium smegmatis, Acinetobacter haemolyticus, and Chromobacterium violaceum, and the yeasts Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis. Anti-quorum sensing (anti-QS), anti-biofilm, and anti-swarming (SW) activities were also studied against Chromobacterium violaceum ATCC 31532, Chromobacterium violaceum ATCC 12472, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01, respectively. Both extracts were rich in ellagic acid and gallic acid and exhibited similar antioxidant properties. Both flower extracts exhibited high antimicrobial and antifungal activities as well as anti-biofilm, anti-QS, and anti-SW activities.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdallah HM, Salama MM, Abd-Elrahman EH, El-Maraghy SA (2011) Antidiabetic activity of phenolic compounds from pecan bark in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Phytochem Lett 4(3):337–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytol.2011.07.004
Barreira JC, Ferreira IC, Oliveira MBP, Pereira JA (2008) Antioxidant activities of the extracts from chestnut flower, leaf, skins and fruit. Food Chem 107(3):1106–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.09.030
Benzie IFF, Strain JJ (1999) Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. In: Abelson J (ed) In methods in enzymol, vol 299. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99005-5
Bottari NB, Lopes LQS, Pizzuti K, dos Santos Alves CF, Corrêa MS, Bolzan P et al (2017) Antimicrobial activity and phytochemical characterization of Carya illinoensis. Microb Pathog 104:190–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.01.037
Can Z, Yildiz O, Sahin H, Turumtay EA, Silici S, Kolayli S (2015) An investigation of Turkish honeys: their physico-chemical properties, antioxidant capacities and phenolic profiles. Food Chem 180:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.024
Caxambu S, Biondo E, Kolchinski EM, Padilha RL, Brandelli A, SANT’ANNA V (2016) Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of pecan nut [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh) C. Koch] shell aqueous extract on minimally processed lettuce leaves. Food Sci Technol 36:42–45. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-457X.0043
Chebil L, Humeau C, Anthoni J, Dehez F, Engasser JM, Ghoul M (2007) Solubility of flavonoids in organic solvents. J Chem Eng Data 52(5):1552–1556. https://doi.org/10.1021/je7001094
Daikh A, Segueni N, Dogan NM, Arslan S, Mutlu D et al (2020) Comparative study of anti-biofilm, cytotoxic activity and chemical composition of algerian propolis. J Apicul Res 59(2):160–169. https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.2019.1701777
De Marco S, Piccioni M, Pagiotti R, Pietrella D (2017) Anti-biofilm and antioxidant activity of propolis and bud poplar resins versus Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Evid-Based Comp Alter Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5163575
do Prado ACP, Aragão AM, Fett R, Block JM (2009) Antioxidant properties of pecan nut [Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) C. Koch] shell infusion. Grasas Aceites 60(4):330–335. https://doi.org/10.3989/gya.107708
Ekşi S, Esertaş ÜZÜ, Kilic AO, Ejder N, Uzunok B (2020) Determination of the antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects and ‘quorum sensing’ inhibition potentials of Castanea sativa mill. extracts. Not Bot Horti Agrobot Cluj-Napoc 48(1):66–78
Fazli M, Almblad H, Rybtke ML, Givskov M, Eberl L, Tolker-Nielsen T (2014) Regulation of biofilm formation in P seudomonas and B urkholderia species. Environ Microbiol 16(7):1961–1981. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.12448
Franklin MJ, Chang C, Akiyama T, Bothner B (2015) New technologies for studying biofilms. Microb Biofilms. https://doi.org/10.1128/9781555817466.ch1
Fukumoto LR, Mazza G (2000) Assessing antioxidant and prooxidant activities of phenolic compounds. J Agric Food Chem 48(8):3597–3604. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf000220w
Krzyżek P (2019) Challenges and limitations of anti-quorum sensing therapies. Front Microbiol 10:2473. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02473
Larrosa M, García-Conesa MT, Espín JC, Tomás-Barberán FA (2010) Ellagitannins, ellagic acid and vascular health. Mol Asp Med 31(6):513–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2010.09.005
Laura A, Vazquez-Flores AA, Alvarez-Parrilla E, Rodrigo-García J, Medina-Campos ON et al (2014) Content of major classes of polyphenolic compounds, antioxidant, antiproliferative, and cell protective activity of pecan crude extracts and their fractions. J Func Foods 7:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2014.02.008
McLean RJC, Pierson LS, Fuquac C (2004) A simple screening protocol for the identification of quorum signal antagonist. J Microbiol Methods 58(3):351–360
Molyneux P (2004) The use of the stable free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) for estimating antioxidant activity. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 26(2):211–219
Müller LG, Pase CS, Reckziegel P, Barcelos RCS, Boufleur N et al (2013) Hepatoprotective effects of pecan nut shells on ethanol-induced liver damage. Exp Toxicol Pathol 65:165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2011.08.002
Pereira C, Barros L, Carvalho AM, Ferreira IC (2013) Use of UFLC-PDA for the analysis of organic acids in thirty-five species of food and medicinal plants. Food Anal Met 6(5):1337–1344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-012-9548-6
Plaza M, Pozzo T, Liu J, Gulshan AKZ, Turner C, Nordberg KE (2014) Substituent effects on in vitro antioxidizing properties, stability, and solubility in flavonoids. J Agric Food Chem 62(15):3321–3333. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf405570u
Rashid MH, Kornberg A (2000) In organic polyphosphate is needed for swimming, swarming, and twitching motilities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(9):4885–4890
Rice SA, Koh KS, Queck SY, Labbate M, Lam K, Kjelleberg S (2005) Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues. J Bacteriol 187(10):3477–3485. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.10.3477-3485.2005
Ronsisvalle S, Lissandrello E, Fuochi V, PetronioPetronio G, Straquadani C et al (2019) Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of Casteanea sativa Miller chestnut honey produced on Mount Etna (Sicily). Nat Prod Res 33(6):843–850. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2017.1413568
Rumbaugh KP, Diggle SP, Watters CM, Ross-Gillespie A, Griffin AS, West SA (2009) Quorum sensing and the social evolution of bacterial virulence. Curr Biol 19(4):341–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.01.050
Salwiczek M, Qu Y, Gardiner J, Strugnell RA, Lithgow T, McLean KM, Thissen H (2014) Emerging rules for effective antimicrobial coatings. Trends Biotech 32(2):82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.09.008
Sapkota K, Park SE, Kim JE, Kim S, Choi HS, Chun HS, Kim SJ (2010) Antioxidant and anti-melanogenic properties of chestnut flower extract. Biosci Biotech Biochem 74(8):1527–1533. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.100058
Savic IM, Jocic E, Nikolic VD, Popsavin MM, Rakic SJ, Savic-Gajic IM (2019) The effect of complexation with cyclodextrins on the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of ellagic acid. Pharm Dev Technol 24(4):410–418. https://doi.org/10.1080/10837450.2018.1502318
Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventós RM (1999) Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. In: Abelson J (ed) In methods in enzymology, vol 299. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 152–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(99)99017-1
Society TM, Grup AÇ (2016) Antibiotic susceptibility testing, EUCAST: practice, interpretation and expert guidelines. Turk Mikrobiol Cem Derg 46
Sorucu A, Ceylan Ö (2021) Determination of antimicrobial and anti-quorum sensing activities of water and ethanol extracts propolis. Ankara Univ Vet Fak Derg 68(4):373–381. https://doi.org/10.33988/auvfd.793632
Svečnjak L, Marijanović Z, Okińczyc P, Marek Kuś P, Jerković I (2020) Mediterranean propolis from the Adriatic sea islands as a source of natural antioxidants: comprehensive chemical biodiversity determined by GC-MS, FTIR-ATR, UHPLC-DAD-QqTOF-MS DPPH and FRAP assay. Antioxidants 9(4):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9040337
Truchado P, Gil-Izqierdo A, Tomas-Barberan F, Allenda A (2009) Inhibition by chestnut honey of N-Acyl-L-homo serine lactones and biofilm formation in Erwinia carotovora, Yersinia enterocolitica and Aeromonas hydrophila. J Agric Food Chem 57(23):11186–11193. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9029139
Turski MP, Chwil S, Turska M, Chwil M, Kocki T et al (2016) An exceptionally high content of kynurenic acid in chestnut honey and flowers of chestnut tree. J Food Comp Anal 48:67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2016.02.003
Woods GL, Brown-Elliott BA, Desmond EP, Hall GS, Heifets L et al (2003) Susceptibility testing of mycobacteria, nocardiae, and other aerobic actinomycetes; approved standard. NCCLS document M24-A, 23 (18)
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by UZES, YK, ASK and SK. The first draft of the manuscript was written by UZES and SK and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Üreyen Esertaş, Ü.Z., Kara, Y., Kiliç, A.O. et al. A comparative study of antimicrobial, anti-quorum sensing, anti-biofilm, anti-swarming, and antioxidant activities in flower extracts of pecan (Carya illinoinensis) and chestnut (Castanea sativa). Arch Microbiol 204, 589 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03172-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03172-6