Abstract
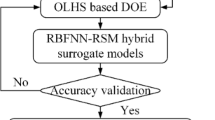
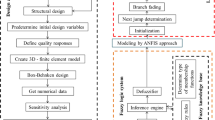
This paper proposes a modified preference selection index (MPSI) to improve the efficiency and reliability of the multi-criteria decision-making process. MPSI absorbs the high efficiency of the preference selection index (PSI) and enhances the anti-interference ability of some performance indicators. Moreover, a lightweight optimization method based on multi-performance is proposed, combining Hammersley, the radial basis function neural networks-response surface method (RBFNN-RSM), and the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II (NSGA-II) and MPSI. First, the finite element model and rigid-flexible coupled virtual prototype model are established and verified and the fatigue life of the original frame is calculated. Second, the size and shape of the frame were taken as variables, and the mass, root mean square stress, and life were taken as objectives. The experimental scheme is determined, and the RBFNN-RSM hybrid surrogate model and NSGA-II are used to find the optimal solution set. Finally, the optimal solution is determined using the PSI, principal component analysis-gray relational analysis (P-GRA), and MPSI. The results show that MPSI has higher reliability than PSI; the MPSI has higher efficiency than P-GRA.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- QSM:
-
Quasi-static method
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- TDVM:
-
Time-domain vibration method
- MPSI:
-
Modified preference selection index
- FDVM:
-
Frequency-domain vibration method
- FEM:
-
Finite element model
- MOOP:
-
Multi-objective optimization problem
- RF-VPM:
-
Rigid-flexible coupled virtual prototype model
- MCDM:
-
Multi-criteria decision-making
- PSD:
-
Power spectral density
- ANN:
-
Artificial neutral network
- FRF:
-
Frequency response function
- RSM:
-
Response surface method
- GRG:
-
Gray relational grade
- RBFNN:
-
Radial basis function neural networks
- LSS:
-
Leaf spring suspension
- SVM:
-
Support vector machine
- ASS:
-
Air spring suspension
- MOACO:
-
Multi-objective ant colony optimization
- DOFs:
-
Degrees of freedom
- MOPSOs:
-
Multi-objective particle swarm optimizers
- UTS:
-
Ultimate tensile strength
- NSGA:
-
Non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm
- RMS:
-
Root mean square
- GRA:
-
Gray relational analysis
- DOE:
-
Design of experiment
- PSI:
-
Preference selection index
- PC:
-
Principal component
- TOPSIS:
-
Technique for order of preference by similarity to ideal solution
- P-GRA:
-
Principal component analysis-gray relational analysis
References
Attri R, Grover S (2015) Application of preference selection index method for decision making over the design stage of production system life cycle. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 27(2):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksues.2013.06.003
Azizian M, Almeida JHS (2022) Stochastic, probabilistic and reliability analyses of internally-pressurised filament wound composite tubes using artificial neural network metamodels. Mater Today Commun. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103627
Carpinteri A, Fortese G, Ronchei C, Scorza D, Spagnoli A, Vantadori S (2016) Fatigue life evaluation of metallic structures under multiaxial random loading. Int J Fatigue 90:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2016.05.007
Ceyhanli UT, Bozca M (2020) Experimental and numerical analysis of the static strength and fatigue life reliability of parabolic leaf springs in heavy commercial trucks. Adv Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814020941956
Cheng J, Li QS (2008) Application of the response surface methods to solve inverse reliability problems with implicit response functions. Comput Mech 43(4):451–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-008-0320-0
Cuong-Le T, Minh H-L, Khatir S, Wahab MA, Tran MT, Mirjalili S (2021) A novel version of Cuckoo search algorithm for solving optimization problems. Expert Syst Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115669
Eaton J, Yang S, Gongora M (2017) Ant colony optimization for simulated dynamic multi-objective railway junction rescheduling. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 18(11):2980–2992. https://doi.org/10.1109/tits.2017.2665042
Epaarachchi JA (2006) Effects of static–fatigue (tension) on the tension–tension fatigue life of glass fibre reinforced plastic composites. Compos Struct 74(4):419–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2005.04.022
Gu Z, Mi C, Wang Y, Jiang J (2012) A-type frame fatigue life estimation of a mining dump truck based on modal stress recovery method. Eng Fail Anal 26:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2012.07.004
Khatir S, Boutchicha D, Le Thanh C, Tran-Ngoc H, Nguyen TN, Abdel-Wahab M (2020) Improved ANN technique combined with Jaya algorithm for crack identification in plates using XIGA and experimental analysis. Theoret Appl Fract Mech. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2020.102554
Khatir S, Wahab MA (2019) Fast simulations for solving fracture mechanics inverse problems using POD-RBF XIGA and Jaya algorithm. Eng Fract Mech 205:285–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.09.032
Khatir S, Wahab MA, Boutchicha D, Khatir T (2019) Structural health monitoring using modal strain energy damage indicator coupled with teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm and isogoemetric analysis. J Sound Vib 448:230–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2019.02.017
Khatir S, Tiachacht S, Le Thanh C, Ghandourah E, Mirjalili S, Wahab MA (2021) An improved artificial neural network using arithmetic optimization algorithm for damage assessment in FGM composite plates. Compos Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114287
Le-Rademacher J, Billard L (2016) Principal component analysis for histogram-valued data. Adv Data Anal Classif 11(2):327–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11634-016-0255-9
Li F, Meng G, Sha L, Zhou L (2011) Robust optimization design for fatigue life. Finite Elem Anal Des 47(10):1186–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.finel.2011.05.009
Lin SJ, Lu IJ, Lewis C (2007) Grey relation performance correlations among economics, energy use and carbon dioxide emission in Taiwan. Energy Policy 35(3):1948–1955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2006.06.012
Maniya KD, Bhatt MG (2011) An alternative multiple attribute decision making methodology for solving optimal facility layout design selection problems. Comput Ind Eng 61(3):542–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2011.04.009
Maniya K, Bhatt MG (2010) A selection of material using a novel type decision-making method: Preference selection index method. Mater Des 31(4):1785–1789. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.11.020
Mi C, Zhengqi Gu, Yang Q, Nie D (2012) Frame fatigue life assessment of a mining dump truck based on finite element method and multibody dynamic analysis. Eng Fail Anal 23:18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2012.01.014
Mi C, Liu J, Xiao X, Liu J, Ming R, Li W, Yao Q (2019) Interval multi-objectives optimization of electric wheel dump truck frame based on blind number theory. Appl Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9204214.
Shi L, Sun B, Ibrahim DS (2019) An active learning reliability method with multiple kernel functions based on radial basis function. Struct Multidiscip Optim 60(1):211–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02210-0
Srinivas N, Deb K (1994) Muiltiobjective optimization using nondominated sorting in genetic algorithms. Evol Comput 2(3):221–248. https://doi.org/10.1162/evco.1994.2.3.221
Tiwari D, Sherwani AF, Muqeem M, Goyal A (2019) Parametric optimization of organic Rankine cycle using TOPSIS integrated with entropy weight method. Energy Sour Part A. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1649755
Tran-Ngoc H, Khatir S, Ho-Khac H, De Roeck G, Bui-Tien T, Abdel Wahab M (2021) Efficient artificial neural networks based on a hybrid metaheuristic optimization algorithm for damage detection in laminated composite structures. Compos Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.113339
Vahdani B, Meysam Mousavi S, Ebrahimnejad S (2014) Soft computing-based preference selection index method for human resource management. J Intel Fuzzy Syst 26(1):393–403. https://doi.org/10.3233/ifs-120748
Wang D, Li S (2021) Collaborative optimization design of lightweight and crashworthiness of the front-end structures of automobile body using HW–GRA for Pareto mining. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406221992802
Wang D, Xie C (2019) Contribution analysis of the cab-in-white for lightweight optimization employing a hybrid multi-criteria decision-making method under static and dynamic performance. Eng Optim 52(11):1903–1922. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215x.2019.1693553
Wang S, Wang D (2021) Crashworthiness-based multi-objective integrated optimization of electric vehicle chassis frame. Arch Civil Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00242-2
Wang D, Zhang X (2022) Application of the preference selection index method in multi-objective lightweight design of heavy commercial vehicle frames. Eng Optim. https://doi.org/10.1080/0305215x.2022.2058498
Wang D, Wenchao Xu, Wang Y, Gao J (2020a) Design and optimization of tapered carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer rim for carbon/aluminum assembled wheel. Polym Compos 42(1):253–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.25822
Wang Z, Almeida Jr JHS, St-Pierre L, Wang Z, Castro SGP (2020b) Reliability-based buckling optimization with an accelerated Kriging metamodel for filament-wound variable angle tow composite cylinders. Compos Struct. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112821
Wang D, Xie C, Wang Y (2021a) Multi-objective lightweight and crashworthiness collaborative optimisation of commercial vehicle cab. Int J Crashworth 27:1017–1031
Wang Q, Zhou J, Gong D, Wang T, Sun Yu (2021b) Fatigue life assessment method of bogie frame with time-domain extrapolation for dynamic stress based on extreme value theory. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2021.107829
Wang Z, Almeida JHS, Ashok A, Wang Z, Castro SGP (2022) Lightweight design of variable-angle filament-wound cylinders combining Kriging-based metamodels with particle swarm optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03227-8
Wauters J, Couckuyt I, Knudde N, Dhaene T, Degroote J (2020) Multi-objective optimization of a wing fence on an unmanned aerial vehicle using surrogate-derived gradients. Struct Multidiscip Optim 61(1):353–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02364-x
Xiong F, Wang D, Ma Z, Chen S, Lv T, Fang L (2017a) Structure-material integrated multi-objective lightweight design of the front end structure of automobile body. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57(2):829–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1778-1
Xiong F, Wang D, Zhang S, Cai K, Wang S, Fang L (2017b) Lightweight optimization of the side structure of automobile body using combined grey relational and principal component analysis. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57(1):441–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1749-6
Yaich A, El Hami A (2019) Multiaxial fatigue damage estimation of structures under random vibrations using Matsubara’s criterion. Int J Fatigue 124:253–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2019.03.003
Zhang H, Huang G, Yu D (2020) Numerical modeling for the frame structure of light van-type electric truck. Sci Progress. https://doi.org/10.1177/0036850420927204
Zheng S, Cheng K, Wang J, Liao Q, Liu X, Liu W (2015) Failure analysis of frame crack on a wide-body mining dump truck. Eng Fail Anal 48:153–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2014.11.013
Zhu P, Pan F, Chen W, Zhang S (2012) Use of support vector regression in structural optimization: application to vehicle crashworthiness design. Math Comput Simul 86:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matcom.2011.11.008
Funding
This work was supported by the [National Natural Science Foundation of China] under Grant [Number 51975244].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this work.
Replication of results
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mehmet Polat Saka
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Wang, D., Kong, D. et al. The anti-fatigue lightweight design of heavy tractor frame based on a modified decision method. Struct Multidisc Optim 65, 280 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03385-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03385-9