Abstract
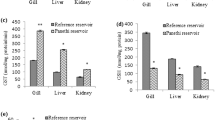
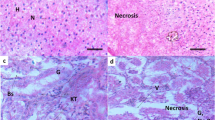
Fish consumption from contaminated water-bodies is a serious health issue. This study conducted to reveal the presence of heavy metals and bisphenols in Vembanad lake, an exploiting tourist spot in Kerala, receiving untreated agricultural, domestic, municipal, and industrial effluents. We evaluated aquatic contaminant impact on hepatic stress markers in Etroplus suratensis from fragile Vembanad lake. The significant difference in water physiochemical parameters, the concentration of heavy metals, and bisphenols (BPA and BPS) were studied. Hepatic tissue of E. suratensis inhabited in lake featured with high iron (11.29 ± 0.39 ppm) and BPA (0.02412 ± 0.0031 µg/mL) content along with an increased hepatic stress marker and distorted hepatic structure. The study highlights the presence of high iron and BPA in edible fish. The study recommends monitoring of physiochemical characters of freshwater lakes is essential for better survival of freshwater flora and fauna.

Source: Google map). a Kumarakom, Vembanad Lake, Kottayam, Kerala, India. The sampling area covered a total distance of 13.06 km from Vechoor to Puthuchara of Kumarakom. b J S farm, Neendoor, Kottayam, Kerala, India


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham R, de Alwis Goonatilake S, Fernado M, Kotagama O (2019) Etroplus suratensis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T172368A60612143
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. In: Methods in enzymology. Academic Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05016-3
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. Am Public Health Assoc. https://doi.org/10.2105/ajph.56.3.387
Aristiawan Y, Aryana N, Putri D, Styarini D (2015) Analytical method development for bisphenol a in tuna by using high performance liquid chromatography UV. Procedia Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2015.12.042
Belfroid A, van Velzen M, van der Horst B, Vethaak D (2002) Occurrence of bisphenol A in surface water and uptake in fish: evaluation of field measurements. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(02)00157-1
Brede C, Fjeldal P, Skjevrak I, Herikstad H (2003) Increased migration levels of bisphenol A from polycarbonate baby bottles after dishwashing boiling and brushing. Food Additi Contam. https://doi.org/10.1080/0265203031000119061
Budhlani GN, Musaddia M, Khan J, Zabir N (2014) Seasonal variation in physicochemical characteristics of Bor and Vidarbha (Idarba) Rivers of Amravati (MS), India. Ind J Appl Res. https://doi.org/10.15373/2249555x/jan2014/153
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52032-6
Canario J, Vale C, Caetano M, Madureira MJ (2003) Mercury in contaminated sediments and pore waters enriched in sulphate Tagus Estuary Portugal. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0269-7491(03)00234-3
Chandrasekar S, Nich T, Tripathi G, Sahu NP, Pal AK, Dasgupta S (2014) Acclimation of brackish water pearl spot (Etroplus suratensis) to various salinities: relative changes in abundance of branchial Na+/K+-ATPase and Na+/K+/2Cl− co-transporter in relation to osmoregulatory parameters. Fish Physiol Biochem 40(3):983–996. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-013-9899-y
Darbre PD (2018) Overview of air pollution and endocrine disorders. Int J Gen Med. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijgm.s102230
Denton G, Burdon JC (1986) Trace metals in fish from the Great Barrier Reef. Mar Pollut Bull. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326x(86)90601-6
Elahee KB, Bhagwant S (2007) Hematological and gill histopathological parameters of three tropical fish species from a polluted lagoon on the west coast of Mauritius. Ecotoxicol Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.06.003
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Faheem M, Lone KP (2017) Oxidative stress and histopathologic biomarkers of exposure to bisphenolA in the freshwater fish Ctenopharyngodon idella. Braz J Pharm. https://doi.org/10.1590/s2175-97902017000317003
Heming TA, Blumhagen KA (1988) Plasma acid base and electrolyte states of rainbow trout exposed to alum aluminum sulphate in acidic and alkaline environments. Aquat Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-445x(88)90030-6
James MO (1986) Xenobiotic conjugation in fish and other aquatic species. ACS Symp Ser. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-1986-0299.ch002
Jin H, Zhu L (2016) Occurrence and partitioning of bisphenol analogues in water and sediment from Liaohe River Basin and Taihu Lake, China. Water Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.059
Kakkar R, Kalra J, Mantha SV, Prasad K (1995) Lipid peroxidation and activity of antioxidant enzymes in diabetic rats. Mol Cell biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01322333
Ke X, Wang J, Yuan J, Gong X (2010) Studies on the pathogenicity and histopathology of Fusarium in fish. Acta Hydrobiol Sin. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1035.2010.00943
Knapton JR (1985) Field guidelines for collection, treatment, and analysis of water samples, Montana District. US Geological Survey, Helena. https://doi.org/10.3133/ofr85409
Laxmilatha P, Velayudhan TS, Kripa V, Jenni B, Alloycious PS (2005) Biology of the black clam Villorita cyprinoides (Gray) in the backwaters of Vembanad Lake. Indian J Fish 52(3):361–366
Ramasamy EV, Jayasooryan KK, Chandran MS, Mohan M (2017) Total and methyl mercury in the water, sediment, and fishes of Vembanad, a tropical backwater system in India. Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5845-2
Rezaee M, Yamini Y, Shariati S, Esrafili A, Shamsipur M (2009) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography UV detection as a very simple rapid and sensitive method for the determination of bisphenol A in water samples. J Chromatogr A. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2008.12.091
Rocha BA, Azevedo LF, Gallimberti M, Campiglia AD, Barbosa JF (2015) High levels of bisphenol A and bisphenol S in Brazilian thermal paper receipts and estimation of daily exposure. J Toxicol Environ Health A. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2015.1083519
Synudeen S (2017) Fish diversity in Vembanad Lake Kerala India. Afr J Aquat Sci. https://doi.org/10.4314/jas.v32i1a.11
Saraswathy R, Muralidhar M, Sundaray JK, Lalitha N, Kumararaja P (2015) Water quality management in fish hatchery and growout systems. In: Advances in marine and brackishwater aquaculture. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2271-2-20
Selvaraj KK, Shanmugam G, Sampath S, Joakim Larsson DG, Ramaswamy BR (2014) GC MS determination of bisphenol A and alkylphenol ethoxylates in river water from India and their ecotoxicological risk assessment. Ecotox Environ Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.09.006
Shyleshchandran MN, Mohan M, Ramasamy EV (2018) Risk assessment of heavy metals in Vembanad Lake sediments (south-west coast of India), based on acid-volatile sulfide (AVS) simultaneously extracted metal (SEM) approach. Environ Sci Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0997-8
Slaninova A, Machova J, Svobodova Z (2014) Fish kill caused by aluminum and iron contamination in a natural pond used for fish rearing a case report. Vet Med. https://doi.org/10.17221/7821-vetmed
Song Y, Ji J, Mao C, Yang Z, Yuan X, Ayoko GA, Frost RL (2010) Heavy metal contamination in suspended solids of Changjiang River environmental implications. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.07.020
Sruthy S, Ramasamy EV (2017) Microplastic pollution in Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India: the first report of microplastics in lake and estuarine sediments in India. Environ Pollut 222:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.038
Vasanthi LA, Revathi P, Mini J, Munuswamy N (2013) Integrated use of histological and ultrastructural biomarkers in Mugil cephalus for assessing heavy metal pollution in Ennore estuary Chennai. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.021
Verma A, Subramanian V, Ramesh R (2002) Methane emissions from a coastal lagoon Vembanad Lake West Coast, India. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00288-0
Vidya V, Prasad G, Sheela AM (2020) Assessment of threats to a Ramsar site from seafood processing operation effluents. Lakes Reserv Res Manag. https://doi.org/10.1111/lre.12321
Vincy MV, Rajan B, Pradeep Kumar AP (2012) Water quality assessment of a tropical wetland ecosystem with special reference to backwater tourism Kerala South India. Int Res J Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2012.657694
Wan Y, Xia W, Yang S, Pan X, He Z, Kannan K (2018) Spatial distribution of bisphenol S in surface water and human serum from Yangtze River watershed China. Implications for exposure through drinking water. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018
Wong YM, Li R, Lee CK, Wan HT, Wong CK (2017) The measurement of bisphenol A and its analogues perfluorinated compounds in twenty species of freshwater and marine fishes a time trend comparison and human health-based assessment. Mar Pollut Bull. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.05.046
Xavier ND, Nandan SB, Jayachandran PR, Anu PR, Midhun AM, Mohan D (2019) Chronic effects of copper and zinc on the fish, Etroplus suratensis (Bloch, 1790) by continuous flow through (CFT) bioassay. Mar Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2018.11.002
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi. We thank the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for the excellent research facilities supported through the DBT-MSUB-IPLS (BUILDER) program. We also thank Mr. Dineep Vasudevan, Inter-University Instrumentation Centre, School of Environmental Sciences, Mahatma Gandhi University for technical assistance on this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pettamanna, A., Raghav, D. & Nair, R.H. Hepatic Toxicity in Etroplus suratensis (Bloch 1790): An Economically Important Edible Fish in Vembanad Fresh Water Lake, Kerala, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 105, 565–571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02987-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02987-7