Abstract
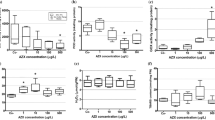
This study investigated the occurrence of toxicity, expressed as damage to the photosynthetic apparatus, in the aquatic fern Azolla filiculoides and the lichen Xanthoria parietina following treatments with diclofenac at different concentrations (0.1, 1, 10 and 100 mg/L) and different exposure times (24, 48, 72 and 240 h). Measurements of photosynthetic efficiency, chlorophyll content and chlorophyll degradation indicated dose- and time-dependent toxicity, since significant differences with control samples as well as among treatments, emerged mainly for the highest concentration (100 mg/L) and the longest time (240 h). In addition, also the mycobiont of the lichen X. parietina showed similar toxic effects, expressed as ergosterol content. The absence of relevant alterations at the lowest concentration (0.1 mg/L) suggested a very limited susceptibility of these species to environmentally relevant levels of this pharmaceutical.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alem MAS, Douglas LJ (2004) Effects of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on biofilms and planktonic cells of Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:41–47
Alem MAS, Douglas LJ (2005) Prostaglandin production during growth of Candida albicans biofilms. J Med Microbiol 54:1001–1005
Augusto S, Shukla V, Upreti DK, Paoli L, Vannini A, Loppi S, Nerín C, Domeño C, Schuhmacher M (2017) Biomonitoring of airborne persistent organic pollutants using lichens. In: Aničić Urošević M, Vuković G, Tomašević M (eds) Biomonitoring of air pollution using mosses and lichens: a passive and active approach—state of the art research and perspectives. Nova Publisher, Serbia, pp 137–175
Bačkor M, Loppi S (2009) Interactions of lichens with heavy metals. Biol Plant 53(2):214–222
Bartha B, Huber C, Schröder P (2014) Uptake and metabolism of diclofenac in Typha latifolia—how plants cope with human pharmaceutical pollution. Plant Sci 227:12–20
Basile A, Rigano D, Loppi S, Di Santi A, Nebbioso A, Sorbo S, Conte B, Paoli L, De Ruberto F, Molinari AM, Altucci L, Bontempo L (2015) Antiproliferative, antibacterial and antifungal activity of the lichen Xanthoria parietina and its secondary metabolite parietin. Int J Mol Sci 16(4):7861–7875
Bink A, Kucharíková S, Neirinck B, Vleugels J, VanDijck P, Cammue BP, Thevissen K (2012) The nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug diclofenac potentiates the in vivo activity of caspofungin against Candida albicans biofilms. J Infect Dis 206:1790–1797
Carvalho PN, Basto MCP, Almeida CMR, Brix H (2014) A review of plant-pharmaceutical interactions: from uptake and effects in crop plants to phytoremediation in constructed wetlands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:11729–11763
Chefetz B, Mualem T, Ben-Ari J (2008) Sorption and mobility of pharmaceutical compounds in soil irrigated with reclaimed wastewater. Chemosphere 73:1335–1343
Cleuvers M (2003) Aquatic ecotoxicity of pharmaceuticals including the assessment of combination effects. Toxicol Lett 142:185–194
Dahlman L, Zetherström M, Sundberg B, Näsholm T, Palmqvist K (2002) Measuring ergosterol and chitin in lichens. In: Kranner I, Beckett R, Varma A (eds) Protocols in lichenology: culturing, biochemistry, ecophysiology and use in biomonitoring. Springer, Berlin, pp 348–362
Domínguez-Morueco N, Moreno H, Barreno E, Catalá M (2014) Preliminary assessment of terrestrial microalgae isolated from lichens as testing species for environmental monitoring: lichen phycobionts present high sensitivity to environmental micropollutants. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 99:35–44
Ells R, Kock JL, Van Wyk PW, Botes PJ, Pohl CH (2009) Arachidonic acid increases antifungal susceptibility of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis. J Antimicrob Chemother 63:124–128
Feito R, Valcárcel Y, Catalá M (2012) Biomarker assessment of toxicity with miniaturised bioassays: diclofenac as a case study. Ecotoxicology 21:289–296
Fekete-Kertész I, Kunglné-Nagy Z, Gruiz K, Magyar Á, Farkas É, Molnár M (2015) Assessing toxicity of organic aquatic micropollutants based on the total chlorophyll content of Lemna minor as a sensitive endpoint. Period Polytech Chem 59(4):262–271
Gessner MO (2005) Ergosterol as a measure of fungal biomass, In: Graça MAS, Bärlocher F, Gessner MO (eds) Methods to study litter decomposition, a practical guide. Springer, Berlin, pp. 189–195
Haap T, Triebskorn R, Köhler HR (2008) Acute effects of diclofenac and DMSO to Daphnia magna: immobilisation and hsp70-induction. Chemosphere 73(3):353–359
Halling-Sørensen B, Nielsen SN, Lanzky PF, Ingerslev F, Lützhøft HH, Jørgensen SE (1998) Occurrence, fate and effects of pharmaceutical substances in the environment—a review. Chemosphere 36(2):357–393
Huber C, Bartha B, Schröder P (2012) Metabolism of diclofenac in plants—hydroxylation is followed by glucose conjugation. J Hazard Mater 243:250–256
Khetan SK, Collins TJ (2007) Human pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment: a challenge to green chemistry. Chem Rev 107:2319–2364
Ku EC, Lee W, Kothari HV, Scholer DW (1986) Effect of diclofenac sodium on the arachidonic acid cascade. Am J Med 80:18–23
Kummerová M, Zezulka Š, Babula P, Tříska J (2016) Possible ecological risk of two pharmaceuticals diclofenac and paracetamol demonstrated on a model plant Lemna minor. J Hazard Mater 302:351–361
Lonappan L, Brar SK, Das RK, Verma M, Surampalli RY (2016) Diclofenac and its transformation products: environmental occurrence and toxicity—a review. Environ Int 96:127–138
Loppi S (2014) Lichens as sentinels for air pollution at remote alpine areas (Italy). Environ Sci Poll Res 21(4):2563–2571
Loppi S, Paoli L (2015) Comparison of the trace element content in transplants of the lichen Evernia prunastri and in bulk atmospheric deposition: a case study from a low polluted environment (C Italy). Biologia 70(4):460–466
Loppi S, Paoli L, Gaggi C (2006) Diversity of epiphytic lichens and Hg contents of Xanthoria parietina thalli as monitors of geothermal air pollution in the Mt. Amiata area (central Italy). J Atmos Chem 53:93–105
Loppi S, Pozo K, Estellano VH, Corsolini S, Sardella G, Paoli L (2015) Accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by lichen transplants: comparison with gas-phase passive air samplers. Chemosphere 134:39–43
Paoli L, Fiorini E, Munzi S, Sorbo S, Basile A, Loppi S (2014) Uptake and acute toxicity of cerium in the lichen Xanthoria parietina. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 104:379–385
Parks LW, Casey WM (1995) Physiological implications of sterol biosynthesis in yeast. Annu Rev Microbiol 49:95–116
Pino MR, Muñiz S, Val J, Navarro E (2016) Phytotoxicity of 15 common pharmaceuticals on the germination of Lactuca sativa and photosynthesis of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Poll Res 23:22530–22541
Rakhshaee R, Khosravi M, Ganji MT (2006) Kinetic modeling and thermodynamic study to remove Pb (II), Cd (II), Ni (II) and Zn (II) from aqueous solution using dead and living Azolla filiculoides. J Hazard Mater 134:120–129
Rivera-Utrilla J, Sánchez-Polo M, Ferro-García M, Prados-Joya G, Ocampo-Pérez R (2013) Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 93:1268–1287
Ronen R, Galun M (1984) Pigment extraction from lichens with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and estimation of chlorophyll degradation. Environ Exp Bot 24(3):239–245
Rusu E, Radu-Popescu M, Pelinescu D, Vassu T (2014) Treatment with some anti-inflammatory drugs reduces germ tube formation in Candida albicans strains. Braz J Microbiol 45:1379–1383
Strasser RJ, Tsimilli-Michael M, Srivastava A (2004) Analysis of the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient. In: Papageorgiou GC, Govindjee (eds) Chlorophyll a fluorescence. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 321–362
Sundberg B, Ekblad A, Näsholm T, Palmqvist K (1999) Lichen respiration in relation to active time, temperature, nitrogen and ergosterol concentrations. Funct Ecol 13:119–125
Tigini V, Franchino M, Bona F, Varese GC (2016) Is digestate safe? A study on its ecotoxicity and environmental risk on a pig manure. Sci Total Environ 551:127–132
Vafaei F, Khataee AR, Movafeghi A, Lisar SS, Zarei M (2012) Bioremoval of an azo dye by Azolla filiculoides: study of growth, photosynthetic pigments and antioxidant enzymes status. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 75:194–200
Vannini A, Guarnieri M, Bačkor M, Biľová I, Loppi S (2015) Uptake and toxicity of glyphosate in the lichen Xanthoria parietina (L.) Th. Fr. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 122:193–197
Vannini A, Guarnieri M, Paoli L, Sorbo S, Basile A, Loppi S (2016) Bioaccumulation, physiological and ultrastructural effects of glyphosate in the lichen Xanthoria parietina (L.) Th. Fr. Chemosphere 164:233–240
Vieno N, Sillanpää M (2014) Fate of diclofenac in municipal wastewater treatment plant—a review. Environ Int 69:28–39
Yamamoto Y, Watanabe A (1974) Fatty acid composition of lichens and their phyco-and mycobionts. J Gen Appl Microbiol 20(2):83–86
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vannini, A., Paoli, L., Vichi, M. et al. Toxicity of Diclofenac in the Fern Azolla filiculoides and the Lichen Xanthoria parietina. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100, 430–437 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2266-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2266-4