Abstract
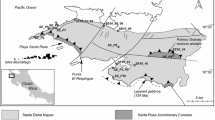
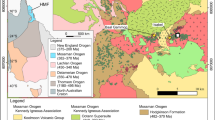
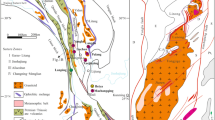
The Tiegelongnan porphyry-epithermal deposit (2089 Mt @ 0.53% Cu, 0.08 g/t Au) is host to a large variety of Cu-sulfide minerals, mainly chalcopyrite, bornite, covellite, digenite, enargite, and tennantite. We used LA-ICP-MS to investigate the trace element geochemistry of the Tiegelongnan Cu-sulfides, as well as pyrite, to understand the correlation between sulfides and trace elements, gold in particular, in the porphyry and epithermal systems. Porphyry mineralization consists of stage 1 chalcopyrite-pyrite ± molybdenite, stage 2 chalcopyrite-bornite, and stage 3 covellite. Epithermal sulfides form stage 4 pyrite-alunite, stage 5 digenite-bornite-chalcopyrite, and stage 6 enargite-tennantite ± tetrahedrite. Stage 2 chalcopyrite (S2 Ccp, median = 9.7 ppm Au) is the primary porphyry Au host, and stage 6 tennantite in alunite veins (S6 Tnt-s, median = 98.0 ppm Au) is the major epithermal Au host. These Au-rich sulfides formed under higher oxidation conditions, suggesting that a high oxidation state favors the incorporation of Au in Cu-sulfides. Gold contents in coeval chalcopyrite and bornite are positively correlated to temperature, and Au is enriched in chalcopyrite over bornite at low temperatures (< 350 ℃). Positive correlations between Au and As and Te in covellite and chalcopyrite result from the reaction of As3+ + (Au+/Ag+) + Te2− ↔ 4Cu+ + S2−. Epithermal chalcopyrite and bornite contain more As and Pd than that in porphyry stages, and high contents of As, Sn, Cd, Zn, Sb, Te, Au, and Bi in epithermal enargite and tennantite are likely the result of partitioning of these elements in sulfides at low epithermal temperatures. Epithermal overprinting likely leached Cu from earlier porphyry stage sulfides to precipitate high Cu-grade epithermal mineralization. The Cu-sulfides and related trace elements show a spatial distribution, potentially useful for the exploration of overprinted porphyry-epithermal systems.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brimhall G (1980) Deep hypogene oxidation of porphyry copper potassium-silicate protore at Butte, Montana; a theoretical evaluation of the copper remobilization hypothesis. Econ Geol 75:384–409
Catchpole H, Kouzmanov K, Fontboté L (2012) Copper-excess stannoidite and tennantite-tetrahedrite as proxies for hydrothermal fluid evolution in a zoned Cordilleran base metal district, Morococha, central Peru. Can Mineral 50:719–743
Charlat M, Levy C (1974) Substitutions multiples dans la série tennantite˗ tétraédrite. Bull Mineral 97:241–250
Chouinard A, Paquette J, Williams-Jones AE (2005) Crystallographic controls on trace-element incorporation in auriferous pyrite from the Pascua epithermal high-sulfidation deposit, Chile-Argentina. Can Mineral 43:951–963
Crespo J, Reich M, Barra F, Verdugo J, Martínez C (2018) Critical metal particles in copper sulfides from the supergiant Río Blanco porphyry Cu–Mo deposit, Chile. Minerals 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8110519
Deditius AP, Utsunomiya S, Ewing RC, Chryssoulis SL, Venter D, Kesler SE (2009) Decoupled geochemical behavior of As and Cu in hydrothermal systems. Geology 37:707–710
Deditius AP, Reich M, Kesler SE, Utsunomiya S, Chryssoulis SL, Walshe J, Ewing RC (2014) The coupled geochemistry of Au and As in pyrite from hydrothermal ore deposits. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 140:644–670
Deyell C, Hedenquist J (2011) Trace element geochemistry of enargite in the Mankayan district, Philippines. Econ Geol 106:1465–1478
Duran CJ, Barnes S-J, Corkery JT (2015) Chalcophile and platinum-group element distribution in pyrites from the sulfide-rich pods of the Lac des Iles Pd deposits, Western Ontario, Canada: implications for post-cumulus re-equilibration of the ore and the use of pyrite compositions in exploration. J Geochem Explor 158:223–242
Egozcue JJ, Pawlowsky-Glahn V, Mateu-Figueras G, Barcelo-Vidal C (2003) Isometric logratio transformations for compositional data analysis. Math Geol 35:279–300
Einaudi MT, Hedenquist JW, Inan EE (2003) Sulfidation state of fluids in active and extinct hydrothermal systems: transitions from porphyry to epithermal environments. Soc Econ Geol Spec Pub 10:285–314
Eldridge DL, Guo W, Farquhar J (2016) Theoretical estimates of equilibrium sulfur isotope effects in aqueous sulfur systems: highlighting the role of isomers in the sulfite and sulfoxylate systems. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 195:171–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2016.09.021
Fang X, Tang J, Song Y, Yang C, Ding S, Wang Y-y, Wang Q, Sun X-g, Li Y-b, Wei L-j (2015) Formation epoch of the South Tiegelong superlarge epithermal Cu (Au-Ag) deposit in Tibet and its geological implications. Acta Geosci Sin 36:168–176
Garza RAP, Titley SR, Pimentel F (2001) Geology of the Escondida porphyry copper deposit, Antofagasta region, Chile. Econ Geol 96:307–324
Genna D, Gaboury D (2015) Deciphering the hydrothermal evolution of a VMS system by LA-ICP-MS using trace elements in pyrite: an example from the Bracemac-McLeod eeposits, Abitibi, Canada, and implications for exploratio. Econ Geol 100:2087–2105
George LL, Cook NJ, Ciobanu CL (2017) Minor and trace elements in natural tetrahedrite-tennantite: effects on element partitioning among base metal sulfides. Minerals 7:1–25
Goh SW, Buckley AN, Lamb RN (2006) Copper (II) sulfide? Minerals Eng 19:204–208
Halley S, Dilles J, Tosdal R (2015) Footprints: hydrothermal alteration and geochemical dispersion around porphyry copper deposits. Soc Econ Geol Newsl 100:12–17
He W, Lin B, Yang HH, Fang X, Song YX, Wei SG, Hou L (2017) Fluid inclusion feature and its internal relationship with mineralization and epithermal alteration of the Tiegelongnan Cu-Au deposit. Acta Geosci Sin 38:638–650
He W, Lin B, Yang HH, Song YX (2018) Studies of metallic and trace minerals of the Tiegelongnan Cu-Au deposit, Central Tibet, China. Acta Geol Sin-Engl 92:1123–1138
Heinrich CA, Driesner T, Stefánsson A, Seward TM (2004) Magmatic vapor contraction and the transport of gold from the porphyry environment to epithermal ore deposits. Geology 32:761–764
Huang XW, Boutroy É, Makvandi S, Beaudoin G, Corriveau L, De Toni AF (2019) Trace element composition of iron oxides from IOCG and IOA deposits: relationship to hydrothermal alteration and deposit subtypes. Miner Deposita 54:525–552
Huston DL, Sie SH, Suter GF, Cooke DR, Both RA (1995) Trace elements in sulfide minerals from eastern Australian volcanic-hosted massive sulfide deposits; Part I, Proton microprobe analyses of pyrite, chalcopyrite, and sphalerite, and Part II, Selenium levels in pyrite; comparison with delta 34 S values and implications for the source of sulfur in volcanogenic hydrothermal systems. Econ Geol 90:1167–1196
Kesler SE, Chryssoulis SL, Simon G (2002) Gold in porphyry copper deposits: its abundance and fate. Ore Geol Rev 21:103–124
King J, Williams-Jones A, van Hinsberg V, Williams-Jones G (2014) High-sulfidation epithermal pyrite-hosted Au (Ag-Cu) ore formation by condensed magmatic vapors on Sangihe Island, Indonesia. Econ Geol 109:1705–1733
Kouzmanov K, Pokrovski GS (2012) Hydrothermal controls on metal distribution in porphyry Cu (-Mo-Au) systems. Soc Econ Geol Spec Pub 16:573–618
Landtwing M, Pettke T, Halter W, Heinrich C, Redmond P, Einaudi M, Kunze K (2005) Copper deposition during quartz dissolution by cooling magmatic–hydrothermal fluids: the Bingham porphyry. Earth Planet Sci Lett 235:229–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.046
Large RR, Danyushevsky L, Hollit C, Maslennikov V, Meffre S, Gilbert S, Bull S, Scott R, Emsbo P, Thomas H (2009) Gold and trace element zonation in pyrite using a laser imaging technique: implications for the timing of gold in orogenic and Carlin-style sediment-hosted deposits. Econ Geol 104:635–668
Large R, Thomas H, Craw D, Henne A, Henderson S (2012) Diagenetic pyrite as a source for metals in orogenic gold deposits, Otago Schist, New Zealand. New Zeal J Geol Geophys 55:137–149
Li JX, Qin KZ, Li GM, Richards JP, Zhao JX, Cao MJ (2014) Geochronology, geochemistry, and zircon Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic intermediate-felsic intrusions in central Tibet: petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Lithos 198–199:77–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.025
Li JX, Qin KZ, Li GM, Xiao B, Zhao JX, Chen L (2016) Petrogenesis of Cretaceous igneous rocks from the Duolong porphyry Cu–Au deposit, central Tibet: evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology, petrochemistry and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf isotope characteristics. Geol J 51:285–307
Li GM, Qin KZ, Li JX, Evans NJ, Zhao JX, Cao MJ, Zhang XN (2017a) Cretaceous magmatism and metallogeny in the Bangong-Nujiang metallogenic belt, central Tibet: Evidence from petrogeochemistry, zircon U-Pb ages, and Hf-O isotopic compositions. Gondwana Res 41:110–127
Li XK, Li C, Sun ZM, Wang M (2017b) Origin and tectonic setting of the giant Duolong Cu–Au deposit, South Qiangtang Terrane, Tibet: evidence from geochronology and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous intrusive rocks. Ore Geol Rev 80:61–78
Li XK, Chen J, Wang RC, Li C (2018) Temporal and spatial variations of Late Mesozoic granitoids in the SW Qiangtang, Tibet: implications for crustal architecture, Meso-Tethyan evolution and regional mineralization. Earth Sci Rev 185:374–396
Lin B, Chen YC, Tang JX, Wang Q, Song Y, Yang C, Wang WL, He W, Zhang LJ (2017a) 40Ar/39Ar and Rb-Sr ages of the Tiegelongnan porphyry Cu-(Au) deposit in the Bangong Co-Nujiang metallogenic belt of Tibet, China: implication for generation of super-large deposit. Acta Geol Sin-Engl 91:602–616
Lin B, Tang JX, Chen YC, Song Y, Hall G, Wang Q, Yang C, Fang X, Duan JL, Yang HH (2017b) Geochronology and genesis of the Tiegelongnan porphyry Cu (Au) deposit in Tibet: Evidence from U-Pb, Re–Os dating and Hf, S, and H–O isotopes. Resour Geol 67:1–21
Liu D, Huang Q, Fan S, Zhang L, Shi R, Ding L (2014) Subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean: constraints from granites in the Bangong Co area, Tibet. Geol J 49:188–206
Liu W, Cook NJ, Ciobanu CL, Gilbert SE (2019) Trace element substitution and grain-scale compositional heterogeneity in enargite. Ore Geol Rev 111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103004
Makvandi S, Ghasemzadeh-Barvarz M, Beaudoin G, Grunsky EC, Beth McClenaghan M, Duchesne C (2016a) Principal component analysis of magnetite composition from volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits: case studies from the Izok Lake (Nunavut, Canada) and Halfmile Lake (New Brunswick, Canada) deposits. Ore Geol Rev 72:60–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.06.023
Makvandi S, Ghasemzadeh-Barvarz M, Beaudoin G, Grunsky EC, McClenaghan MB, Duchesne C, Boutroy E (2016b) Partial least squares-discriminant analysis of trace element compositions of magnetite from various VMS deposit subtypes: application to mineral exploration. Ore Geol Rev 78:388–408
Marcoux E, Milési J, Moëlo Y (1994) Vinciennite and Cu-excess tennantite from the Layo (Cu, Sn, As, Au) epithermal deposit (southern Peru). Mineral Petrol 51:21–36
Maske S, Skinner BJ (1971) Studies of the sulfosalts of copper; I, Phases and phase relations in the system Cu-As-S. Econ Geol 66:901–918
Maydagán L, Franchini M, Lentz D, Pons J, McFarlane C (2013) Sulfide composition and isotopic signature of the Altar Cu-Au deposit, Argentina: constraints on the evolution of the porphyry-epithermal system. Can Mineral 51:813–840
Maydagán L, Franchini M, Rusk B, Lentz DR, McFarlane C, Impiccini A, Ríos FJ, Rey R (2015) Porphyry to epithermal transition in the Altar Cu-(Au-Mo) deposit, Argentina, studied by cathodoluminescence, LA-ICP-MS, and fluid inclusion analysis. Econ Geol 110:889–923
Ossandón G, Gustafson LB, Lindsay DD, Zentilli M (2001) Geology of the Chuquicamata mine: a progress report. Econ Geol 96:249–270
Pacevski A, Libowitzky E, Zivkovic P, Dimitrijevic R, Cvetkovic L (2008) Copper-bearing pyrite from the Coka Marin polymetallic deposit, Serbia: mineral inclusions or true solid-solution? Can Mineral 46:249–261. https://doi.org/10.3749/canmin.46.1.249
Pan G, Wang L, Li R, Yuan S, Ji W, Yin F, Zhang W, Wang B (2012) Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. J Asian Earth Sci 53:3–14
Paton C, Hellstrom J, Paul B, Woodhead J, Hergt J (2011) Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data. J Anal At Spectrom 26. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ja10172b
Pearce C, Pattrick R, Vaughan D, Henderson C, Van der Laan G (2006) Copper oxidation state in chalcopyrite: mixed Cu d9 and d10 characteristics. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:4635–4642
Pokrovski GS, Zakirov IV, Roux J, Testemale D, Hazemann J-L, Bychkov AY, Golikova GV (2002) Experimental study of arsenic speciation in vapor phase to 500 C: Implications for As transport and fractionation in low-density crustal fluids and volcanic gases. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:3453–3480
Pokrovski GS, Roux J, Harrichoury J-C (2005) Fluid density control on vapor-liquid partitioning of metals in hydrothermal systems. Geology 33. https://doi.org/10.1130/g21475.1
Posfai M, Buseck PR (1998) Relationships between microstructure and composition in enargite and luzonite. Am Mineral 83:373–382
Redmond PB, Einaudi MT (2010) The Bingham canyon porphyry Cu-Mo-Au deposit. I. Sequence of intrusions, vein formation, and sulfide deposition. Econ Geol 105:43–68
Redmond P, Einaudi M, Inan E, Landtwing M, Heinrich C (2004) Copper deposition by fluid cooling in intrusion-centered systems: new insights from the Bingham porphyry ore deposit, Utah. Geology 32:217–220
Reich M, Kesler SE, Utsunomiya S, Palenik CS, Chryssoulis SL, Ewing RC (2005) Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:2781–2796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.01.011
Reich M, Chryssoulis SL, Deditius A, Palacios C, Zuniga A, Weldt M, Alvear M (2010) “Invisible” silver and gold in supergene digenite (Cu1.8S). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:6157–6173
Reich M, Deditius A, Chryssoulis S, Li JW, Ma CQ, Parada MA, Barra F, Mittermayr F (2013) Pyrite as a record of hydrothermal fluid evolution in a porphyry copper system: a SIMS/EMPA trace element study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 104:42–62
Rottier B, Kouzmanov K, Wälle M, Bendezú R, Fontboté L (2016) Sulfide replacement processes revealed by textural and LA-ICP-MS trace element analyses: example from the early mineralization stages at Cerro de Pasco, Peru. Econ Geol 111:1347–1367
Rottier B, Kouzmanov K, Casanova V, Wälle M, Fontboté L (2018) Cyclic dilution of magmatic metal-rich hypersaline fluids by magmatic low-salinity fluid: a major process generating the giant epithermal polymetallic deposit of Cerro de Pasco, Peru. Econ Geol 113:825–856. https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.2018.4573
Rye RO (1993) The evolution of magmatic fluids in the epithermal environment; the stable isotope perspective. Econ Geol 88:733–752
Rye RO, Ohmoto H (1974) Sulfur and carbon isotopes and ore genesis: a review. Econ Geol 69:826–842
Seo JH, Guillong M, Heinrich CA (2009) The role of sulfur in the formation of magmatic–hydrothermal copper–gold deposits. Earth Planet Sci Lett 282:323–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.03.036
Seward TM (1973) Thio complexes of gold and the transport of gold in hydrothermal ore solutions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37:379–399
Sillitoe RH (2010) Porphyry copper systems. Econ Geol 105:3–41
Sillitoe RH (1999) Styles of high-sulphidation gold, silver and copper mineralisation in porphyry and epithermal environments. In Weber G (ed) Pacrim ’99 Congress, Bali, Indonesia, 1999, Proceedings: Parkville, Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: 29–44
Simmons SF, Brown KL, Tutolo BM (2016) Hydrothermal transport of Ag, Au, Cu, Pb, Te, Zn, and other metals and metalloids in New Zealand geothermal systems: spatial patterns, fluid-mineral equilibria, and implications for epithermal mineralization. Econ Geol 111:589–618
Simon G, Kesler SE, Essene EJ, Chryssoulis SL (2000) Gold in porphyry copper deposits: Experimental determination of the distribution of gold in the Cu-Fe-S system at 400 to 700 C. Econ Geol 95:259–270
Song Y, Yang C, Wei SG, Yang HH, Fang X, Lu HT (2018) Tectonic control, reconstruction and preservation of the Tiegelongnan porphyry and epithermal overprinting Cu (Au) deposit, Central Tibet, China. Minerals 8:398–415. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8090398
Sun J, Mao J, Beaudoin G, Duan X, Yao F, Ouyang H, Wu Y, Li Y, Meng X (2017) Geochronology and geochemistry of porphyritic intrusions in the Duolong porphyry and epithermal Cu-Au district, central Tibet: Implications for the genesis and exploration of porphyry copper deposits. Ore Geol Rev 80:1004–1019
Sykora S, Cooke DR, Meffre S, Stephanov AS, Gardner K, Scott R, Selley D, Harris AC (2018) Evolution of pyrite trace element compositions from porphyry-style and epithermal conditions at the Lihir gold deposit: implications for ore genesis and mineral processing. Econ Geol 113:193–208
Tang J, Sun X, Ding S, Wang Q, Wang Y, Yang C, Chen H, Li Y, Li Y, Wei L (2014) Discovery of the epithermal deposit of Cu (Au-Ag) in the Duolong ore concentrating area, Tibet. Acta Geosci Sin 35:6–10
Tang JX, Wang Q, Yang HH, Gao X, Zhang ZB, Zou B (2017) Mineralization, exploration and resource potential of porphyry-skarn-epithermal copper polymetallic deposits in Tibet. Acta Geosci Sin 38:571–613
Wang Q, Tang JX, Fang X, Lin B, Song Y, Wang YY, Yang HH, Yang C, Li Y, Wei LJ (2015) Petrogenetic setting of andsites in Rongna ore block, Tiegelong Cu (Au–Ag) deposit, Duolong ore concentration area, Tibet: evidence from zircon U-Pb LA–ICP–MS dating and petrogeochemistry of andsites. Chin Geol 42:1324–1336
Wang YY, Tang JX, Song Y, Yang C, Lin B, Wang Q, Sun M, Gao K, Fang X, Yang HH (2018) Characteristics of the main ore minerals in Tiegelongnan porphyry-high sulfidation deposit, Tibet, China. Acta Min Sin 38:109–122
Wei SG, Tang JX, Song Y, Liu ZB, Feng J, Li YB (2017) Early Cretaceous bimodal volcanism in the Duolong Cu mining district, western Tibet: Record of slab breakoff that triggered ca. 108–113 Ma magmatism in the western Qiangtang terrane. J Asian Earth Sci 138:588–607
Wilson S, Ridley W, Koenig A (2002) Development of sulfide calibration standards for the laser ablation inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry technique. J Anal at Spectrom 17:406–409
Wu YF, Evans K, Li JW, Fougerouse D, Large RR, Guagliardo P (2019a) Metal remobilization and ore-fluid perturbation during episodic replacement of auriferous pyrite from an epizonal orogenic gold deposit. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 245:98–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2018.10.031
Wu YF, Fougerouse D, Evans K, Reddy SM, Saxey DW, Guagliardo P, Li JW (2019b) Gold, arsenic, and copper zoning in pyrite: a record of fluid chemistry and growth kinetics. Geology. https://doi.org/10.1130/g46114.1
Xie Y, Riedinger A, Prato M, Casu A, Genovese A, Guardia P, Sottini S, Sangregorio C, Miszta K, Ghosh S, Pellegrino T, Manna L (2013) Copper sulfide nanocrystals with tunable composition by reduction of covellite nanocrystals with Cu+ ions. J Am Chem Soc 135:17630–17637. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja409754v
Yang C, Tang J, Wang Y, Yang H, Wang Q, Sun X, Feng J, Yin X, Ding S, Fang X (2014) Fluid and geological characteristics researches of Southern Tiegelong epithermal porphyry Cu-Au deposit in Tibet. Mineral Deposits 33:1287–1305
Yang C, Tang J, Beaudoin G, Song Y, Lin B, Wang Q, Fang X (2020) Geology and geochronology of the Tiegelongnan porphyry-epithermal Cu (Au) deposit, Tibet, China: formation, exhumation and preservation history. Ore Geol Rev 123:103575
Yang C, Beaudoin G, Tang J-X, Song Y, Zhang Z (2020a) Hydrothermal fluid evolution at the Tiegelongnan porphyry-epithermal Cu(Au) deposit, Tibet, China: Constraints from H and O stable isotope and in-situ S isotope. Ore Geol Rev 125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103694
Yin A, Harrison TM (2000) Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 28:211–280
Zhang KJ, Zhang YX, Tang XC, Xia B (2012) Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution and growth of the Tibetan plateau prior to the Indo-Asian collision. Earth Sci Rev 114:236–249
Zhang Z, Yao XF, Tang JX, Li ZJ, Wang LQ, Yang Y, Duan JL, Song JL, Lin X (2015) Lithogeochemical, Re-Os and U-Pb geochronological, Hf-Lu and S-Pb isotope data of the Ga’erqiong-Galale Cu-Au ore concentrated area: evidence for the Late Cretaceous magmatism and metallogenic event in the Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone, Northwestern Tibet, China. Resour Geol 65:76–102
Zhang XN, Li GM, Qin KZ, Lehmann B, Li JX, Zhao JX, Cao MJ, Zou XY (2018) Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of Early Cretaceous granodioritic porphyry from the giant Rongna porphyry Cu deposit, central Tibet. J Asian Earth Sci 161:74–92
Zhang XN, Li GM, Qin KZ, Lehmann B, Li JX, Zhao JX (2020) Porphyry to epithermal transition at the Rongna Cu-(Au) deposit, Tibet: insights from HO isotopes and fluid inclusion analysis. Ore Geol Rev 123:103585
Zhu DC, Li SM, Cawood PA, Wang Q, Zhao ZD, Liu SA, Wang LQ (2016) Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction. Lithos 245:7–17
Acknowledgements
Marc Choquette and Suzie Cote (Université Laval) are thanked for their help with EMPA and SEM analysis. Dany Savard and Audrey Lavoie (UQAC) are thanked for their assistance with LA-ICP-MS analyses and data reduction. We thank Jinlong Mining Co., Ltd. for the support of the fieldwork. The Editor-in-Chief Bernd Lehmann, Associate Editor Peter Hollings, Robert G. Lee, and an anonymous reviewer are acknowledged for their insightful comments, which significantly improved the paper.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, Deep Resources Exploration and Mining project (2018YFC0604101), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41902097), the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada, and the CAS Hundred Talents Program (Y9CJ034000) to XW Huang. The first author’s study in Canada is supported by China Scholarship Council (CSC) and NSERC Discovery grant to G. Beaudoin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: P. Hollings.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Beaudoin, G., Tang, JX. et al. Cu-sulfide mineralogy, texture, and geochemistry in the Tiegelongnan porphyry-epithermal copper system, Tibet, China. Miner Deposita 57, 759–779 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01075-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01075-y