Abstract
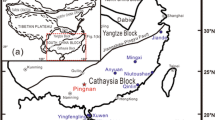
More than 90% of the tungsten resources of China are in the Nanling region of South China, and the Yaogangxian vein deposit is the largest tungsten deposit in this region. The tungsten deposits have ages of 150–160 Ma, and are spatially, temporally and genetically related to granites which were previously believed to be produced by crustal anatexis. This paper provides He and Ar isotope data of fluid inclusions in pyrite and arsenopyrite from the Yaogangxian W veins. 3He/4He ratios range from 0.41 to 3.03 Ra (where Ra is the 3He/4He ratio of air = 1.39 × 10−6), and 40Ar/36Ar ratios from 328 to 1,191. Moreover, there are excellent correlations between He and Ar isotopic compositions. The results suggest that the ore-forming fluids are a mixture between a crustal fluid containing atmospheric Ar and crustal 4He and a fluid containing mantle components. It is likely that the former is a low temperature meteoric fluid, and the later is a fluid exsolved from the W-associated granitic magma, which formed by crustal melting induced by intrusion of a mantle-derived magma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballentine C J, Burnard P G (2002) Production, release and transport of noble gases in the continental crust. Rev Mineral Geochem 47: 481–538
Baptiste PJ, Fouquet Y (1996) Abundance and isotopic composition of helium in hydrothermal sulfides from the East Pacific Rise at 13 N. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:87–93
Burnard PG, Polya DA (2004) Importance of mantle derived fluids during granite associated hydrothermal circulation: He and Ar isotopes of ore minerals from Panasqueira. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:1607–1615
Burnard PG, Stuart F, Ayliffe L, Turner G (1993) Noble gas isotopic and elemental abundances in inclusion and vesicle trapped fluids: method. Seventh meeting of the European Union of Geosciences. abstract supplement, Seventh meeting of the European Union of Geosciences 5(Suppl. 1):368
Burnard PG, Farley KA, Turner G (1998) Multiple fluid pulses in a Samoan harzburgite. Chem Geol 147:99–114
Burnard PG, Hu RZ, Turner G, Bi XW (1999) Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan gold deposit, Yunnan province, China. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:1595–1604
Cao XF, Lu XB, He MC, Niu H, Du BF, Mei W (2009) An infrared microscope investigation og fluid inclusions in coexisting quartz and wolframite: a case study of Yaogangxian quartz-vein wolframite deposit. Miner Depos 28:611–620 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen YR (1981) Geological features and ore-prospecting indications in the Yaogangxian vein-type tungsten deposit. Geol Prospect 17(2):25–30 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen YR (1992) Analysis of the control fractors and conditions of the mineralization in Yaogangxian orefield, Yizhang county, Hunan. Hunan Geol 11(4):285–293 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Chen J, Lu JJ, Chen WF, Wang RC, Ma DS, Zhu JC, Zhang WL Ji JF (2008) W-Sn-Nb-Ta-bearing granites in the Nanling Range and their relationship to metallogengesis. Geological Journal of China Universities 14: 459–473
Dunai TJ, Baur H (1995) Helium, neon and argon systematics of the European subcontinental mantle: implications for its geochemical evolution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:2767–2784
Elliot T, Ballentine CJ, O’Nions RK, Ricchiuto T (1993) Carbon, helium, neon and argon isotopes in a Po basin natural gas field. Chem Geol 106:429–440
England PC, Thompson AB (1984) Presssure-temperature-time paths of regional metamorphism, I, Heat transfer during evolution of regions of thickened continental crust. J Petrol 25:894–928
Gautheron C, Moreira M (2002) Helium signature of the subcontinental lithospheric mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 199:39–47
Guo CL, Wang DH, Che YC, Wang YB, Chen ZH, Liu SB (2007) Precise zircon SHRIMP U-Pb and quartz vein Rb-Sr dating of Mesozoic Taoxikeng tungsten polymetallic deposit in southern Jiangxi. Miner Depos 26:432–442 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hu RZ, Burnard PG, Turner G, Bi XW (1998) Helium and argon systematics in fluid inclusions of Machangqing copper deposit in west Yunnan province, China. Chem Geol 146:55–63
Hu RZ, Burnard PG, Bi XW, Zhou MF, Peng JT, Su WC, Wu KX (2004) Helium and argon isotope geochemistry of alkaline intrusion-associated gold and copper deposits along the Red River-Jingshajiang fault belt, SW China. Chem Geol 203:305–317
Hu RZ, Burnard PG, Bi XW, Zhou MF, Peng JT, Su WC, Zhao JH (2009) Mantle-derived gaseous components in ore-forming fluids of the Xiangshan uranium deposit, Jiangxi province, China: evidence from He, Ar and C isotopes. Chem Geol 266:86–95
Hua RM, Zhang WL, Chen PR, Wang RC (2003) Comparison in the characteristics, origin, and related metallogeny between granites in Dajishan and Piaotang, Southern Jiangxi, China. Geol J China Univ 9:609–619 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hua RM, Zhang WL, Gu SY, Chen PR (2007) Comparison between REE granite and W-Sn granite in the Nanling region, South China, and their mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica 23:2321–2328 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hua RM, Li GL, Zhang WL, Hu DQ, Chen PR, Chen WF, Wang XD (2010) A tentative discussion on differences between large-scale tungsten and tin mineralization in South China. Miner Depos 29:9–23 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huppert HE, Sparks RSJ (1988) The generation of granitic magmas by intrusion of basalt into the continental crust. J Petrol 29:599–624
Jiang GH, Hu RZ, Xie GQ, Zhao JH, Tang QL (2004) K-Ar ages of plutonism and mineralization at the Dajishan tungsten deposit, Jiangxi province, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica 24:253–256 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Kendrick MA, Burgess R, Pattrick RAD, Turner G (2001) Fluid inclusion noble gas and halogen evidence on the origin of Cu-porphyry mineralizing fluids. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:2651–2668
Kendrick MA, Burgess R, Leach D, Pattrick RAD (2002a) Hydrothermal fluid origins in Mississippi valley-type ore districts: combined noble gas (He, Ar, Kr) and halogen (Cl, Br, I) analysis of fluid inclusions from the Illinois-Kentucky fluorspar district, ViburnumTrend and Tri-State districts, Midcontinent United States. Econ Geol 97:453–469
Kendrick MA, Burgess R, Pattrick RAD, Turner G (2002b) Hydrothermal fluid origins in a fluorite-rich Mississippi valley-type district: combined noble gas (He, Ar, Kr) and halogen (Cl, Br, I) analysis of fluid inclusions from the South Pennine ore field, United Kingdom. Econ Geol 97:435–451
Kendrick MA, Burgess R, Harrison D, Bjorlykke A (2005) Noble gas and halogen evidence for the origin of Scandinavian sandstone-hosted Pb-Zn deposits. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:109–129
Kendrick MA, Honda M, Oliver NHS, Phillips D (2011) The noble gas systematics of late-orogenic H2O–CO2 fluids, Mt Isa, Australia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75:1428–1450
Li XH, Li WX, Li ZX (2007a) On the genetic classification and tectonic implications of the Early Yanshanian granitoids in the Nanling range, South China. Chin Sci Bull 52:1885–1973
Li XH, Li ZX, Li WX, Liu Y, Yuan C, Wei GJ, Qi CS (2007b) U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic I- and A-type granitoids from central Guangdong, SE China: a major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab? Lithos 96:186–204
Li ZL, Hu RZ, Yang JS, Peng JT, Li XM, Bi XW (2007c) He, Pb and S isotopic constraints on the relationship between the A-type Qitianling granite and the Furong tin deposit, Hunan Province, China. Lithos 97:161–173
Li XH, Li WX, Wang XC, Li QL, Liu Y, Tang GQ (2009) Role of mantle-derived magma in genesis of early Yanshanian granites in the Nanling Range, South China: in situ zircon Hf-O isotopic constraints. Sci China Ser D- Earth Sci 52:1262–1278
Lippolt HJ, Weigel E (1988) 4He diffusion in Ar-retentive minerals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:1449–1458
Lu HZ (1986) Origin of tungsten mineral deposit in South China. Publishing House of Chongqing, Chongqing, pp 1–232 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mamyrin BA, Tolstikhin I (1984) Helium isotopes in nature. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 267
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Guo CL, Chen YC (2007) Large-scale tungsten-tin mineralization in the Nanling region, South China: metallogenic ages and corresponding geodynamic process. Acta Petrologica Sinica 23:2329–2338 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Marty B, Jambon A, Sano Y (1989) Helium isotope and CO2 in volcanic gases of Japan. Chem Geol 76:25–40
McDougall I, Harrison TM (1988) Geochronology and thermochronology by the 40Ar-39Ar method. Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, pp 212
Mckee EH, Rytuba J, Xu KQ (1987) Geochronology of the Xihuashan composite granitic body and tungsten mineralization, Jiangxi province, south China. Econ Geol 82:218–223
Morrison P, Pine J (1955) Radiogenic origin of the helium isotopes in rock. Ann N Y Acad Sci 62:71–92
Ni JW (1994) Research on fluid inclusion and ore-forming fluid characters of the Yaogangxian tungsten deposit. J Zhejiang Univ 28:73–81 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Peng JT, Zhou MF, Hu RZ, Shen NP, Yuan SD, BI XW, Du AD, Qu WJ (2006) Precise molybdenite Re-Os and mica Ar-Ar dating of the Mesozoic Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, central Nanling district, South China. Miner Depos 41:661–669
Qiu HN (1996) 40Ar/39Ar dating of the quartz samples from two mineral deposits in western Yunnan (SW China) by crushing in vacuum. Chem Geol 127:211–222
RGNTD (Research Group for Nanling Tungsten Deposits, Chinese Ministry of Metallurgy) (1985) Tungsten Deposits in South China. Publishing House of Metallurgical Industry, Beijing, pp 1–496 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Simmons SF, Sawkins FJ, Schlutter DJ (1987) Mantle-derived helium in two Peruvian hydrothermal ore deposits. Nature 329:429–432
Smith PE, Evensen NM, York D, Szatmari P, Oliveira DC (2001) Single-crystal 40Ar/39Ar dating of pyrite: no fool’s clock. Geology 29:403–406
Stuart FM, Turner G, Duckworth RC, Fallick AE (1994) Helium isotopes as tracers of trapped hydrothermal fluids in ocean-floor sulfides. Geology 22:823–826
Stuart FM, Burnard PG, Taylor RP, Turner G (1995) Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W-Mo mineralisation, South Korea. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:4663–4673
Sun J, Ni YJ, Bai DY, Ma TQ (2009) Geochemistry, petrogenesis and tectonic setting of early Yanshanian Yaogangxian granite pluton, Southeastern Hunan province (in Chinese with English abstract). Geology and Mineral Resources in South China (3):12–18
Torgersen T, Kennedy BM, Hiyagon H (1988) Argon accumulation and the crustal degassing flux of 40Ar in the Great Artesian Basin, Australia. Earth Planet Sci Lett 92:43–59
Turner G, Stuart FM (1992) Helium/heat ratios and deposition temperatures of sulphides from the ocean floor. Nature 357:581–583
Turner G, Wang SS (1992) Excess argon, crustal fluid and apparent isochrons from crushing K feldspar. Earth Planet Sci Lett 110:193–211
Turner G, Burnard PG, Ford JL, Gilmour JD, Lyon IC, Stuart FM (1993) Tracing fluid sources and interaction. Phil Trans R Soc Lond, A 344:127–140
Wang Y (2008) Some further discussion on the granitic types of the Early Yanshanian (Jurassic) granitoids in the Nanling area, SE China. Geol Rev 54:162–174 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang LK, Zhang SL, Yang WJ, Xu WX (1989) Granites of different series and types in South China: their Sr, O, Pb and Nd isotopic compositions and formation environment. Geol Prospect 25:29–33 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang QY, Hu RZ, Peng JT, Bi XW, Wu LY, Liu H, Su BX (2007) Characteristics and significance of the fluid inclusions from Yaogangxian tungsten deposit in south Hunan. Acta Petrologica Sinica 23:2263–2273 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang YL, Per RF, Li JW, Liu XF (2009) Geochemical characteristics of granites from the Jiangjunzhai tungsten deposit of Southeast Hunan province and its Re-Os isotopic dating. Rock Miner Anal 28:274–278 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu LY, Hu RZ, Peng JT, Bi XW, Jiang GH, Chen HW, Wang QY, Liu YY (2011) He and Ar isotopic compositions and genetic implications for the giant Shizhuyuan W-Sn-Bi-Mo deposit, Hunan Province, South China. Int Geol Rev 53:677–690
Xiao J, Wang Y, Hong YL, Zhou YZ, Xie MH, Wang DS, Guo JS (2009) Geochemistry characteristics of Xihuashan tungsten granite and its relationship to tungsten metallogenesis. J East China Inst Technol 32:22–31 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu KQ, Sun N, Wang DZ (1984) Petrogenesis of the granitoids and their metallogenetic relations in south China. In: Xu KQ, Tu GC (eds) Geology of granites and their metallogenetic relations. Science Press, China, pp 1–31
Yan D P, Zhou M F, Song H L, Wang X W, Malpas J (2003) Origin and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic multi-layer over-thrust system within the Yangtze Block (South China). Tectonophysics, 361: 239–254
York D, Masliwec A, Kuybida P, Hanes JE, Hall CM, Kenyon WJ, Spooner ETC, Scott SD (1982) 40 Ar/39 Ar dating of pyrite. Nature 300:52–53
Zhang LG (1987) Oxygen isotopic studies of wolframite in tungsten ore deposits of South China. Geochimica 3:233–242 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang GX, Xie YN, Yu FJ, Zhang HB (1997) Stable isotope geochemistry of different metallogenic stages of tungsten deposit in Dajishan mine. Jiangxi 18(suppl):197–199 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang WL, Hua RM, Wang RC, Chen PR, Li HM (2006) New dating of the Dajishan granite and related tungsten mineralization in Southern Jiangxi. Acta Geologica Sinica 80:956–962 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang WL, Hua RM, Wang RC, Li HM, Qu WJ, Ji JQ (2009) New dating of the Piaotang granite and related tungsten mineralization in southern Jiangxi. Acta Petrologica Sinica 83:659–670 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
The field work was supported by the Yaogangxian Mine Company. The authors are grateful to Dr. Lehmann B. and Prof. Zhou M.F. for their constructive comments on this manuscript, and to Turner G. and Kendrick M.A. for their thoughtful reviews. This research was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2007CB411408) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (40903023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: Hua and Zhou
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, RZ., Bi, XW., Jiang, GH. et al. Mantle-derived noble gases in ore-forming fluids of the granite-related Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, Southeastern China. Miner Deposita 47, 623–632 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-011-0396-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-011-0396-x