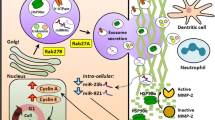
Abstract
Rectal cancer represents one third of the colorectal cancers that are diagnosed. Neoadjuvant chemoradiation is a well-established protocol for rectal cancer treatment reducing the risk of local recurrence. However, a pathologic complete response is only achieved in 10–40% of cases and the mechanisms associated with resistance are poorly understood. To identify potential targets for preventing therapy resistance, a proteomic analysis of biopsy specimens collected from stage II and III rectal adenocarcinoma patients before neoadjuvant treatment was performed and compared with residual tumor tissues removed by surgery after neoadjuvant therapy. Three proteins, Ku70, Ku80, and Rab5C, exhibited a significant increase in expression after chemoradiation. To better understand the role of these proteins in therapy resistance, a rectal adenocarcinoma cell line was irradiated to generate a radiotherapy-resistant lineage. These cells overexpressed the same three proteins identified in the tissue samples. Furthermore, radiotherapy resistance in this in vitro model was found to involve modulation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) internalization by Rab5C in response to irradiation, affecting expression of the DNA repair proteins, Ku70 and Ku80, and cell resistance. Taken together, these findings indicate that EGFR and Rab5C are potential targets for the sensitization of rectal cancer cells and they should be further investigated.
Key messages
• Rab5C orchestrates a mechanism of radioresistance in rectal adenocarcinoma cell.
• Rab5C modulates EGFR internalization and its relocalization to the nucleus.
• In the nucleus, EGFR can modulate the expression of the DNA repair proteins, Ku70 and Ku80.
• Rab5C, Ku70, and Ku80 are overexpressed in tumor tissues that contain tumor cells that are resistant to chemoradiation treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Tamas K, Walenkamp AM, de Vries EGE, van Vugt MA, Beets-Tan RG, van Etten B, et al. (2015) Rectal and colon cancer: Not just a different anatomic site. Cancer Treat Rev [Internet]. Elsevier Ltd; Available from: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0305737215001292
Sauer R, Becker H, Hohenberger W, Rödel C, Wittekind C, Fietkau R, Martus P, Tschmelitsch J, Hager E, Hess CF, Karstens JH, Liersch T, Schmidberger H, Raab R (2004) Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351:1731–1740
Bosset J, Collette L, Callais G, Mineur L, Maingon P, Radosevic-Jelic L et al (2006) Chemotherapy with preoperative radiotherapy in rectal cancer. N Engl J Med 355:1114–1123
Maas M, Nelemans P, Valentini V, Das P, Rödel C, Kuo L et al (2010) Long-term outcome in patients with a pathological complete response after chemoradiation for rectal cancer: a pooled analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Oncol 11:835–844
Wasmuth HH, Rekstad LC, Tranø G (2015) The outcome and the frequency of pathological complete response after neoadjuvant radiotherapy in curative resections for advanced rectal cancer: a population-based study. Color Dis [Internet];n/a-n/a. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/codi.13072
Huber SM, Butz L, Stegen B, Klumpp D, Braun N, Ruth P et al (2013) Ionizing radiation, ion transports, and radioresistance of cancer cells. Front Physiol 4:1–14
Liccardi G, Hartley J, Hochhauser D (2011) EGFR nuclear translocation modulates DNA repair following cisplatin and ionizing radiation treatment. Cancer Res 71:1103–1114
Dittmann K, Mayer C, Rodemann H-P (2005) Inhibition of radiation-induced EGFR nuclear import by C225 (Cetuximab) suppresses DNA-PK activity. Radiother Oncol 76:157–161 Available from: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0167814005002513
Schmidt-Ullrich RK, Mikkelsen RB, Dent P, Todd DG, Valerie K, Kavanagh BD, Contessa JN, Rorrer WK, Chen PB (1997) Radiation-induced proliferation of the human A431 squamous carcinoma cells is dependent on EGFR tyrosine phosphorylation. Oncogene 15:1191–1197
Dittmann K, Mayer C, Kehlbach R, Rodemann HP (2008) Radiation-induced caveolin-1 associated EGFR internalization is linked with nuclear EGFR transport and activation of DNA-PK. Mol Cancer 7:69 Available from: http://www.molecular-cancer.com/content/7/1/69
Dittmann K, Mayer C, Fehrenbacher B, Schaller M, Raju U, Milas L, Chen DJ, Kehlbach R, Rodemann HP (2005) Radiation-induced epidermal growth factor receptor nuclear import is linked to activation of DNA-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 280:31182–31189
Begg AC, Stewart FA, Vens C (2011) Strategies to improve radiotherapy with targeted drugs. Nat Rev Cancer [Internet]. Nature Publishing Group;11:239–53. Available from: http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/nrc3007
Vizoso M, Ferreira HJ, Lopez-Serra P, Carmona FJ, Martínez-Cardús A, Girotti MR, Villanueva A, Guil S, Moutinho C, Liz J, Portela A, Heyn H, Moran S, Vidal A, Martinez-Iniesta M, Manzano JL, Fernandez-Figueras MT, Elez E, Muñoz-Couselo E, Botella-Estrada R, Berrocal A, Pontén F, Oord J, Gallagher WM, Frederick DT, Flaherty KT, McDermott U, Lorigan P, Marais R, Esteller M (2015) Epigenetic activation of a cryptic TBC1D16 transcript enhances melanoma progression by targeting EGFR. Nat Med 21:741–750 Available from: http://www.nature.com.gate1.inist.fr/nm/journal/v21/n7/full/nm.3863.html
Chen P-I, Kong C, Su X, Stahl PD (2009) Rab5 isoforms differentially regulate the trafficking and degradation of epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem 284:30328–30338 Available from: http://www.jbc.org/cgi/doi/10.1074/jbc.M109.034546
Komuro Y, Watanabe T, Hosoi Y, Matsumoto Y, Nakagawa K, Tsuno N, Kazama S, Kitayama J, Suzuki N, Nagawa H (2002) The expression pattern of Ku correlates with tumor radiosensitivity and disease free survival in patients with rectal carcinoma. Cancer 95:1199–1205
Mazzarelli P, Parrella P, Seripa D, Signori E, Perrone G, Rabitti C, Borzomati D, Gabbrielli A, Matera MG, Gravina C, Caricato M, Poeta ML, Rinaldi M, Valeri S, Coppola R, Fazio VM (2005) DNA end binding activity and Ku70/80 heterodimer expression in human colorectal tumor. World J Gastroenterol 11:6694–6700
Wang Y, Li H, Li Y, Min J (2011) The expression and clinical significance of RABEX-5 and RAB5 in breast cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 42:185–189. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21500550
Zhao Z, Liu X-F, Wu H-C, Zou S-B, Wang J-Y, Ni P-H et al (2010) Rab5a overexpression promoting ovarian cancer cell proliferation may be associated with APPL1-related epidermal growth factor signaling pathway. Cancer Sci 101:1454–1462 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20412119
Li Y, Meng X, Feng H, Zhang G, Liu C, Li P (1999) Over-expression of the RAB5 gene in human lung adenocarcinoma cells with high metastatic potential. Chin Med Sci J 14:96–101 Available from: http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/12901617
O’Driscoll M, Jeggo PA (2006) The role of double-strand break repair—insights from human genetics. Nat Rev Genet 7:45–54 Available from: http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/nrg1746
Hu L, Wu QQ, Wang WB, Jiang HG, Yang L, Liu Y, Yu HJ, Xie CH, Zhou YF, Zhou FX (2013) Suppression of Ku80 correlates with radiosensitivity and telomere shortening in the U2OS telomerase-negative osteosarcoma cell line. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14:795–799
Koike M, Yutoku Y, Koike A (2011) Establishment of ku70-deficient lung epithelial cell lines and their hypersensitivity to low-dose x-irradiation. J Vet Med Sci:73, 549–554 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21160137
Veuger SJ, Curtin NJ, Richardson CJ, Smith GCM, Durkacz BW (2003) Radiosensitization and DNA repair inhibition by the combined use of novel inhibitors of DNA-dependent protein kinase and. Cancer Res ;63:6008–15
Lin SY, Makino K, Xia W, Matin A, Wen Y, Kwong KY, Bourguignon L, Hung MC (2001) Nuclear localization of EGF receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nat Cell Biol 3:802–808
Lo H-W, Xia W, Wei Y, Ali-Seyed M, Huang S-F, Hung M-C (2005) Novel prognostic value of nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor in breast cancer. Cancer Res 65:338–348
Xia W, Wei Y, Du Y, Liu J, Chang B, Yu Y-L et al (2009) Nuclear expression of epidermal growth factor receptor is a novel prognostic value in patients with ovarian cancer. Mol Carcinog 48:610–617 Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2718429&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
Chen P-I, Schauer K, Kong C, Harding AR, Goud B, Stahl PD (2014) Rab5 isoforms orchestrate a “division of labor” in the endocytic network; Rab5C modulates RAC-mediated cell motility. PLoS One 9:e90384 Available from: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090384
Wheeler DB, Zoncu R, Root DE, Sabatini DM, Sawyers CL (2015) Identification of an oncogenic RAB protein. Science
Zeigerer A, Gilleron J, Bogorad RL, Marsico G, Nonaka H, Seifert S, Epstein-Barash H, Kuchimanchi S, Peng CG, Ruda VM, Conte-Zerial PD, Hengstler JG, Kalaidzidis Y, Koteliansky V, Zerial M (2012) Rab5 is necessary for the biogenesis of the endolysosomal system in vivo. Nature. Nature Publishing Group;485:465–70. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11133
Hoepfner S, Severin F, Cabezas A, Habermann B, Runge A, Gillooly D, Stenmark H, Zerial M (2005) Modulation of receptor recycling and degradation by the endosomal kinesin KIF16B. Cell 121:437–450 Available from: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0092867405001625
Barbieri MA, Roberts RL, Gumusboga A, Highfield H, Alvarez-Dominguez C, Wells A, Stahl PD (2000) Epidermal growth factor and membrane trafficking. J Cell Biol 151:539–550
Gurkan C, Lapp H, Alory C, Su AI, Hogenesch JB, Balch WE (2005) Large-scale profiling of Rab GTPase trafficking networks: the membrome. Mol Biol Cell 16:3847–3864
Onodera Y, Nam J-M, Hashimoto A, Norman JC, Shirato H, Hashimoto S et al (2012) Rab5c promotes AMAP1-PRKD2 complex formation to enhance 1 integrin recycling in EGF-induced cancer invasion. J Cell Biol 197:983–996 Available from: http://www.jcb.org/cgi/doi/10.1083/jcb.201201065
Benvenuti S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Di Nicolantonio F, Zanon C, Moroni M, Veronese S et al (2007) Oncogenic activation of the RAS/RAF signaling pathway impairs the response of metastatic colorectal cancers to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody therapies. Cancer Res 67:2643–2648 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17363584
Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, O’Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC et al (2008) K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 359:1757–1765 Available from: http://www.nejm.org/doi/abs/10.1056/NEJMoa0804385
Kasper S, Breitenbuecher F, Reis H, Brandau S, Worm K, Köhler J, Paul A, Trarbach T, Schmid KW, Schuler M (2013) Oncogenic RAS simultaneously protects against anti-EGFR antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and EGFR signaling blockade. Oncogene 32:2873–2881 Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/onc2012302
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Haridas D, Jain M, Ganti AK, Batra SK (2012) Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 16:15–31 Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22239438
Tanos B, Pendergast AM (2006) Abl tyrosine kinase regulates endocytosis of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem 281:32714–32723 Available from: http://www.jbc.org/lookup/doi/10.1074/jbc.M603126200
Sousa LP, Lax I, Shen H, Ferguson SM, Camilli PD, Schlessinger J (2012) Suppression of EGFR endocytosis by dynamin depletion reveals that EGFR signaling occurs primarily at the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:4419–4424 Available from: http://www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1200164109
Bazzani L, Donnini S, Giachetti A, Christofori G, Ziche M (2018) PGE2 mediates EGFR internalization and nuclear translocation via caveolin endocytosis promoting its transcriptional activity and proliferation in human NSCLC cells. Oncotarget. Available from: http://www.oncotarget.com/fulltext/24499
Al-Akhrass H, Naves T, Vincent F, Magnaudeix A, Durand K, Bertin F et al (2017) Sortilin limits EGFR signaling by promoting its internalization in lung cancer. Nat Commun 8:1182 Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-01172-5
Walsh AM, Lazzara MJ (2013) Regulation of EGFR trafficking and cell signaling by Sprouty2 and MIG6 in lung cancer cells. J Cell Sci 126:4339–4348 Available from: http://jcs.biologists.org/cgi/doi/10.1242/jcs.123208
Berg KCG, Eide PW, Eilertsen IA, Johannessen B, Bruun J, Danielsen SA et al (2017) Multi-omics of 34 colorectal cancer cell lines—a resource for biomedical studies. Mol Cancer 16:116 Available from: http://molecular-cancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12943-017-0691-y
Huang S-M, Bock JM, Harari PM (1999) Epidermal growth factor receptor blockade with C225 modulates proliferation, apoptosis, and radiosensitivity in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res 59:1935–1940 Available from: http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org.ezproxy.auckland.ac.nz/content/59/8/1935
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB et al (2006) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 354:567–578
Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur RK et al (2010) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: 5-year survival data from a phase 3 randomised trial, and relation between cetuximab-induced rash and survival. Lancet Oncol 11:21–28 Available from: http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1470204509703110
Dewdney A, Cunningham D, Tabernero J, Capdevila J, Glimelius B, Cervantes A et al (2012) Multicenter randomized phase II clinical trial comparing neoadjuvant oxaliplatin, capecitabine, and preoperative radiotherapy with or without cetuximab followed by total mesorectal excision in patients with high-risk rectal cancer (EXPERT-C). J Clin Oncol 30:1620–1627 Available from: http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/doi/10.1200/JCO.2011.39.6036
Sclafani F, Gonzalez D, Cunningham D, Hulkki Wilson S, Peckitt C, Giralt J, Glimelius B, Roselló Keränen S, Wotherspoon A, Brown G, Tait D, Oates J, Chau I (2014) RAS mutations and cetuximab in locally advanced rectal cancer: results of the EXPERT-C trial. Eur J Cancer 50:1430–1436
Jo U, Park KH, Whang YM, Sung JS, Won NH, Park JK et al (2014) EGFR endocytosis is a novel therapeutic target in lung cancer with wild-type EGFR. Oncotarget 5:1265–1278 Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=4012721&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
Hong L, Simons P, Waller A, Strouse J, Surviladze Z, Ursu O et al. A small molecule pan-inhibitor of Ras-superfamily GTPases with high efficacy towards Rab7. Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program [Internet]. National Center for Biotechnology Information, Bethesda
Hong L, Guo Y, BasuRay S, Agola JO, Romero E, Simpson DS et al (2015) A Pan-GTPase Inhibitor as a Molecular Probe. PLoS One 10:e0134317 Available from: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134317
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Marina França de Resende from the Department of Anatomic Pathology, A.C. Camargo Cancer Center, for help with the IHC staining. We also acknowledge the A.C. Camargo Biobank in the name of Dr. Antônio Hugo Campos and Dr. Dirce Carraro for providing great quality tumor samples and complete patient data. This study was supported by grants from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP; VRM 2009/14027-2), the National Institute for Science and Technology in Oncogenomics (INCITO) and CAPES. Fellowships from FAPESP were awarded to A.R.B (2013/04913-0), M.V.S.D. (2010/19200-1), F.G (2013/23285-8), and T.C.L (2011/18718-0).
Funding
This study received funding from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP; VRM 2009/14027-2) and the National Institute for Science and Technology in Oncogenomics (INCITO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ARB: Study concept and design; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript. MCL: performed experiments and analysis and interpretation of data. MVSD: Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript. FSG: Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript. BRR: Analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript. PPCES: Study concept and design; performed the ionizing irradiation assay. EKC: Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data. TCL: Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data. FAM: Analysis and interpretation of data; bioinformatics analysis and drafting of the manuscript. AFPL: Study concept and design, performed the proteomic analysis and interpretation of data. MDB: Study concept and design, immunohistochemistry analysis and analysis and interpretation of data. SAJ: Study concept and design; analysis and interpretation of data; critical revision of the manuscript. VRM: Study concept and design; analysis and interpretation of data; drafting of the manuscript; critical revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee (CEP) of A.C. Camargo Cancer Center (243.157) and all patients gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
(PNG 3862 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(PNG 418 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(PNG 311 kb)
ESM 1
(DOC 47 kb)
Supplementary Figure 2
(PNG 56 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baptistella, A.R., Landemberger, M.C., Dias, M.V.S. et al. Rab5C enhances resistance to ionizing radiation in rectal cancer. J Mol Med 97, 855–869 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01760-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01760-6