Purpose:
To compare commercial treatment-planning systems (TPS) for inverse planning (IP) and to assess constraint variations for specific IMRT indications.
Material and Methods:
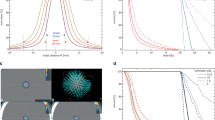
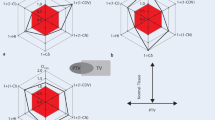
For IP, OTP, XiO and BrainSCAN were used and step-and-shoot intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) delivery was assumed. Based on identical constraints, IP was performed for a prostate, head and neck, brain, and gynecologic case. IMRT plans were compared in terms of conformity/homogeneity, dose-volume histograms (DVHs), and delivery efficiency. For ten patients each of a class of indications, constraint variations were evaluated.
Results:
IMRT plans were comparable concerning minimum target dose, homogeneity, conformity, and maximum doses to organs at risk. Larger differences were seen in dose gradients outside the target, monitor units, and segment number. Using help structures proved efficient to shape isodoses and to reduce segmentation workload. For IMRT class solutions, IP constraint variations depended on anatomic site.
Conclusion:
IP systems requiring doses as input and having objective functions based on physical parameters had a very similar performance. Constraint templates can be established for a class of IMRT indications.
Ziel:
Die Funktionalität der inversen Planung (IP) von kommerziellen Bestrahlungsplanungssystemen (TPS) sowie die Unterschiede von Dosiszielgrößen bei typischen IMRT-Indikationen (intensitätsmodulierte Strahlentherapie) wurden untersucht.
Material und Methodik:
Für die IP fanden OTP, XiO und BrainSCAN Verwendung, und eine „Step-and-shoot“-IMRT wurde angenommen. Basierend auf gleichen Zielgrößenvorgaben wurde für je einen Fall mit Prostatakarzinom, Hirntumor, HNO-Tumor sowie gynäkologischem Tumor eine IP durchgeführt. Die IMRT-Pläne wurden anhand von Dosis-Volumen-Histogrammen (DVHs), Konformität, Homogenität und Bestrahlungseffizienz bewertet. Für je zehn Patienten mit bestimmten Indikationen wurde die Schwankung der IP-Zielgrößen untersucht.
Ergebnisse:
Mit allen drei TPS konnten ähnliche IMRT-Pläne mit vergleichbarer Zielgebietsauslastung, Dosishomogenität, Konformität und maximaler Dosisbelastung der Risikoorgane erstellt werden. Größere Unterschiede wurden hinsichtlich des Dosisgradienten außerhalb des Zielgebiets, der Monitoreinheiten sowie der Segmentzahlen beobachtet. Die Verwendung von Hilfsstrukturen erwies sich als zeitsparend. Für eine IMRT-Indikation schwanken die Zielgrößenvorgaben in Abhängigkeit von der Patientenanatomie.
Schlussfolgerung:
Mit TPS, deren Zielgrößen und Zielfunktionen auf physikalischen Dosen beruhen, konnten ähnliche IMRT-Pläne erzielt werden. Für IMRT-Konzepte lassen sich Standardzielvorgaben festlegen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georg, D., Kroupa, B., Georg, P. et al. Inverse Planning – a Comparative Intersystem and Interpatient Constraint Study. Strahlenther Onkol 182, 473–480 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-006-1531-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-006-1531-y