Abstract
Purpose
To study the clinical potential of a deep learning neural network (convolutional neural networks [CNN]) as a supportive tool for detection of intracranial aneurysms from 3D time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography (TOF-MRA) by comparing the diagnostic performance to that of human readers.
Methods
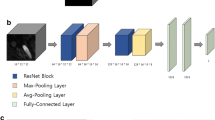
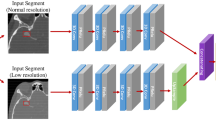
In this retrospective study a pipeline for detection of intracranial aneurysms from clinical TOF-MRA was established based on the framework DeepMedic. Datasets of 85 consecutive patients served as ground truth and were used to train and evaluate the model. The ground truth without annotation was presented to two blinded human readers with different levels of experience in diagnostic neuroradiology (reader 1: 2 years, reader 2: 12 years). Diagnostic performance of human readers and the CNN was studied and compared using the χ2-test and Fishers’ exact test.
Results
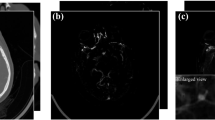
Ground truth consisted of 115 aneurysms with a mean diameter of 7 mm (range: 2–37 mm). Aneurysms were categorized as small (S; <3 mm; N = 13), medium (M; 3–7 mm; N = 57), and large (L; >7 mm; N = 45) based on the diameter. No statistically significant differences in terms of overall sensitivity (OS) were observed between the CNN and both of the human readers (reader 1 vs. CNN, P = 0.141; reader 2 vs. CNN, P = 0.231). The OS of both human readers was improved by combination of each readers’ individual detections with the detections of the CNN (reader 1: 98% vs. 95%, P = 0.280; reader 2: 97% vs. 94%, P = 0.333).
Conclusion
A CNN is able to detect intracranial aneurysms from clinical TOF-MRA data with a sensitivity comparable to that of expert radiologists and may have the potential to improve detection rates of incidental findings in a clinical setting.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACA:
-
Anterior cerebral artery
- ADPKD:
-
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- CAD:
-
Computer-aided detection
- CNN:
-
Deep learning neural network
- CTA:
-
Computed tomography angiography
- DSA:
-
Digital subtraction angiography
- ICA:
-
Internal carotid artery
- MCA:
-
Middle cerebral artery
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- OECD:
-
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
- PACS:
-
Picture archiving and communication system
- POST:
-
Posterior circulation
- T:
-
Tesla
References
McDonald RJ, Schwartz KM, Eckel LJ, Diehn FE, Hunt CH, Bartholmai BJ, Erickson BJ, Kallmes DF. The effects of changes in utilization and technological advancements of cross-sectional imaging on radiologist workload. Acad Radiol. 2015;22:1191–8.
OECD (2018) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) exams (indicator). https://doi.org/10.1787/1d89353f-en. Accessed on 6 December 2018.
Berbaum KS, Franken EA, Dorfman DD, Rooholamini SA, Kathol MH, Barloon TJ, Behlke FM, Sato Y, Lu CH, el-Khoury GY, Flickinger FW, Montgomery WJ. Satisfaction of search in diagnostic radiology. Invest Radiol. 1990;25:133–40.
Lindgren AE, Koivisto T, Björkman J, Von Und Zu Fraunberg M, Helin K, Jääskeläinen JE, Frösen J. Irregular shape of Intracranial aneurysm indicates rupture risk irrespective of size in a population-based cohort. Stroke. 2016;47:1219–26.
Thompson BG, Brown RD Jr, Amin-Hanjani S, Broderick JP, Cockroft KM, Connolly ES Jr, Duckwiler GR, Harris CC, Howard VJ, Johnston SC, Meyers PM, Molyneux A, Ogilvy CS, Ringer AJ, Torner J; American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing, and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; American Heart Association; American Stroke Association. Guidelines for the management of patients with Unruptured Intracranial aneurysms: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2015;46:2368–400.
Backes D, Vergouwen MD, Tiel Groenestege AT, Bor AS, Velthuis BK, Greving JP, Algra A, Wermer MJ, van Walderveen MA, terBrugge KG, Agid R, Rinkel GJ. PHASES score for prediction of Intracranial aneurysm growth. Stroke. 2015;46:1221–6.
Choi HH, Cho YD, Jeon JP, Yoo DH, Moon J, Lee J, Kang HS, Cho WS, Kim JE, Zhang L, Han MH. Growth of untreated unruptured small-sized aneurysms (≺7 mm): incidence and related factors. Clin Neuroradiol. 2018;28:183–9.
Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, Clarke M, Sneade M, Yarnold JA, Sandercock P; International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial ( ISAT ) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet. 2005;366:809–17.
Etminan N, Brown RD Jr, Beseoglu K, Juvela S, Raymond J, Morita A, Torner JC, Derdeyn CP, Raabe A, Mocco J, Korja M, Abdulazim A, Amin-Hanjani S, Al-Shahi Salman R, Barrow DL, Bederson J, Bonafe A, Dumont AS, Fiorella DJ, Gruber A, Hankey GJ, Hasan DM, Hoh BL, Jabbour P, Kasuya H, Kelly ME, Kirkpatrick PJ, Knuckey N, Koivisto T, Krings T, Lawton MT, Marotta TR, Mayer SA, Mee E, Pereira VM, Molyneux A, Morgan MK, Mori K, Murayama Y, Nagahiro S, Nakayama N, Niemelä M, Ogilvy CS, Pierot L, Rabinstein AA, Roos YB, Rinne J, Rosenwasser RH, Ronkainen A, Schaller K, Seifert V, Solomon RA, Spears J, Steiger HJ, Vergouwen MD, Wanke I, Wermer MJ, Wong GK, Wong JH, Zipfel GJ, Connolly ES Jr, Steinmetz H, Lanzino G, Pasqualin A, Rüfenacht D, Vajkoczy P, McDougall C, Hänggi D, LeRoux P, Rinkel GJ, Macdonald RL. The unruptured intracranial aneurysm treatment score: a multidisciplinary consensus. Neurology. 2015;85:881–9.
Walendy V, Stang A. Clinical management of unruptured intracranial aneurysm in Germany: a nationwide observational study over a 5-year period. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e12294.
Brisman J, Song J, Newell D. Cerebral aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:928–39.
Wardlaw JM, White PM. The detection and management of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Brain. 2000;123:205–21.
White PM, Wardlaw JM, Easton V. Can noninvasive imaging accurately depict intracranial aneurysms? A systematic review. Radiology. 2000;217:361–70.
Okahara M, Kiyosue H, Yamashita M, Nagatomi H, Hata H, Saginoya T, Sagara Y, Mori H. Diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance angiography for cerebral aneurysms in correlation with 3D-digital subtraction angiographic images: a study of 133 aneurysms. Stroke. 2002;33:1803–8.
Prevedello LM, Erdal BS, Ryu JL, Little KJ, Demirer M, Qian S, White RD. Automated critical test findings identification and online notification system using artificial intelligence in imaging. Radiology. 2017;285:923–31.
Larson DB, Chen MC, Lungren MP, Halabi SS, Stence NV, Langlotz CP. Performance of a deep-learning neural network model in assessing skeletal maturity on pediatric hand radiographs. Radiology. 2018;287:313–22.
Ueda D, Yamamoto A, Nishimori M, Shimono T, Doishita S, Shimazaki A, Katayama Y, Fukumoto S, Choppin A, Shimahara Y, Miki Y. Deep learning for MR angiography: automated detection of cerebral aneurysms. Radiology. 2019;290:187–94.
Sichtermann T, Faron A, Sijben R, Teichert N, Freiherr J, Wiesmann M. Deep-learning-based detection of Intracranial aneurysms in 3D TOF-MRA. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2019;40:25-32.
Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett CH, Smith RG, Ho S, Gee JC, Gerig G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage. 2006;31:1116–28.
Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe VFJ, Simpson JP, Kane AD, Menon DK, Rueckert D, Glocker B. Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal. 2017;36:61–78.
Rodríguez JD, Pérez A, Lozano JA. Sensitivity analysis of k‑fold cross validation in prediction error estimation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2010;32:569–75.
Miki S, Hayashi N, Masutani Y, Nomura Y, Yoshikawa T, Hanaoka S, Nemoto M, Ohtomo K. Computer-assisted detection of cerebral aneurysms in MR angiography in a routine image-reading environment: effects on diagnosis by radiologists. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016;37:1038–43.
Nomura Y, Masutani Y, Miki S, Nemoto M, Hanaoka S, Yoshikawa T, Hayashi N, Ohtomo K. Performance improvement in computerized detection of cerebral aneurysms by retraining classifier using feedback data collected in routine reading environment. J Biomed Graph Comput. 2014;4:12–21.
Štepán-Buksakowska IL, Accurso JM, Diehn FE, Huston J, Kaufmann TJ, Luetmer PH, Wood CP, Yang X, Blezek DJ, Carter R, Hagen C, Hořínek D, Hejčl A, Roček M, Erickson BJ. Computer-aided diagnosis improves detection of small intracranial aneurysms on MRA in a clinical setting. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;35:1897–902.
Nakao T, Hanaoka S, Nomura Y, Sato I, Nemoto M, Miki S, Maeda E, Yoshikawa T, Hayashi N, Abe O. Deep neural network-based computer-assisted detection of cerebral aneurysms in MR angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018;47:948–53.
Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston J 3rd, Meissner I, Brown RD Jr, Piepgras DG, Forbes GS, Thielen K, Nichols D, O’Fallon WM, Peacock J, Jaeger L, Kassell NF, Kongable-Beckman GL, Torner JC; International Study of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms Investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet. 2003;362:103–10.
Li MH, Li YD, Tan HQ, Gu BX, Chen YC, Wang W, Chen SW, Hu DJ. Contrast-free MRA at 3.0 T for the detection of intracranial aneurysms. Neurology. 2011;77:667–76.
Funding
The work was supported by Nvidia Corporation (Santa Clara, CA, USA) with the donation of a Titan XP GPU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Faron, T. Sichtermann, N. Teichert, J.A. Luetkens, A. Keulers, O. Nikoubashman, J. Freiherr, A. Mpotsaris and M. Wiesmann declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
A. Faron and T. Sichtermann contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faron, A., Sichtermann, T., Teichert, N. et al. Performance of a Deep-Learning Neural Network to Detect Intracranial Aneurysms from 3D TOF-MRA Compared to Human Readers. Clin Neuroradiol 30, 591–598 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-019-00809-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-019-00809-w