Abstract
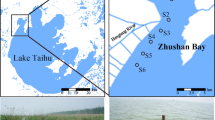
Sedimentation and resuspension processes, are known to govern nutrient cycling and lake metabolic processes, but have not been well studied in littoral zones with multi-ecotypes of shallow wind-disturbed lakes. This time-series study used sediment traps to estimate the spatiotemporal changes in sedimentation and resuspension rates, during the four seasonal continuous deployment periods, in the littoral zone of Lake Taihu. The effect of sedimentation processes on nutrient accumulation was also investigated. Results showed that the sedimentation rates at six observation sites were highly variable, with gross sedimentation rates ranging from 184.83 to 2150.74 g m−2 day−1. Almost 88% of the total observed sedimentation originated from sediment resuspension. Cyanobacterial blooms coupled with the frequently changeable wind conditions in the littoral zone, were the key factors in lacustrine sediment redistribution and a large pool of organic material accumulated during cyanobacterial blooms. Moreover, the contribution of resuspended total phosphorous and total nitrogen to the water column, were 0.22 mg L−1 and 0.46 mg L−1, respectively. The high rate of rapid nutrient cycling observed at the sediment water interface due to resuspension, may be a key factor in maintaining eutrophication in large and shallow lakes, which is of high relevance to the future management of aquatic ecosystems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloesch J (1994) A review of methods used to measure sediment resuspension. Hydrobiologia 284:13–18
Bloesch J, Uehlinger U (1986) Horizontal sedimentation differences in a eutrophic Swiss Lake. Limnol Oceanogr 31:1094–1109
Chalar G, Tundisi JG (2015) Phosphorus fractions and fluxes in the water column and sediments of a tropical reservoir (Lobo-Broa-SP). Int Rev Hydrobiol 86:183–194
Chung EG, Bombardelli FA, Schladow SG (2009) Sediment resuspension in a shallow lake. Water Resour Res 45:5422
Ding Y, Qin B, Deng J, Ma J (2017) Effects of episodic sediment resuspension on phytoplankton in Lake Taihu: focusing on photosynthesis, biomass and community composition. Aquat Sci 79:1–13
Ding S, Chen M, Gong M, Fan X, Qin B, Xu H, Gao S, Jin Z, Tsang D, Zhang C (2018) Internal phosphorus loading from sediments causes seasonal nitrogen limitation for harmful algal blooms. Sci Total Environ 625:872–884
Douglas RW, Rippey B, Gibson CE (2003) Estimation of the in-situ settling velocity of particles in lakes using a time series sediment trap. Freshw Biol 48:512–518
Ebina J, Tsutsui T, Shirai T (1983) Simultaneous determination of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in water using peroxodisulfate oxidation. Water Res 17:1721–1726
Eckert W, Didenko J, Uri E, Eldar D (2003) Spatial and temporal variability of particulate phosphorus fractions in seston and sediments of Lake Kinneret under changing loading scenario. Hydrobiologia 494:223–229
Evans RD (1994) Empirical evidence of the importance of sediment resuspension in lakes. Hydrobiologia 284:5–12
Ganaoui OE, Schaaff E, Boyer P, Amielh M, Anselmet F, Grenz C (2004) The deposition and erosion of cohesive sediments determined by a multi-class model. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 60:457–475
Gasith A (1975) Tripton sedimentation in eutrophic lakes: simple correction for the resuspended matter. Verh Int Ver Theor Angew Limnol 19:116–122
Håkanson L, Floderus S, Wallin M (1989) Sediment trap assemblages—a methodological description. Hydrobiologia 176/177:481–490
Hofmann H, Lorke A, Peeters F (2011) Wind and ship wave-induced resuspension in the littoral zone of a large lake. Water Resour Res 47:1995–2021
Horppila J, Niemistö J (2008) Horizontal and vertical variations in sedimentation and resuspension rates in a stratifying lake—effects of internal seiches. Sedimentology 55:1135–1144
Horppila J, Nurminen L (2005) Effects of calculation procedure and sampling site on trap method estimates of sediment resuspension in a shallow lake. Sedimentology 52:903–913
Horppila J, Kaitaranta J, Joensuu L, Nurminen L (2013) Influence of emergent macrophyte (Phragmites australis) density on water turbulence and erosion of organic-rich sediment. J Hydrodyn 25:288–293
Hu CH, Hu WP, Zhang FB, Hu ZX, Li XH, Chen YG (2005) Observation of sediment resuspension in Lake Taihu. Chin Sci Bull 50:2541–2545 (in Chinese)
Huang J, Xu Q, Xi B, Wang X, Li W, Gao G, Huo S, Xia X, Jiang T, Ji D (2015) Impacts of hydrodynamic disturbance on sediment resuspension, phosphorus and phosphatase release, and cyanobacterial growth in Lake Tai. Environ Earth Sci 74:3945–3954
James WF (2004) Shear stress and sediment resuspension in relation to submersed macrophyte biomass. Hydrobiologia 515:181–191
Kaitaranta J, Niemistö J, Buhvestova O, Nurminen L (2013) Quantifying sediment resuspension and internal phosphorus loading in shallow near-shore areas in the gulf of Finland. Boreal Environ Res 18:473–487
Kling HJ, Watson SB, Mccullough GK, Stainton MP (2011) Bloom development and phytoplankton succession in Lake Winnipeg: a comparison of historical records with recent data. Aquat Ecosyst Health 14:219–224
Li F, Pan Y, Xie Y, Chen X, Deng Z, Li X, Hou Z, Tang Y (2016) Different roles of three emergent macrophytes in promoting sedimentation in Dongting Lake, China. Aquat Sci 78:159–169
Li Y, Tang C, Wang J, Acharya K, Wei D, Gao X, Luo L, Li H, Dai S, Mercy J (2017) Effect of wave-current interactions on sediment resuspension in large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:1–11
Liu X, Zhang Y, Yin Y, Wang M, Qin B (2013) Wind and submerged aquatic vegetation influence bio-optical properties in large shallow Lake Taihu, China. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 118:713–727
Lu J, Bunn SE, Burford MA (2018) Nutrient release and uptake by littoral macrophytes during water level fluctuations. Sci Total Environ 622/623:29–40
Matisoff G, Watson SB, Guo J, Duewiger A, Steely R (2017) Sediment and nutrient distribution and resuspension in Lake Winnipeg. Sci Total Environ 575:173–186
Pejrup M, Valeur J, Jensen A (2013) Vertical fluxes of particulate matter in Aarhus Bight, Denmark. Cont Shelf Res 16:1047–1064
Qi S, Zhang X, Wang D, Zhu J, Fang C (2014) Study of morphologic change in Poyang Lake basin caused by sand dredging using multi-temporal landsat images and DEMs. ISPRS J Photogramm XL-1 40:355–362
Qin B, Hu WP, Gao G, Luo LC, Zhang JS (2004) Dynamics of sediment resuspension and the conceptual schema of nutrient release in the large shallow Lake Taihu, China. Chin Sci Bull 49:54–64
Qin B, Xu P, Wu Q, Luo L, Zhang Y (2007) Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581:3–14
Sedláček J, Bábek O, Kielar O (2016) Sediment accumulation rates and high-resolution stratigraphy of recent fluvial suspension deposits in various fluvial settings, Morava River catchment area, Czech Republic. Geomorphology 254:73–87
Søndergaard M, Kristensen P, Jeppesen E (1992) Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind-exposed Lake Arresø, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 228:91–99
Storlazzi CD, Field ME, Bothner MH (2011) The use (and misuse) of sediment traps in coral reef environments: theory, observations, and suggested protocols. Coral Reefs 30:23–38
Tammeorg O, Niemistö J, Möls T, Laugaste R, Panksep K, Kangur K (2013) Wind-induced sediment resuspension as a potential factor sustaining eutrophication in large and shallow Lake Peipsi. Aquat Sci 75:559–570
Voulgaris G, Meyers ST (2004) Temporal variability of hydrodynamics, sediment concentration and sediment settling velocity in a tidal creek. Cont Shelf Res 24:1659–1683
Wang P, Hu B, Wang C, Lei Y (2015) Phosphorus adsorption and sedimentation by suspended sediments from Zhushan Bay, Taihu Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:1–11
Whinney J, Jones R, Duckworth A, Ridd P (2017) Continuous in situ monitoring of sediment deposition in shallow benthic environments. Coral Reefs 36:1–13
Wu Z, Liu Y, Liang Z, Wu S, Guo H (2017) Internal cycling, not external loading, decides the nutrient limitation in eutrophic lake: a dynamic model with temporal bayesian hierarchical inference. Water Res 116:231
Xing P, Guo L, Tian W, Wu QL (2011) Novel clostridium populations involved in the anaerobic degradation of Microcystis blooms. ISME J 5:792–800
Zaja̧czkowski M (2002) On the use of sediment traps in sedimentation measurements in glaciated fjords. Pol Polar Res 23:161–174
Zhang Y, Lu X, Shao X, Chen C, Li X, Zhao F, Li G, Matsumoto E (2016) Temporal variation of sedimentation rates and potential factors influencing those rates over the last 100 years in Bohai Bay, China. Sci Total Environ 572:68–76
Zhu M, Zhu G, Nurminen L, Wu T, Deng J, Zhang Y, Qin B, Ventelä AM (2015) The influence of macrophytes on sediment resuspension and the effect of associated nutrients in a shallow and large lake (Lake Taihu, China). PLoS One 10:e012791
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Water Pollution Control and Treatment Science and Technology Major Project (no. 2017ZX07203003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 41703105, 41573061), the Natural Science Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Jiangsu Province (no. 17KJB170009), the Research Projects of Water Environment Comprehensive Management in Lake Taihu of Jiangsu Province (no. TH2014402), Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (no. KYCX17_1065). Finally, gratitude is extended to Ran Lu and Ziya Liu (School of Environment, Nanjing Normal University) for their valuable assistance with nutrient analysis in the laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, C., Zhou, Y., Xu, Xg. et al. Dynamic monitoring of resuspension in the multiple eco-types of the littoral zone of a shallow wind-disturbed lake. Aquat Sci 81, 33 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-019-0620-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-019-0620-9