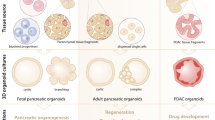
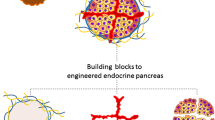
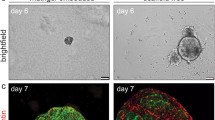
Abstract
Over the past few years, extensive efforts have been made to generate in-vitro pancreatic micro-tissue, for disease modeling or cell replacement approaches in pancreatic related diseases such as diabetes mellitus. To obtain these goals, a closer look at the diverse cells participating in pancreatic development is necessary. Five major non-epithelial pancreatic (pN-Epi) cell populations namely, pancreatic endothelium, mesothelium, neural crests, pericytes, and stellate cells exist in pancreas throughout its development, and they are hypothesized to be endogenous inducers of the development. In this review, we discuss different pN-Epi cells migrating to and existing within the pancreas and their diverse effects on pancreatic epithelium during organ development mediated via associated signaling pathways, soluble factors or mechanical cell–cell interactions. In-vivo and in-vitro experiments, with a focus on N-Epi cells’ impact on pancreas endocrine development, have also been considered. Pluripotent stem cell technology and multicellular three-dimensional organoids as new approaches to generate pancreatic micro-tissues have also been discussed. Main challenges for reaching a detailed understanding of the role of pN-Epi cells in pancreas development in utilizing for in-vitro recapitulation have been summarized. Finally, various novel and innovative large-scale bioengineering approaches which may help to recapitulate cell–cell interactions and are crucial for generation of large-scale in-vitro multicellular pancreatic micro-tissues, are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
a Lipophilic cationic indocarbocyanine fluorescent dye for membrane staining.
A cell-surface chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan.
The epithelium lining the surface layer of the embryonic mesoderm.
Magnetic levitation method (MLM) applies growing 3D tissue by inducing cells treated with magnetic nanoparticle assemblies in spatially varying magnetic fields using neodymium magnetic drivers and promoting cell–cell interactions by levitating the cells up to the air/liquid interface of a standard petri dish.
Abbreviations
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- α-SMA:
-
Alpha-smooth muscle actin
- AAT:
-
Alpha-1 antitrypsin
- Ang-1:
-
Angiopoietin
- BM-MSC:
-
Bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells
- BMP4:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 4
- CF:
-
Cystic fibrosis
- CFTR:
-
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DKK1:
-
Dickkopf-related protein 1
- DPC:
-
Days post-conception
- EB:
-
Embryoid bodies
- E:
-
Embryonic day
- EC:
-
Endothelial cell
- ECM:
-
Extra cellular matrix
- EGFL7:
-
Epidermal growth factor‐like domain 7
- EPC:
-
Endothelial progenitor cell
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric-oxide synthase
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- FGF10:
-
Fibroblast growth factor 10
- FOXD3:
-
Forkhead Box D3
- GDNF:
-
Glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GLUT2:
-
Glucose transporter 2
- GP2:
-
Glycoprotein 2
- GSIS:
-
Glucose -stimulated insulin secretion
- hESC:
-
Human embryonic stem cell
- HGF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
- hiPSC:
-
Human induced pluripotent stem cell
- hPSC:
-
Human pluripotent stem cell
- HOX:
-
Homeobox
- HUVEC:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cell
- IGF:
-
Insulin growth factor
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IRS2:
-
Insulin receptor substrate-2
- ISL-1:
-
Insulin gene enhancer protein ISL-1
- LAMA2:
-
α2 Laminins
- LGALS1:
-
Galectin 1
- MAFA:
-
Musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene family A.
- mESC:
-
Mouse embryonic stem cell
- MIDY:
-
Mutant insulin-gene-induced diabetes of youth
- MIN6:
-
Mouse insulinoma 6
- MMP:
-
Metalloproteinases
- MPCs:
-
Multipotent progenitor cells
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- NC:
-
Neural crest
- NG2:
-
Neural-glial Antigen 2
- NGN3:
-
Neurogenin3
- NKX3.2:
-
NK3 Homeobox 2 /NKX2.2: NK2 Homeobox 2 /NKX6.1: NK6 Homeobox 1
- PDAC:
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PAX3:
-
Paired box gene 3
- PHOX2B:
-
Paired-like homeobox 2b
- PECAM1:
-
Platelet and endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1
- PEG:
-
Poly Ethylene Glycol
- PES/PBP:
-
Poly ether sulfone/poly vinyl pyrrolidone
- PBX1:
-
Pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 1
- PDX1:
-
Pancreas-duodenum homeobox protein1
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- PDGFRβ:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta
- PGA:
-
Poly glycolic acid
- PTF1a:
-
Pancreas transcription factor 1 subunit alpha
- pN-Epi:
-
Pancreatic non-epithelial
- RAS:
-
Renin–angiotensin system
- RHMVEC:
-
Rat heart microvascular endothelial cell
- S1P:
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate
- SC-β CELLS:
-
Stem cell-derived β-cells
- SDC4:
-
Syndecan4
- SFRP3:
-
Secreted frizzled-related protein 3
- SOX9/10:
-
SRY-Box 9/10
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- SynCAM:
-
Synaptic cell adhesion molecule/CADM-1
- T1DM:
-
Type 1 diabetes mellitus
- T2DM:
-
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- TCF7L2:
-
Transcription factor 7 like 2
- TGFβ:
-
Transforming growth factor β
- Tie-2:
-
Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-2
- TIMP-1:
-
TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 1
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
- TFAP2α:
-
Transcription factor AP-2 alpha
- Vcan:
-
Versican
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- vSMC:
-
Vascular smooth muscle cell
- WPC:
-
Weeks post-conception
- WNT:
-
Wingless
References
Nair GG, Tzanakakis ES, Hebrok M (2020) Emerging routes to the generation of functional β-cells for diabetes mellitus cell therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol 1–13
Bourgeois S, Sawatani T, Van Mulders A, De Leu N, Heremans Y, Heimberg H, Cnop M, Staels W (2021) Towards a functional cure for diabetes using stem cell-derived beta cells: are we there yet? Cells 10:191
Johnson JD (2016) The quest to make fully functional human pancreatic beta cells from embryonic stem cells: climbing a mountain in the clouds. Diabetologia 59:2047–2057
Rezania A, Bruin JE, Riedel MJ, Mojibian M, Asadi A, Xu J, Gauvin R, Narayan K, Karanu F, O’Neil JJ, Ao Z, Warnock GL, Kieffer TJ (2012) Maturation of human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitors into functional islets capable of treating pre-existing diabetes in mice. Diabetes 61:2016–2029. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1711
Pagliuca FW, Millman JR, Gurtler M, Segel M, Van Dervort A, Ryu JH, Peterson QP, Greiner D, Melton DA (2014) Generation of functional human pancreatic beta cells in vitro. Cell 159:428–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.040
Clevers H (2016) Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell 165:1586–1597
Abdelalim EM, Emara MM (2015) Advances and challenges in the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into pancreatic β cells. World J Stem Cells 7:174–181
Larsen HL, Grapin-Botton A (2017) The molecular and morphogenetic basis of pancreas organogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 66:51–68
Petersen MB, Gonçalves CA, Kim YH, Grapin-Botton A (2018) Recapitulating and deciphering human pancreas development from human pluripotent stem cells in a dish. Current topics in developmental biology. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 143–190
Ghani MW, Ye L, Yi Z, Ghani H, Birmani MW, Nawab A, Cun LG, Bin L, Mei X (2019) Pancreatic β-cell replacement: advances in protocols used for differentiation of pancreatic progenitors to β-like cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 57:101–115
Jennings RE, Berry AA, Strutt JP, Gerrard DT, Hanley NA (2015) Human pancreas development. Development 142:3126–3137
Khosravi-Maharlooei M, Hajizadeh-Saffar E, Tahamtani Y, Basiri M, Montazeri L, Khalooghi K, Ashtiani MK (2015) Islet transplantation for type 1 diabetes: so close and yet so far away. Eur J Endoerinol 173:R165–R183
Bastidas-Ponce A, Scheibner K, Lickert H, Bakhti M (2017) Cellular and molecular mechanisms coordinating pancreas development. Development 144:2873–2888
Shih HP, Wang A, Sander MJAroc (2013) Pancreas organogenesis: from lineage determination to morphogenesis. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 29:81–105
Yang K, Wang Y, Du Z, Zhang X (2014) Short-reactivation of neurogenin-3 and mesenchymal microenvironment is require for β-cells differentiation during fetal pancreas development and islet regeneration. Romanian J Morphol Embryol Revue Roumaine de Morphol Embryol 55:305–311
Benitez CM, Goodyer WR, Kim SK (2012) Deconstructing pancreas developmental biology. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 4:a012401
Sznurkowska MK, Hannezo E, Azzarelli R, Rulands S, Nestorowa S, Hindley CJ, Nichols J, Göttgens B, Huch M, Philpott A (2018) Defining lineage potential and fate behavior of precursors during pancreas development. Dev Cell 46:360–375365
Edlund H (2001) Developmental biology of the pancreas. Diabetes 50:S5
Larsen BM, Hrycaj SM, Newman M, Li Y, Wellik DM (2015) Mesenchymal Hox6 function is required for mouse pancreatic endocrine cell differentiation. Development 142:3859–3868
Sakhneny L, Khalifa-Malka L, Landsman L (2019) Pancreas organogenesis: Approaches to elucidate the role of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. Semin Cell Dev Biol 92:89–96
Olsson R, Carlsson P-O (2006) The pancreatic islet endothelial cell: emerging roles in islet function and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38:710–714
Ranjan AK, Joglekar MV, Hardikar A (2009) Endothelial cells in pancreatic islet development and function. Islets 1:2–9
Aird WC (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100:158–173
Lammert E, Cleaver O, Melton D (2003) Role of endothelial cells in early pancreas and liver development. Mech Dev 120:59–64
Pierreux CE, Cordi S, Hick A-C, Achouri Y, de Almodovar CR, Prévot P-P, Courtoy PJ, Carmeliet P, Lemaigre FPJDb (2010) Epithelial: Endothelial cross-talk regulates exocrine differentiation in developing pancreas. Dev Biol 347:216–227
Talavera-Adame D, Dafoe DC (2015) Endothelium-derived essential signals involved in pancreas organogenesis. World J Exp Med 5:40
Yoshitomi H, Zaret KS (2004) Endothelial cell interactions initiate dorsal pancreas development by selectively inducing the transcription factor Ptf1a. Development 131:807–817
Guney MA (2009) Gannon MJBDRPCETR. Pancreas cell fate 87:232–248
Hogan MF, Hull RLJD (2017) The islet endothelial cell: a novel contributor to beta cell secretory dysfunction in diabetes. Diabetologia 60:952–959
Staels W, Heremans Y, Heimberg H, De Leu N (2019) VEGF-A and blood vessels: a beta cell perspective. Diabetologia 62:1961–1968
Ning FC, Jensen N, Mi J, Lindström W, Balan M, Muhl L, Eriksson U, Nilsson I, Nyqvist D (2020) VEGF-B ablation in pancreatic β-cells upregulates insulin expression without affecting glucose homeostasis or islet lipid uptake. Sci Rep 10:1–13
Johansson Å, Lau J, Sandberg M, Borg L, Magnusson P, Carlsson P-O (2009) Endothelial cell signalling supports pancreatic beta cell function in the rat. Diabetologia 52:2385–2394
Nikolova G, Jabs N, Konstantinova I, Domogatskaya A, Tryggvason K, Sorokin L, Fässler R, Gu G, Gerber H-P, Ferrara N (2006) The vascular basement membrane: a niche for insulin gene expression and β cell proliferation. Dev Cell 10:397–405
Pan FC, Brissova M (2014) Pancreas development in humans. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 21:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1097/med.0000000000000047
Hashimoto S, Kubota N, Sato H, Sasaki M, Takamoto I, Kubota T, Nakaya K, Noda M, Ueki K, Kadowaki T (2015) Insulin receptor substrate-2 (Irs2) in endothelial cells plays a crucial role in insulin secretion. Diabetes 64:876–886
Coultas L, Chawengsaksophak K, Rossant J (2005) Endothelial cells and VEGF in vascular development. Nature 438:937
Cai Q, Brissova M, Reinert RB, Pan FC, Brahmachary P, Jeansson M, Shostak A, Radhika A, Poffenberger G, Quaggin SE (2012) Enhanced expression of VEGF-A in β cells increases endothelial cell number but impairs islet morphogenesis and β cell proliferation. Dev Biol 367:40–54
Hadi HA, Al Suwaidi J (2007) Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Vasc Health Risk Manag 3:853
Peiris H, Bonder CS, Coates PTH, Keating DJ, Jessup CF (2014) The β-cell/EC axis: how do islet cells talk to each other? Diabetes 63:3–11
Pan FC, Wright C (2011) Pancreas organogenesis: from bud to plexus to gland. Dev Dyn 240:530–565
Seymour PA, Serup P (2019) Mesodermal induction of pancreatic fate commitment. Semin Cell Dev Biol 92:77–88
Landsman L, Nijagal A, Whitchurch TJ, VanderLaan RL, Zimmer WE, MacKenzie TC, Hebrok M (2011) Pancreatic mesenchyme regulates epithelial organogenesis throughout development. PLoS Biol 9:e1001143
Angelo JR, Tremblay KD (2018) Identification and fate mapping of the pancreatic mesenchyme. Dev Biol 435:15–25
Attali M, Stetsyuk V, Basmaciogullari A, Aiello V, Zanta-Boussif MA, Duvillie B, Scharfmann R (2007) Control of β-cell differentiation by the pancreatic mesenchyme. Diabetes 56:1248–1258
Duvillié B, Attali M, Bounacer A, Ravassard P, Basmaciogullari A, Scharfmann R (2006) The mesenchyme controls the timing of pancreatic β-cell differentiation. Diabetes 55:582–589
Byrnes LE, Wong DM, Subramaniam M, Meyer NP, Gilchrist CL, Knox SM, Tward AD, Chun JY, Sneddon JB (2018) Lineage dynamics of murine pancreatic development at single-cell resolution. Nat Commun 9:1–17
Cooper TT, Sherman SE, Bell GI, Ma J, Kuljanin M, Jose SE, Lajoie GA, Hess DA (2020) Characterization of a Vimentin high/Nestin high proteome and tissue regenerative secretome generated by human pancreas-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells 38:666–682
Cozzitorto C, Mueller L, Ruzittu S, Mah N, Willnow D, Darrigrand J-F, Wilson H, Khosravinia D, Mahmoud A-A, Risolino M (2020) A specialized niche in the pancreatic microenvironment promotes endocrine differentiation. Dev Cell 55:150-162 e156
Miralles F, Lamotte L, Couton D, Joshi RL (2003) Interplay between FGF10 and Notch signalling is required for the self-renewal of pancreatic progenitors. Int J Dev Biol 50:17–26
Ye F, Duvillie B, Scharfmann R (2005) Fibroblast growth factors 7 and 10 are expressed in the human embryonic pancreatic mesenchyme and promote the proliferation of embryonic pancreatic epithelial cells. Diabetologia 48:277–281
Kobberup S, Schmerr M, Dang M-L, Nyeng P, Jensen JN, MacDonald RJ, Jensen J (2010) Conditional control of the differentiation competence of pancreatic endocrine and ductal cells by Fgf10. Mech Dev 127:220–234
Seymour PA, Shih HP, Patel NA, Freude KK, Xie R, Lim CJ, Sander M (2012) A Sox9/Fgf feed-forward loop maintains pancreatic organ identity. Development 139:3363–3372
Otonkoski T, Cirulli V, Beattie M, Mally MI, Soto G, Rubin JS, Hayek A (1996) A role for hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor in fetal mesenchyme-induced pancreatic beta-cell growth. Endocrinology 137:3131–3139
Guo T, Landsman L, Li N, Hebrok M (2013) Factors expressed by murine embryonic pancreatic mesenchyme enhance generation of insulin-producing cells from hESCs. Diabetes 62:1581–1592
Hammerle CM, Sandovici I, Brierley GV, Smith NM, Zimmer WE, Zvetkova I, Prosser HM, Sekita Y, Lam BY, Ma M (2020) Mesenchyme-derived IGF2 is a major paracrine regulator of pancreatic growth and function. PLoS Genet 16:e1009069
Guerriero I, De Angelis MT, D’Angelo F, Leveque R, Savignano E, Roberto L, Lucci V, Mazzone P, Laurino S, Storto G (2019) Exploring the molecular crosstalk between pancreatic bud and mesenchyme in embryogenesis: novel signals involved. Int J Mol Sci 20:4900
Russ HA, Landsman L, Moss CL, Higdon R, Greer RL, Kaihara K, Salamon R, Kolker E, Hebrok M (2016) Dynamic proteomic analysis of pancreatic mesenchyme reveals novel factors that enhance human embryonic stem cell to pancreatic cell differentiation. Stem Cells Int 2016
Tulachan SS, Doi R, Hirai Y, Kawaguchi Y, Koizumi M, Hembree M, Tei E, Crowley A, Yew H, McFall C (2006) Mesenchymal epimorphin is important for pancreatic duct morphogenesis. Dev Growth Differ 48:65–72
Miralles F, Czernichow P, Scharfmann R (1998) Follistatin regulates the relative proportions of endocrine versus exocrine tissue during pancreatic development. Development 125:1017–1024
Gilbert JM, Adams MT, Sharon N, Jayaraaman H, Blum B (2021) Morphogenesis of the islets of Langerhans is guided by extra-endocrine Slit2/3 signals. Molecular and cellular biology 41
Epshtein A, Rachi E, Sakhneny L, Mizrachi S, Baer D, Landsman L (2017) Neonatal pancreatic pericytes support β-cell proliferation. Mol Metab 6:1330–1338
Armulik A, Genové G, Betsholtz C (2011) Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev Cell 21:193–215
Lin PY, Peng SJ, Shen CN, Pasricha PJ, Tang SC (2016) PanIN-associated pericyte, glial, and islet remodeling in mice revealed by 3D pancreatic duct lesion histology. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 311:412–422
Tang S-C, Jessup CF, Campbell-Thompson M (2018) The role of accessory cells in Islet homeostasis. Curr Diabetes Rep 18:117
Baron M, Veres A, Wolock SL, Faust AL, Gaujoux R, Vetere A, Ryu JH, Wagner BK, Shen-Orr SS, Klein AM (2016) A single-cell transcriptomic map of the human and mouse pancreas reveals inter-and intra-cell population structure. Cell Syst 3:346-360 e344
Muraro MJ, Dharmadhikari G, Grün D, Groen N, Dielen T, Jansen E, van Gurp L, Engelse MA, Carlotti F, de Koning EJ (2016) A single-cell transcriptome atlas of the human pancreas. Cell Syst 3:385-394 e383
Ferdek PE, Jakubowska MA (2017) Biology of pancreatic stellate cells—more than just pancreatic cancer. Pflügers Archiv Eur J Physiol 469:1039–1050
Zhou Y, Sun B, Li W, Zhou J, Gao F, Wang X, Cai M, Sun Z (2019) Pancreatic stellate cells: a rising translational physiology star as a potential stem cell type for beta cell neogenesis. Front Physiol 10:218
Xue R, Jia K, Wang J, Yang L, Wang Y, Gao L, Hao J (2018) A rising star in pancreatic diseases: pancreatic stellate cells. Front Physiol 9:754
Tang S-C, Chiu Y-C, Hsu C-T, Peng S-J, Fu Y-Y (2013) Plasticity of Schwann cells and pericytes in response to islet injury in mice. Diabetologia 56:2424–2434
Harari N, Sakhneny L, Khalifa-Malka L, Busch A, Hertel KJ, Hebrok M, Landsman L (2019) Pancreatic pericytes originate from the embryonic pancreatic mesenchyme. Dev Biol 449:14–20
Asahina K, Zhou B, Pu WT, Tsukamoto H (2011) Septum transversum-derived mesothelium gives rise to hepatic stellate cells and perivascular mesenchymal cells in developing mouse liver. Hepatology 53:983–995
Simsek S, Zhou T, Robinson CL, Tsai S-Y, Crespo M, Amin S, Lin X, Hon J, Evans T, Chen S (2016) Modeling cystic fibrosis using pluripotent stem cell-derived human pancreatic ductal epithelial cells. Stem Cells Transl Med 5:572–579
Almaça J, Weitz J, Rodriguez-Diaz R, Pereira E, Caicedo A (2018) The pericyte of the pancreatic islet regulates capillary diameter and local blood flow. Cell Metab 27:630–644634
Sasson A, Rachi E, Sakhneny L, Baer D, Lisnyansky M, Epshtein A, Landsman L (2016) Islet pericytes are required for β-cell maturity. Diabetes 65:3008–3014
Sakhneny L, Rachi E, Epshtein A, Guez HC, Wald-Altman S, Lisnyansky M, Khalifa-Malka L, Hazan A, Baer D, Priel A (2018) Pancreatic pericytes support β-cell function in a Tcf7l2-dependent manner. Diabetes 67:437–447
Landsman L (2019) Pancreatic pericytes in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Adv Exp Med Biol 1122:27–40
Goulley J, Dahl U, Baeza N, Mishina Y, Edlund H (2007) BMP4-BMPR1A signaling in β cells is required for and augments glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Cell Metab 5:207–219
Hammes H-P (2018) Diabetic retinopathy: hyperglycaemia, oxidative stress and beyond. Diabetologia 61:29–38
Pfister F, Wang Y, Schreiter K, Vom Hagen F, Altvater K, Hoffmann S, Deutsch U, Hammes H-P, Feng Y (2010) Retinal overexpression of angiopoietin-2 mimics diabetic retinopathy and enhances vascular damages in hyperglycemia. Acta Diabetol 47:59–64
Zhang Z-S, Zhou H-N, He S-S, Xue M-Y, Li T, Liu L-M (2020) Research advances in pericyte function and their roles in diseases. Chin J Traumatol 23:89–95
Yang Y, Kim JW, Park HS, Lee EY, Yoon KH (2020) Pancreatic stellate cells in the islets as a novel target to preserve the pancreatic β-cell mass and function. J Diabetes Investig 11:268–280
Hutchins EJ, Kunttas E, Piacentino ML, Howard AG IV, Bronner ME, Uribe RA (2018) Migration and diversification of the vagal neural crest. Dev Biol 444:S98–S109
Plank JL, Mundell NA, Frist AY, LeGrone AW, Kim T, Musser MA, Walter TJ, Labosky PA (2011) Influence and timing of arrival of murine neural crest on pancreatic beta cell development and maturation. Dev Biol 349:321–330
Shimada K, Tachibana T, Fujimoto K, Sasaki T, Okabe M (2012) Temporal and spatial cellular distribution of neural crest derivatives and alpha cells during islet development. Acta Histochem et Cytochem 1202130134–1202130134
Arntfield M, van der Kooy D (2013) The adult mammalian pancreas contains separate precursors of pancreatic and neural crest developmental origins. Stem Cells Dev 22:2145–2157
Pearse A, Polak JM (1971) Neural crest origin of the endocrine polypeptide (APUD) cells of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas. Gut 12:783–788
Pictet RL, Rall LB, Phelps P, Rutter WJ (1976) The neural crest and the origin of the insulin-producing and other gastrointestinal hormone-producing cells. Science 191:191–192
Nekrep N, Wang J, Miyatsuka T, German MS (2008) Signals from the neural crest regulate beta-cell mass in the pancreas. Development 135:2151–2160
Muñoz-Bravo JL, Hidalgo-Figueroa M, Pascual A, López-Barneo J, Leal-Cerro A, Cano DA (2013) GDNF is required for neural colonization of the pancreas. Development 140:3669–3679
Kozlova EN, Jansson L (2009) Differentiation and migration of neural crest stem cells are stimulated by pancreatic islets. NeuroReport 20:833–838
Vargas-Valderrama A, Messina A, Mitjavila-Garcia MT, Guenou H (2020) The endothelium, a key actor in organ development and hPSC-derived organoid vascularization. J Biomed Sci 27:1–13
Banerjee I, Sharma N, Yarmush M (2011) Impact of co-culture on pancreatic differentiation of embryonic stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 5:313–323
Jaramillo M, Mathew S, Mamiya H, Goh SK, Banerjee I (2015) Endothelial cells mediate islet-specific maturation of human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitor cells. Tissue Eng Part A 21:14–25
Talavera-Adame D, Wu G, He Y, Ng TT, Gupta A, Kurtovic S, Hwang JY, Farkas DL, Dafoe DC (2011) Endothelial cells in co-culture enhance embryonic stem cell differentiation to pancreatic progenitors and insulin-producing cells through BMP signaling. Stem Cell Rev Rep 7:532–543
Weizman A, Michael I, Wiesel-Motiuk N, Rezania A, Levenberg S (2014) The effect of endothelial cells on hESC-derived pancreatic progenitors in a 3D environment. Biomater Sci 2:1706–1714
Kao D-I, Lacko LA, Ding B-S, Huang C, Phung K, Gu G, Rafii S, Stuhlmann H, Chen SJScr (2015) Endothelial cells control pancreatic cell fate at defined stages through EGFL7 signaling. Stem Cell Rep 4:181–189
Augsornworawat P, Velazco-Cruz L, Song J, Millman JR (2019) A hydrogel platform for in vitro three dimensional assembly of human stem cell-derived islet cells and endothelial cells. Acta Biomater 97:272–280
Candiello J, Grandhi TSP, Goh SK, Vaidya V, Lemmon-Kishi M, Eliato KR, Ros R, Kumta PN, Rege K, Banerjee I (2018) 3D heterogeneous islet organoid generation from human embryonic stem cells using a novel engineered hydrogel platform. Biomaterials 177:27–39
Skrzypek K, Barrera YB, Groth T, Stamatialis D (2018) Endothelial and beta cell composite aggregates for improved function of a bioartificial pancreas encapsulation device. Int J Artif Organs 41:152–159
Li Y, Fan P, Ding X-M, Tian X-H, Feng X-S, Yan H, Pan X-M, Tian P-X, Zheng J, Ding C-G (2017) Polyglycolic acid fibrous scaffold improving endothelial cell coating and vascularization of islet. Chin Med J 130:832
Urbanczyk M, Zbinden A, Layland SL, Duffy G, Schenke-Layland K (2020) Controlled heterotypic pseudo-islet assembly of human β-cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells using magnetic levitation. Tissue Eng Part A 26:387–399
Golosow N, Grobstein C (1962) Epitheliomesenchymal interaction in pancreatic morphogenesis. Dev Biol 4:242–255
Wessells NK, Cohen JH (1967) Early pancreas organogenesis: morphogenesis, tissue interactions, and mass effects. Dev Biol 15:237–270
Li Z, Manna P, Kobayashi H, Spilde T, Bhatia A, Preuett B, Prasadan K, Hembree M, Gittes GK (2004) Multifaceted pancreatic mesenchymal control of epithelial lineage selection. Dev Biol 269:252–263
Rose MI, Crisera CA, Colen KL, Connelly PR, Longaker MT, Gittes GK (1999) Epithelio-mesenchymal interactions in the developing mouse pancreas: morphogenesis of the adult architecture. J Pediatr Surg 34:774–780
Li XY, Wu SY, Leung PS (2019) Human fetal bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote the proliferation and differentiation of pancreatic progenitor cells and the engraftment function of islet-like cell clusters. Int J Mol Sci 20:4083
Sneddon JB, Borowiak M, Melton DA (2012) Self-renewal of embryonic-stem-cell-derived progenitors by organ-matched mesenchyme. Nature 491:765–768
Scavuzzo MA, Yang D, Borowiak M (2017) Organotypic pancreatoids with native mesenchyme develop Insulin producing endocrine cells. Sci Rep 7:10810
Scuteri A, Donzelli E, Rodriguez-Menendez V, Ravasi M, Monfrini M, Bonandrini B, Figliuzzi M, Remuzzi A, Tredici G (2014) A double mechanism for the mesenchymal stem cells’ positive effect on pancreatic islets. PLoS ONE 9:e84309
Quaranta P, Antonini S, Spiga S, Mazzanti B, Curcio M, Mulas G, Diana M, Marzola P, Mosca F, Longoni B (2014) Co-transplantation of endothelial progenitor cells and pancreatic islets to induce long-lasting normoglycemia in streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. PLoS ONE 9:e94783
Oh B, Oh S, Jin S, Suh S, Bae J, Park CG, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim J (2013) Co-transplantation of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells improves revascularization and organization in islet grafts. Am J Transplant 13:1429–1440
Coppens V, Heremans Y, Leuckx G, Suenens K, Jacobs-Tulleneers-Thevissen D, Verdonck K, Lahoutte T, Luttun A, Heimberg H, De Leu NJD (2013) Human blood outgrowth endothelial cells improve islet survival and function when co-transplanted in a mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 56:382–390
Nyqvist D, Speier S, Rodriguez-Diaz R, Molano RD, Lipovsek S, Rupnik M, Dicker A, Ilegems E, Zahr-Akrawi E, Molina J (2011) Donor islet endothelial cells in pancreatic islet revascularization. Diabetes 60:2571–2577
Grapensparr L, Christoffersson G, Carlsson P-O (2018) Bioengineering with endothelial progenitor cells improves the vascular engraftment of transplanted human islets. Cell Transplant 27:948–956
Barba-Gutierrez DA, Daneri-Navarro A, Villagomez-Mendez JJA, Kanamune J, Robles-Murillo AK, Sanchez-Enriquez S, Villafan-Bernal JR, Rivas-Carrillo JD (2016) Facilitated engraftment of isolated islets coated with expanded vascular endothelial cells for islet transplantation. Transpl Proc 48:669–672
Jung E-J, Kim S-C, Wee Y-M, Kim Y-H, Choi MY, Jeong S-H, Lee J, Lim D-G, Han D-J (2011) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells support rat pancreatic islet survival and insulin secretory function in vitro. Cytotherapy 13:19–29
Johansson U, Rasmusson I, Niclou SP, Forslund N, Gustavsson L, Nilsson B, Korsgren O, Magnusson PU (2008) Formation of composite endothelial cell–mesenchymal stem cell islets: a novel approach to promote islet revascularization. Diabetes 57:2393–2401
Park K-S, Kim Y-S, Kim J-H, Choi B, Kim S-H, Tan AH-K, Lee M-S, Lee M-K, Kwon C-H, Joh J-W (2010) Trophic molecules derived from human mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival, function, and angiogenesis of isolated islets after transplantation. Transplantation 89:509–517
Gao X, Song L, Shen K, Wang H, Qian M, Niu W, Qin X (2014) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote the repair of islets from diabetic mice through paracrine actions. Mol Cell Endocrinol 388:41–50
Figliuzzi M, Cornolti R, Perico N, Rota C, Morigi M, Remuzzi G, Remuzzi A, Benigni A (2009) Bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells improve islet graft function in diabetic rats. Transpl Proc 41:1797–1800
Lu Y, Jin X, Chen Y, Li S, Yuan Y, Mai G, Tian B, Long D, Zhang J, Zeng L (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells protect islets from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury. Cell Biochem Funct 28:637–643
Li F, Wang X, Deng C, Qi H, Ren L, Zhou H (2010) Immune modulation of co-transplantation mesenchymal stem cells with islet on T and dendritic cells. Clin Exp Immunol 161:357–363
Berman DM, Willman MA, Han D, Kleiner G, Kenyon NM, Cabrera O, Karl JA, Wiseman RW, O’connor DH, Bartholomew AM (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells enhance allogeneic islet engraftment in nonhuman primates. Diabetes 59:2558–2568
Kono TM, Sims EK, Moss DR, Yamamoto W, Ahn G, Diamond J, Tong X, Day KH, Territo PR, Hanenberg H (2014) Human adipose-derived stromal/stem cells protect against STZ-induced hyperglycemia: Analysis of hASC-derived paracrine effectors. Stem Cells 32:1831–1842
Ding Y, Xu D, Feng G, Bushell A, Muschel RJ, Wood KJ (2009) Mesenchymal stem cells prevent the rejection of fully allogenic islet grafts by the immunosuppressive activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and-9. Diabetes 58:1797–1806
Hajizadeh-Saffar E, Tahamtani Y, Aghdami N, Azadmanesh K, Habibi-Anbouhi M, Heremans Y, De Leu N, Heimberg H, Ravassard P, Shokrgozar M (2015) Inducible VEGF expression by human embryonic stem cell-derived mesenchymal stromal cells reduces the minimal islet mass required to reverse diabetes. Sci Rep 5:1–10
Olerud J, Kanaykina N, Vasilovska S, King D, Sandberg M, Jansson L, Kozlova E (2009) Neural crest stem cells increase beta cell proliferation and improve islet function in co-transplanted murine pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 52:2594–2601
D’Amour KA, Agulnick AD, Eliazer S, Kelly OG, Kroon E, Baetge EE (2005) Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat Biotechnol 23:1534–1541. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1163
D’Amour KA, Bang AG, Eliazer S, Kelly OG, Agulnick AD, Smart NG, Moorman MA, Kroon E, Carpenter MK, Baetge EE (2006) Production of pancreatic hormone–expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 24:1392–1401
Nostro MC, Sarangi F, Ogawa S, Holtzinger A, Corneo B, Li X, Micallef SJ, Park IH, Basford C, Wheeler MB, Daley GQ, Elefanty AG, Stanley EG, Keller G (2011) Stage-specific signaling through TGFbeta family members and WNT regulates patterning and pancreatic specification of human pluripotent stem cells. Development 138:861–871. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.055236
Nostro MC, Keller G (2012) Generation of beta cells from human pluripotent stem cells: potential for regenerative medicine. Semin Cell Dev Biol 23:701–710
Kroon E, Martinson LA, Kadoya K, Bang AG, Kelly OG, Eliazer S, Young H, Richardson M, Smart NG, Cunningham J, Agulnick AD, D’Amour KA, Carpenter MK, Baetge EE (2008) Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 26:443–452
Bruin JE, Rezania A, Xu J, Narayan K, Fox JK, O’Neil JJ, Kieffer TJ (2013) Maturation and function of human embryonic stem cell-derived pancreatic progenitors in macroencapsulation devices following transplant into mice. Diabetologia 56:1987–1998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-013-2955-4
Rezania A, Bruin JE, Arora P, Rubin A, Batushansky I, Asadi A, Odwyer S, Quiskamp N, Mojibian M, Albrecht T (2014) Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nature Biotechnol 32:1121–1133
Rezania A, Bruin JE, Xu J, Narayan K, Fox JK, O’Neil JJ, Kieffer TJ (2013) Enrichment of human embryonic stem cell-derived NKX6. 1-expressing pancreatic progenitor cells accelerates the maturation of insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Stem cells 31:2432–2442
Nostro MC, Sarangi F, Yang C, Holland A, Elefanty AG, Stanley EG, Greiner DL, Keller G (2015) Efficient generation of NKX6-1+ pancreatic progenitors from multiple human pluripotent stem cell lines. Stem Cell Rep 4:591–604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2015.02.017
Soltanian A, Ghezelayagh Z, Mazidi Z, Halvaei M, Mardpour S, Ashtiani MK, Hajizadeh-Saffar E, Tahamtani Y, Baharvand H (2019) Generation of functional human pancreatic organoids by transplants of embryonic stem cell derivatives in a 3D-printed tissue trapper. J Cell Physiol 234:9564–9576
Ghezelayagh Z, Zabihi M, Zarkesh I, Gonçalves CA, Larsen M, Hagh-parast N, Pakzad M, Vosough M, Arjmand B, Baharvand H (2021) Improved differentiation of hESC-derived pancreatic progenitors by using human fetal pancreatic mesenchymal cells in a micro-scalable three-dimensional co-culture system. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-021-10266-z
Bonfanti P, Nobecourt E, Oshima M, Albagli-Curiel O, Laurysens V, Stangé G, Sojoodi M, Heremans Y, Heimberg H, Scharfmann R (2015) Ex vivo expansion and differentiation of human and mouse fetal pancreatic progenitors are modulated by epidermal growth factor. Stem Cells Dev Biol 24:1766–1778
Nair GG, Liu JS, Russ HA, Tran S, Saxton MS, Chen R, Juang C, Li M-l, Nguyen VQ, Giacometti S (2019) Recapitulating endocrine cell clustering in culture promotes maturation of human stem-cell-derived β cells. Nat Cell Biol 21:263–274
Ameri J, Borup R, Prawiro C, Ramond C, Schachter KA, Scharfmann R, Semb H (2017) Efficient generation of glucose-responsive beta cells from isolated GP2+ human pancreatic progenitors. Cell Rep 19:36–49
Davis JC, Alves TC, Helman A, Chen JC, Kenty JH, Cardone RL, Liu DR, Kibbey RG, Melton DA (2020) Glucose response by stem cell-derived β cells in vitro is inhibited by a bottleneck in glycolysis. Cell Rep 31:107623
Liu X, Qin J, Chang M, Wang S, Li Y, Pei X, Wang Y (2020) Enhanced differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into pancreatic endocrine cells in 3D culture by inhibition of focal adhesion kinase. Stem Cell Res Ther 11:1–12
Hogrebe NJ, Augsornworawat P, Maxwell KG, Velazco-Cruz L, Millman JR (2020) Targeting the cytoskeleton to direct pancreatic differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 38:460–470
Qadir MMF, Álvarez-Cubela S, Belle K, Sapir T, Messaggio F, Johnson KB, Umland O, Hardin D, Klein D, Pérez-Álvarez I (2019) A double fail-safe approach to prevent tumorigenesis and select pancreatic β cells from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Rep 12:611–623
Lutolf MP, Blau HM (2009) Artificial stem cell niches. Adv Mater 21:3255–3268
Bao M, Xie J, Huck WT (2018) Recent advances in engineering the stem cell microniche in 3D. Adv Sci 5:1800448
Melton D (2021) The promise of stem cell-derived islet replacement therapy. Diabetologia 1–7
Lanzoni G, Ricordi C (2021) Transplantation of stem cell-derived pancreatic islet cells. Nat Rev Endocrinol 17:7–8
De Klerk E, Hebrok M (2021) Stem cell-based clinical trials for diabetes mellitus. Front Endocrinol 12
Stock AA, Manzoli V, De Toni T, Abreu MM, Poh Y-C, Ye L, Roose A, Pagliuca FW, Thanos C, Ricordi C (2020) Conformal coating of stem cell-derived islets for β cell replacement in type 1 diabetes. Stem Cell Rep 14:91–104
Alam M, Arunagiri A, Haataja L, Torres M, Larkin D, Kappler J, Jin N, Arvan P (2021) Predisposition to proinsulin misfolding as a genetic risk to diet-induced diabetes. biorxiv 70:488
Millman JR, Xie C, Van Dervort A, Gurtler M, Pagliuca FW, Melton DA (2016) Generation of stem cell-derived beta-cells from patients with type 1 diabetes. Nat Commun 7:11463. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11463
Rajaei B, Shamsara M, Amirabad LM, Massumi M, Sanati MH (2017) Pancreatic endoderm-derived from diabetic patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell generates glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells. J Cell Physiol 232:2616–2625
Jang J, Yoo J-E, Lee J-A, Lee DR, Kim JY, Huh YJ, Kim D-S, Park C-Y, Hwang D-Y, Kim H-S (2012) Disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cells: a platform for human disease modeling and drug discovery. Exp Mol Med 44:202–213
Park IH, Arora N, Huo H, Maherali N, Ahfeldt T, Shimamura A, Lensch MW, Cowan C, Hochedlinger K, Daley GQ (2008) Disease-specific induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell 134:877–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.07.041
Takahashi Y, Sekine K, Kin T, Takebe T, Taniguchi H (2018) Self-condensation culture enables vascularization of tissue fragments for efficient therapeutic transplantation. Cell Rep 23:1620–1629
Takebe T, Enomura M, Yoshizawa E, Kimura M, Koike H, Ueno Y, Matsuzaki T, Yamazaki T, Toyohara T, Osafune K (2015) Vascularized and complex organ buds from diverse tissues via mesenchymal cell-driven condensation. Cell Stem Cell 16:556–565
Chen H, Zhuo Q, Ye Z, Xu X, Ji S (2020) Organoid model: A new hope for pancreatic cancer treatment? Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Rev Cancer 188466
Frappart P-O, Hofmann TG (2020) Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (Pdac) organoids: The shining light at the end of the tunnel for drug response prediction and personalized medicine. Cancers 12:2750
Balak JR, Juksar J, Carlotti F, Nigro AL, de Koning EJ (2019) Organoids from the human fetal and adult pancreas. Curr DiabRep 19:160
Öhlund D, Handly-Santana A, Biffi G, Elyada E, Almeida AS, Ponz-Sarvise M, Corbo V, Oni TE, Hearn SA, Lee EJ (2017) Distinct populations of inflammatory fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Med 214:579–596
Funata M, Nio Y, Erion DM, Thompson WL, Takebe T (2021) The promise of human organoids in the digestive system. Cell Death Differ 28:84–94
Ouchi R, Togo S, Kimura M, Shinozawa T, Koido M, Koike H, Thompson W, Karns RA, Mayhew CN, McGrath PS (2019) Modeling steatohepatitis in humans with pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids. Cell Metab 30:374-384 e376
Enge M, Arda HE, Mignardi M, Beausang J, Bottino R, Kim SK, Quake SR (2017) Single-cell analysis of human pancreas reveals transcriptional signatures of aging and somatic mutation patterns. Cell 171:321-330 e314
Toda S, Frankel NW, Lim WA (2019) Engineering cell–cell communication networks: programming multicellular behaviors. Curr Opin Chem Biol 52:31–38
Hunckler MD, García AJ (2020) Engineered biomaterials for enhanced function of insulin-secreting β-cell organoids. Adv Funct Mater 30:2000134
Woodford C, Zandstra PW (2012) Tissue engineering 2.0: guiding self-organization during pluripotent stem cell differentiation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 23:810–819
Bal T, Nazli C, Okcu A, Duruksu G, Karaöz E, Kizilel S (2017) Mesenchymal stem cells and ligand incorporation in biomimetic poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogels significantly improve insulin secretion from pancreatic islets. J Tissue Eng Regenerat Med 11:694–703
Broguiere N, Isenmann L, Hirt C, Ringel T, Placzek S, Cavalli E, Ringnalda F, Villiger L, Züllig R, Lehmann R (2018) Growth of epithelial organoids in a defined hydrogel. Adv Mater 30:1801621
Tumarkin E, Tzadu L, Csaszar E, Seo M, Zhang H, Lee A, Peerani R, Purpura K, Zandstra PW, Kumacheva E (2011) High-throughput combinatorial cell co-culture using microfluidics. Integr Biol 3:653–662
Chwalek K, Levental KR, Tsurkan MV, Zieris A, Freudenberg U, Werner C (2011) Two-tier hydrogel degradation to boost endothelial cell morphogenesis. Biomaterials 32:9649–9657
Jung T-H, Chung E-B, Kim HW, Choi SW, Park S-J, Mukhtar AS, Chung H-M, Kim E, Huh KM, Kim DS (2020) Application of co-culture technology of epithelial type cells and mesenchymal type cells using nanopatterned structures. PLoS ONE 15:232899
Torisawa Y-s, Mosadegh B, Luker GD, Morell M, O’Shea KS, Takayama S (2009) Microfluidic hydrodynamic cellular patterning for systematic formation of co-culture spheroids. Integr Biol 1:649–654
Barati G, Nadri S, Hajian R, Rahmani A, Mostafavi H, Mortazavi Y, Taromchi AH (2019) Differentiation of microfluidic-encapsulated trabecular meshwork mesenchymal stem cells into insulin producing cells and their impact on diabetic rats. J Cell Physiol 234:6801–6809
Yu Y, Gamble A, Pawlick R, Pepper AR, Salama B, Toms D, Razian G, Ellis C, Bruni A, Gala-Lopez B (2018) Bioengineered human pseudoislets form efficiently from donated tissue, compare favourably with native islets in vitro and restore normoglycaemia in mice. Diabetologia 61:2016–2029
Derakhshanfar S, Mbeleck R, Xu K, Zhang X, Zhong W, Xing M (2018) 3D bioprinting for biomedical devices and tissue engineering: A review of recent trends and advances. Bioactive materials 3:144–156
Murphy SV, Atala A (2014) 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat Biotechnol 32:773–785
Ma Z, Holle AW, Melde K, Qiu T, Poeppel K, Kadiri VM, Fischer P (2020) Acoustic holographic cell patterning in a biocompatible hydrogel. Adv Mater 32:1904181
Zwi-Dantsis L, Wang B, Marijon C, Zonetti S, Ferrini A, Massi L, Stuckey DJ, Terracciano CM, Stevens MM (2020) Remote magnetic nanoparticle manipulation enables the dynamic patterning of cardiac tissues. Adv Mater 32:1904598
Mao H, Yang L, Zhu H, Wu L, Ji P, Yang J, Gu Z (2020) Recent advances and challenges in materials for 3D bioprinting. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 30:618–634
Armstrong JP, Stevens MM (2020) Using remote fields for complex tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol 38:254–263
Bouyer C, Chen P, Güven S, Demirtaş TT, Nieland TJ, Padilla F, Demirci U (2016) A bio-acoustic levitational (BAL) assembly method for engineering of multilayered, 3D brain-like constructs, using human embryonic stem cell derived neuro-progenitors. Adv Mater 28:161–167
Serpooshan V, Chen P, Wu H, Lee S, Sharma A, Hu DA, Venkatraman S, Ganesan AV, Usta OB, Yarmush M (2017) Bioacoustic-enabled patterning of human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes into 3D cardiac tissue. Biomaterials 131:47–57
Kirkham GR, Britchford E, Upton T, Ware J, Gibson GM, Devaud Y, Ehrbar M, Padgett M, Allen S, Buttery LD (2015) Precision assembly of complex cellular microenvironments using holographic optical tweezers. Sci Rep 5:1–7
Jafari J, Han X-l, Palmer J, Tran PA, O’Connor AJ (2019) Remote control in formation of 3D multicellular assemblies using magnetic forces. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5:2532–2542
Bobbert F, Zadpoor A (2017) Effects of bone substitute architecture and surface properties on cell response, angiogenesis, and structure of new bone. J Mater Chem B 5:6175–6192
Zhao D, Xue C, Li Q, Liu M, Ma W, Zhou T, Lin Y (2018) Substrate stiffness regulated migration and angiogenesis potential of A549 cells and HUVECs. J Cell Physiol 233:3407–3417
Phelps EA, Landázuri N, Thulé PM, Taylor WR, García AJ (2010) Bioartificial matrices for therapeutic vascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:3323–3328
Lee P-F, Bai Y, Smith R, Bayless K, Yeh A (2013) Angiogenic responses are enhanced in mechanically and microscopically characterized, microbial transglutaminase crosslinked collagen matrices with increased stiffness. Acta Biomater 9:7178–7190
Zhou YL, Yang QQ, Zhang L, Tang JB (2021) Nanoparticle-coated sutures providing sustained growth factor delivery to improve the healing strength of injured tendons. Acta Biomater 124:301–314
Limasale YDP, Atallah P, Werner C, Freudenberg U, Zimmermann R (2020) Tuning the local availability of VEGF within glycosaminoglycan-based hydrogels to modulate vascular endothelial cell morphogenesis. Adv Func Mater 30:2000068
Song H-HG, Rumma RT, Ozaki CK, Edelman ER, Chen CS (2018) Vascular tissue engineering: progress, challenges, and clinical promise. Cell Stem Cell 22:340–354
Moeinvaziri F, Shojaei A, Haghparast N, Yakhkeshi S, Nemati S, Hassani S-N, Baharvand H (2021) Towards maturation of human otic hair cell–like cells in pluripotent stem cell–derived organoid transplants. Cell Tissue Res 28:1–13
Hanjaya-Putra D, Bose V, Shen Y-I, Yee J, Khetan S, Fox-Talbot K, Steenbergen C, Burdick JA, Gerecht S (2011) Controlled activation of morphogenesis to generate a functional human microvasculature in a synthetic matrix. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 118:804–815
Lesman A, Koffler J, Atlas R, Blinder YJ, Kam Z, Levenberg S (2011) Engineering vessel-like networks within multicellular fibrin-based constructs. Biomaterials 32:7856–7869
Jalili RB, Moeen Rezakhanlou A, Hosseini-Tabatabaei A, Ao Z, Warnock GL, Ghahary A (2011) Fibroblast populated collagen matrix promotes islet survival and reduces the number of islets required for diabetes reversal. J Cell Physiol 226:1813–1819
Du C, Narayanan K, Leong MF, Wan AC (2014) Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes and endothelial cells in multi-component hydrogel fibers for liver tissue engineering. Biomaterials 35:6006–6014
Lim TC, Leong MF, Lu H, Du C, Gao S, Wan AC, Ying JY (2013) Follicular dermal papilla structures by organization of epithelial and mesenchymal cells in interfacial polyelectrolyte complex fibers. Biomaterials 34:7064–7072
Skrzypek K, Nibbelink MG, Karbaat LP, Karperien M, van Apeldoorn A, Stamatialis D (2018) An important step towards a prevascularized islet macroencapsulation device—effect of micropatterned membranes on development of endothelial cell network. J Mater Sci Mater Med 29:91
Nibbelink MG, Skrzypek K, Karbaat L, Both S, Plass J, Klomphaar B, van Lente J, Henke S, Karperien M, Stamatialis D (2018) An important step towards a prevascularized islet microencapsulation device: in vivo prevascularization by combination of mesenchymal stem cells on micropatterned membranes. J Mater Sci Mater Med 29:174
Luo B-H, Xiong F, Wang J-P, Li J-H, Zhong M, Liu Q-L, Luo G-Q, Yang X-J, Xiao N, Xie B (2014) Epidermal growth factor-like domain-containing protein 7 (EGFL7) enhances EGF receptor—AKT signaling, epithelial—mesenchymal transition, and metastasis of gastric cancer cells. PLoS ONE 9:e99922
Sand FW, Hörnblad A, Johansson JK, Lorén C, Edsbagge J, Ståhlberg A, Magenheim J, Ilovich O, Mishani E, Dor Y, Ahlgren U (2011) Growth-limiting role of endothelial cells in endoderm development. Dev Biol 352:267–277
Edsbagge J, Johansson JK, Esni F, Luo Y, Radice GL, Semb H (2005) Vascular function and sphingosine-1-phosphate regulate development of the dorsal pancreatic mesenchyme 132:1085–1092
Guney MA, Petersen CP, Boustani A, Duncan MR, Gunasekaran U, Menon R, Warfield C, Grotendorst GR, Means AL, Economides AN (2011) Connective tissue growth factor acts within both endothelial cells and β cells to promote proliferation of developing β cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:15242–15247
Crawford LA, Guney MA, Oh YA, DeYoung RA, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Yancopoulos GD, Lyons KM, Brigstock DR, Economides A (2009) Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) inactivation leads to defects in islet cell lineage allocation and β-cell proliferation during embryogenesis. Mol Endocrinol 23:324–336
Olerud J, Mokhtari D, Johansson M, Christoffersson G, Lawler J, Welsh N, Carlsson PO (2011) Thrombospondin-1: an islet endothelial cell signal of importance for β-cell function. Diabetes 60:1946–1954
García-Ocaña A, Vasavada RC, Cebrian A, Reddy V, Takane KK, López-Talavera J-C, Stewart AF (2001) Transgenic overexpression of hepatocyte growth factor in the β-cell markedly improves islet function and islet transplant outcomes in mice. Diabetes 50:2752–2762
Garcia-Ocaña A, Takane KK, Syed MA, Philbrick WM, Vasavada RC, Stewart AF (2000) Hepatocyte growth factor overexpression in the islet of transgenic mice increases beta cell proliferation, enhances islet mass, and induces mild hypoglycemia. J Biol Chem 275:1226–1232
Johansson M, Mattsson GR, Andersson A, Jansson L, Carlsson PO (2006) Islet endothelial cells and pancreatic β-cell proliferation: studies in vitro and during pregnancy in adult rats. Endocrinology 147:2315–2324
Yao Y, Zebboudj AF, Shao E, Perez M, Boström K (2006) Regulation of bone morphogenetic protein-4 by matrix GLA protein in vascular endothelial cells involves activin-like kinase receptor 1. J Biol Chem 281:33921–33930
Clarkin CE, Mahmoud M, Liu B, Sobamowo EO, King A, Arthur H, Jones PM, Wheeler-Jone CPJBrn (2016) Modulation of endoglin expression in islets of langerhans by VEGF reveals a novel regulator of islet endothelial cell function. BMC Res Notes 9:362
Sarafidis PA, Bakris GL (2006) Insulin and endothelin: an interplay contributing to hypertension development? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:379–385
De Carlo E, Milanesi A, Martini C, Maffei P, Sicolo N, Scandellari C (2000) Endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 stimulate insulin release by isolated rat pancreatic islets. J Endocrinol Invest 23:240–245
Narayanan S, Loganathan G, Dhanasekaran M, Tucker W, Patel A, Subhashree V, Mokshagundam S, Hughes MG, Williams SK, Balamurugan AN (2017) Intra-islet endothelial cell and β-cell crosstalk: Implication for islet cell transplantation. World J Transplant 7:117
Ahnfelt-Rønne J, Ravassard P, Pardanaud-Glavieux C, Scharfmann R, Serup P (2010) Mesenchymal bone morphogenetic protein signaling is required for normal pancreas development. Diabetes 59:1948–1956
Kobayashi H, Spilde TL, Bhatia AM, Buckingham RB, Hembree MJ, Prasadan K, Preuett BL, Imamura M, Gittes GK (2002) Retinoid signaling controls mouse pancreatic exocrine lineage selection through epithelial–mesenchymal interactions. Gastroenterology 123:1331–1340
Öström M, Loffler KA, Edfalk S, Selander L, Dahl U, Ricordi C, Jeon J, Correa-Medina M, Diez J, Edlund H (2008) Retinoic acid promotes the generation of pancreatic endocrine progenitor cells and their further differentiation into β-cells. PLoS ONE 3:e2841
Arregi I, Climent M, Iliev D, Strasser J, Gouignard N, Johansson JK, Singh T, Mazur M, Semb H, Artner I (2016) Retinol dehydrogenase-10 regulates pancreas organogenesis and endocrine cell differentiation via paracrine retinoic acid signaling. Endocrinology 157:4615–4631
Jonckheere N, Mayes E, Shih H-P, Li B, Lioubinski O, Dai X, Sander M (2008) Analysis of mPygo2 mutant mice suggests a requirement for mesenchymal Wnt signaling in pancreatic growth and differentiation. Dev Biol 318:224–235
Afelik S, Pool B, Schmerr M, Penton C, Jensen J (2015) Wnt7b is required for epithelial progenitor growth and operates during epithelial-to-mesenchymal signaling in pancreatic development. Dev Biol 399:204–217
Apelqvist Å, Ahlgren U, Edlund H (1997) Sonic hedgehog directs specialised mesoderm differentiation in the intestine and pancreas. Curr Biol 7:801–804
Kawahira H, Scheel DW, Smith SB, German MS, Hebrok M (2005) Hedgehog signaling regulates expansion of pancreatic epithelial cells. Dev Biol 280:111–121
Nakayama S, Arakawa M, Uchida T, Ogihara T, Kanno R, Ikeda F, Azuma K, Hirose T, Kawamori R, Fujitani Y (2008) Dose-dependent requirement of patched homologue 1 in mouse pancreatic beta cell mass. Diabetologia 51:1883–1892
Hibsher D, Epshtein A, Oren N, Landsman L (2016) Pancreatic mesenchyme regulates islet cellular composition in a patched/hedgehog-dependent manner. Sci Rep 6:38008
Yung T, Poon F, Liang M, Coquenlorge S, McGaugh EC, Hui C-c, Wilson MD, Nostro MC, Kim T-H (2019) Sufu-and Spop-mediated downregulation of Hedgehog signaling promotes beta cell differentiation through organ-specific niche signals. Nat Commun 10:1–17
Kang S, Park HS, Jo A, Hong SH, Lee HN, Lee YY, Park JS, Jung HS, Chung SS, Park KS (2012) Endothelial progenitor cell cotransplantation enhances islet engraftment by rapid revascularization. Diabetes 61:866–876
Karaoz E, Genc Z, Demircan PÇ, Aksoy A, Duruksu G (2010) Protection of rat pancreatic islet function and viability by coculture with rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell death Dis 1:e36–e36
Ito T, Itakura S, Todorov I, Rawson J, Asari S, Shintaku J, Nair I, Ferreri K, Kandeel F, Mullen Y (2010) Mesenchymal stem cell and islet co-transplantation promotes graft revascularization and function. Transplantation 89:1438–1445
Davis NE, Beenken-Rothkopf LN, Mirsoian A, Kojic N, Kaplan DL, Barron AE, Fontaine MJ (2012) Enhanced function of pancreatic islets co-encapsulated with ECM proteins and mesenchymal stromal cells in a silk hydrogel. Biomaterials 33:6691–6697
Hamilton DC, Shih HH, Schubert RA, Michie SA, Staats PN, Kaplan DL, Fontaine MJ (2017) A silk-based encapsulation platform for pancreatic islet transplantation improves islet function in vivo. J Tissue Eng Regenerat Med 11:887–895
Kogawa R, Nakamura K, Mochizuki Y (2020) A new islet transplantation method combining mesenchymal stem cells with recombinant peptide pieces, microencapsulated islets, and mesh bags. Biomedicines 8:299
Wang H, Li S, Dai Q, Gonzalez A, Tran ON, Sun H, DeFronzo RA, Dean DD, Yeh CK, Chen XD (2020) Culture on a native bone marrow-derived extracellular matrix restores the pancreatic islet basement membrane, preserves islet function, and attenuates islet immunogenicity. FASEB J 34:8044–8056
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Royan Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Technology (RI-SCBT) and Royan’s Lotus Charity Investment Foundation.
Funding
This study was funded by Royan Institute for Stem Cell Biology and Technology (RI-SCBT) and the Lotus Charity Investment Foundation, Royan Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The conception and design of the study was done by [YT]. Administrative support was done by [FCL]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [ZG, MZ, MKA, and ZG], and all authors commented on previous version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghezelayagh, Z., Zabihi, M., Kazemi Ashtiani, M. et al. Recapitulating pancreatic cell–cell interactions through bioengineering approaches: the momentous role of non-epithelial cells for diabetes cell therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 78, 7107–7132 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03951-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03951-2