Abstract
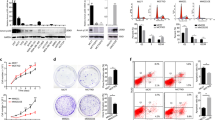
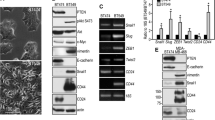
Ablation of tetraspanin protein TSPAN12 from human MDA-MB-231 cells significantly decreased primary tumor xenograft growth, while increasing tumor apoptosis. Furthermore, TSPAN12 removal markedly enhanced tumor-endothelial interactions and increased metastasis to mouse lungs. TSPAN12 removal from human MDA-MB-231 cells also caused diminished association between FZD4 (a key canonical Wnt pathway receptor) and its co-receptor LRP5. The result likely explains substantially enhanced proteosomal degradation of β-catenin, a key effecter of canonical Wnt signaling. Consistent with disrupted canonical Wnt signaling, TSPAN12 ablation altered expression of LRP5, Naked 1 and 2, DVL2, DVL3, Axin 1, and GSKβ3 proteins. TSPAN12 ablation also altered expression of several genes regulated by β-catenin (e.g. CCNA1, CCNE2, WISP1, ID4, SFN, ME1) that may help to explain altered tumor growth and metastasis. In conclusion, these results provide the first evidence for TSPAN12 playing a role in supporting primary tumor growth and suppressing metastasis. TSPAN12 appears to function by stabilizing FZD4–LRP5 association, in support of canonical Wnt-pathway signaling, leading to enhanced β-catenin expression and function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia-Espana A, Chung PJ, Sarkar IN, Stiner E, Sun TT, Desalle R (2008) Appearance of new tetraspanin genes during vertebrate evolution. Genomics 91:326–334
Poulter JA, Ali M, Gilmour DF, Rice A, Kondo H, Hayashi K, Mackey DA, Kearns LS, Ruddle JB, Craig JE, Pierce EA, Downey LM, Mohamed MD, Markham AF, Inglehearn CF, Toomes C (2010) Mutations in TSPAN12 cause autosomal-dominant familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Hum Genet 86:248–253
Nikopoulos K, Gilissen C, Hoischen A, van Nouhuys CE, Boonstra FN, Blokland EA, Arts P, Wieskamp N, Strom TM, Ayuso C, Tilanus MA, Bouwhuis S, Mukhopadhyay A, Scheffer H, Hoefsloot LH, Veltman JA, Cremers FP, Collin RW (2010) Next-generation sequencing of a 40 Mb linkage interval reveals TSPAN12 mutations in patients with familial exudative vitreoretinopathy. Am J Hum Genet 86:240–247
Junge HJ, Yang S, Burton JB, Paes K, Shu X, French DM, Costa M, Rice DS, Ye W (2009) TSPAN12 regulates retinal vascular development by promoting Norrin- but not Wnt-induced FZD4/beta-catenin signaling. Cell 139:299–311
Clevers H (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127:469–480
Valenta T, Hausmann G, Basler K (2012) The many faces and functions of beta-catenin. EMBO J 31:2714–2736
Crawford HC, Dempsey PJ, Brown G, Adam L, Moss ML (2009) ADAM10 as a therapeutic target for cancer and inflammation. Curr Pharm Des 15:2288–2299
Xu D, Sharma C, Hemler ME (2009) Tetraspanin12 regulates ADAM10-dependent cleavage of amyloid precursor protein. FASEB J 23:3674–3681
Lara H, Wang Y, Beltran AS, Juarez-Moreno K, Yuan X, Kato S, Leisewitz AV, Cuello FM, Licea AF, Connolly DC, Huang L, Blancafort P (2012) Targeting serous epithelial ovarian cancer with designer zinc finger transcription factors. J Biol Chem 287:29873–29886
Wachi S, Yoneda K, Wu R (2005) Interactome-transcriptome analysis reveals the high centrality of genes differentially expressed in lung cancer tissues. Bioinformatics 21:4205–4208
Liu R, Wang X, Chen GY, Dalerba P, Gurney A, Hoey T, Sherlock G, Lewicki J, Shedden K, Clarke MF (2007) The prognostic role of a gene signature from tumorigenic breast-cancer cells. N Engl J Med 356:217–226
Casey T, Bond J, Tighe S, Hunter T, Lintault L, Patel O, Eneman J, Crocker A, White J, Tessitore J, Stanley M, Harlow S, Weaver D, Muss H, Plaut K (2009) Molecular signatures suggest a major role for stromal cells in development of invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 114:47–62
Kudo Y, Kitajima S, Ogawa I, Hiraoka M, Sargolzaei S, Keikhaee MR, Sato S, Miyauchi M, Takata T (2004) Invasion and metastasis of oral cancer cells require methylation of E-cadherin and/or degradation of membranous beta-catenin. Clin Cancer Res 10:5455–5463
Creighton CJ, Bromberg-White JL, Misek DE, Monsma DJ, Brichory F, Kuick R, Giordano TJ, Gao W, Omenn GS, Webb CP, Hanash SM (2005) Analysis of tumor-host interactions by gene expression profiling of lung adenocarcinoma xenografts identifies genes involved in tumor formation. Mol Cancer Res 3:119–129
Reich M, Liefeld T, Gould J, Lerner J, Tamayo P, Mesirov JP (2006) GenePattern 2.0. Nat Genet 38:500–501
Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY, Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, Maurice MM, Mahmoudi T, Clevers H (2012) Wnt signaling through inhibition of beta-catenin degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell 149:1245–1256
Rousset R, Mack JA, Wharton KA Jr, Axelrod JD, Cadigan KM, Fish MP, Nusse R, Scott MP (2001) Naked cuticle targets dishevelled to antagonize Wnt signal transduction. Genes Dev 15:658–671
Wharton KA Jr, Zimmermann G, Rousset R, Scott MP (2001) Vertebrate proteins related to Drosophila Naked Cuticle bind Dishevelled and antagonize Wnt signaling. Dev Biol 234:93–106
Yasmeen A, Berdel WE, Serve H, Muller-Tidow C (2003) E- and A-type cyclins as markers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 3:617–633
Xu L, Corcoran RB, Welsh JW, Pennica D, Levine AJ (2000) WISP-1 is a Wnt-1- and beta-catenin-responsive oncogene. Genes Dev 14:585–595
Perathoner A, Pirkebner D, Brandacher G, Spizzo G, Stadlmann S, Obrist P, Margreiter R, Amberger A (2005) 14-3-3sigma expression is an independent prognostic parameter for poor survival in colorectal carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res 11:3274–3279
Lasorella A, Uo T, Iavarone A (2001) Id proteins at the cross-road of development and cancer. Oncogene 20:8326–8333
Jiang P, Du W, Mancuso A, Wellen KE, Yang X (2013) Reciprocal regulation of p53 and malic enzymes modulates metabolism and senescence. Nature 493:689–693
Lobov IB, Rao S, Carroll TJ, Vallance JE, Ito M, Ondr JK, Kurup S, Glass DA, Patel MS, Shu W, Morrisey EE, McMahon AP, Karsenty G, Lang RA (2005) WNT7b mediates macrophage-induced programmed cell death in patterning of the vasculature. Nature 437:417–421
Ji P, Baumer N, Yin T, Diederichs S, Zhang F, Beger C, Welte K, Fulda S, Berdel WE, Serve H, Muller-Tidow C (2007) DNA damage response involves modulation of Ku70 and Rb functions by cyclin A1 in leukemia cells. Int J Cancer 121:706–713
Wegiel B, Bjartell A, Culig Z, Persson JL (2008) Interleukin-6 activates PI3K/Akt pathway and regulates cyclin A1 to promote prostate cancer cell survival. Int J Cancer 122:1521–1529
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Wang S (2012) Targeting disease through novel pathways of apoptosis and autophagy. Expert Opin Ther Targets 16:1203–1214
Matsuda Y, Schlange T, Oakeley EJ, Boulay A, Hynes NE (2009) WNT signaling enhances breast cancer cell motility and blockade of the WNT pathway by sFRP1 suppresses MDA-MB-231 xenograft growth. Breast Cancer Res 11:R32
Pancione M, Forte N, Fucci A, Sabatino L, Febbraro A, Di BA, Daniele B, Parente D, Colantuoni V (2010) Prognostic role of beta-catenin and p53 expression in the metastatic progression of sporadic colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol 41:867–876
Soon LL, Yie TA, Shvarts A, Levine AJ, Su F, Tchou-Wong KM (2003) Overexpression of WISP-1 down-regulated motility and invasion of lung cancer cells through inhibition of Rac activation. J Biol Chem 278:11465–11470
Umetani N, Mori T, Koyanagi K, Shinozaki M, Kim J, Giuliano AE, Hoon DS (2005) Aberrant hypermethylation of ID4 gene promoter region increases risk of lymph node metastasis in T1 breast cancer. Oncogene 24:4721–4727
Ikushima H, Miyazono K (2010) TGFbeta signaling: a complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 10:415–424
Kouprina N, Mullokandov M, Rogozin IB, Collins NK, Solomon G, Otstot J, Risinger JI, Koonin EV, Barrett JC, Larionov V (2004) The SPANX gene family of cancer/testis-specific antigens: rapid evolution and amplification in African great apes and hominids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:3077–3082
Mitamura T, Iwamoto R, Umata T, Yomo T, Urabe I, Tsuneoka M, Mekada E (1992) The 27-kD diphtheria toxin receptor-associated protein (DRAP27) from Vero Cells is the monkey homologue of human CD9 antigen: expression of DRAP27 elevates the number of diphtheria toxin receptors on toxin-sensitive cells. J Cell Biol 118:1389–1399
Feigelson SW, Grabovsky V, Shamri R, Levy S, Alon R (2003) The CD81 tetraspanin facilitates instantaneous leukocyte VLA-4 adhesion strengthening to vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) under shear flow. J Biol Chem 278:51203–51212
Moribe H, Konakawa R, Koga D, Ushiki T, Nakamura K, Mekada E (2012) Tetraspanin is required for generation of reactive oxygen species by the dual oxidase system in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet 8:e1002957
Sadej R, Romanska H, Baldwin G, Gkirtzimanaki K, Novitskaya V, Filer AD, Krcova Z, Kusinska R, Ehrmann J, Buckley CD, Kordek R, Potemski P, Eliopoulos AG, Lalani E, Berditchevski F (2009) CD151 regulates tumorigenesis by modulating the communication between tumor cells and endothelium. Mol Cancer Res 7:787–798
Yang XH, Richardson AL, Torres-Arzayus MI, Zhou P, Sharma C, Kazarov AR, Andzelm MM, Strominger JL, Brown M, Hemler ME (2008) CD151 accelerates breast cancer by regulating a6 integrin functions, signaling, and molecular organization. Cancer Res 68:3204–3213
Li Q, Yang XH, Xu F, Sharma C, Wang HX, Knoblich K, Rabinovitz I, Granter SR, Hemler ME (2013) Tetraspanin CD151 plays a key role in skin squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 32:1772–1783
Deng X, Li Q, Hoff J, Novak M, Yang H, Jin H, Erfani SF, Sharma C, Zhou P, Rabinovitz I, Sonnenberg A, Yi A, Zhou P, Stipp CS, Kaetzel DM, Hemler ME, Yang HY (2012) Integrin-associated CD151 drives ErbB2-evoked mammary tumor onset and metastasis. Neoplasia 14:678–689
Kazarov AR, Yang X, Stipp CS, Sehgal B, Hemler ME (2002) An extracellular site on tetraspanin CD151 determines a3 and a6 integrin-dependent cellular morphology. J Cell Biol 158:1299–1309
Miranti CK (2009) Controlling cell surface dynamics and signaling: how CD82/KAI1 suppresses metastasis. Cell Signal 21:196–211
Miyake M, Inufusa H, Adachi M, Ishida H, Hashida H, Tokuhara T, Kakehi Y (2000) Suppression of pulmonary metastasis using adenovirally motility related protein-1 (MRP-1/CD9) gene delivery. Oncogene 19:5221–5226
Chigita S, Sugiura T, Abe M, Kobayashi Y, Shimoda M, Onoda M, Shirasuna K (2012) CD82 inhibits canonical Wnt signaling by controlling the cellular distribution of beta-catenin in carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 41:2021–2028
Huang CL, Liu D, Masuya D, Kameyama K, Nakashima T, Yokomise H, Ueno M, Miyake M (2004) MRP-1/CD9 gene transduction downregulates Wnt signal pathways. Oncogene 23:7475–7483
Wong SY, Haack H, Kissil JL, Barry M, Bronson RT, Shen SS, Whittaker CA, Crowley D, Hynes RO (2007) Protein 4.1B suppresses prostate cancer progression and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12784–12789
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant CA42368 (to M.E.H.).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knoblich, K., Wang, HX., Sharma, C. et al. Tetraspanin TSPAN12 regulates tumor growth and metastasis and inhibits β-catenin degradation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71, 1305–1314 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1444-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1444-8