Abstract
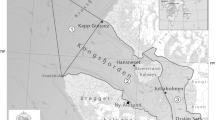
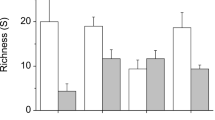
Approximately 35 hectares ofSpartina alterniflora marsh has, over a 14-year period, developed naturally on unconfined dredged material placed within the intertidal zone of Winyah Bay, South Carolina. The above-and below-ground vegetative structure, benthic macrofauna, and resident fish and shellfish assemblages of two varying-aged zones (4 and 8 years) of this marsh were evaluated and compared in September 1988. Vegetative structure (stem height, density, percent cover, and biomass) in both zones was within the range reported for natural sites, with a trend toward greater below-ground development with age. The macrofaunal assemblages of both zones were similar in both species composition and numbers of species (17–21 species), with oligochaetes and polychaetes dominating both assemblages. Overall density of macrofauna in the 8-year-old zone (19,943 individuals per m2) was significantly greater than that in the 4-year-old zone (4,628 individuals per m2). Differences between zones (particularly the presence of large-bodied molluscs in the older site) seemed to reflect age. The fish and shellfish assemblage collected from the younger site was dominated byFundulus heteroclitus andPalaemonetes pugio. Gut contents ofF. heteroclitus included a variety of marsh-surface prey, similar to that reported elsewhere. Overall, both zones seemed to represent well established, viable, low intertidal marsh habitat.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Baker-Dittus, A. M. 1978. Foraging patterns of three sympatric killifish. Copeia 1978:383–389.
Berger, W. H., and F. L. Parker 1970. Diversity of planktonic Foraminifera in deep-sea sediments. Science 168:1345–1347.
Bishop, T. D., and C. T. Hackney 1987. A comparative study of the molluse communities of two oligohaline intertidal marshes: spatial and temporal distribution of their abundance and biomass. Estuaries 10:141–152.
Bray, J. R., and C. T. Curtis 1957. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecological Monographs 27:325–349.
Breder, C. M. 1960. Design for a fry trap. Zoologica 45:155–160.
Buchanan, J. B., and J. M. Kain. 1971. Measurement of the physical and chemical environment. p. 30–58.In N. A. Holme and A. D. McIntyre (eds.) Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, UK.
Cammen, L. M. 1976. Macroinvertebrate colonization ofSpartina marshes artificially established on dredge spoil. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Sciences 4:357–372.
Fell, P.E., N.C. Olmstead, E. Carlson, W. Jacob, D. Hitchcock, and G. Silber. 1982. Distribution and abundance of macroinvertebrates on certain Connecticut tidal marshes, with emphasis on dominant, molluses. Estuaries 5:234–239.
Folk, R. L. 1968. Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks. Hemphill Publishing Company, Austin, TX, USA.
Fox, R. S., and E. E. Ruppert. 1985. Shallow-Water Marine Benthic Macroinvertebrates of South Carolina. University of South Carolina Press, Columbia, SC USA.
Good, R., N. Good, and B. Frasco 1982. A review of primary production and decomposition dynamics of the belowground marsh component. p. 139–157.In V. S. Kennedy (ed.) Estuarine Comparisons. Academic Press, New York, NY, USA.
Hackney, C. T., and R. F. Ganucheau, 1989. A new species ofCyathura (Isopoda, Anthuridae) from a high intertidal marsh in North Carolina, U.S.A.. Crustaceana 57:304–310.
Heard, R. W. 1982. Guide to common tidal marsh invertebrates of the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Mississippi-Alabama Sea Grant Consortium, Biloxi, MS, USA.
Hellawell, J. M., and R. Abel. 1971. A rapid volumetric method for the analysis of the food of fishes. Journal of Fish Biology 3:29–37.
Kneib, R. T. 1984. Patterns of invertebrate distribution and abundance in the intertidal salt marsh: causes and questions. Estuaries 7:392–412.
Kneib, R. T., and A. E. Stiven. 1978. Growth, reproduction, and feeding ofFundulus heteroclitus (L.) on a North Carolina salt marsh. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 31:121–140.
LaSalle, M. W., and T. D. Bishop 1987. Seasonal abundance of aquatic Diptera in two oligohaline tidal marshes in Mississippi. Estuaries 10:303–315.
Osenga, G. A., and B. C. Coull 1983.Spartina alterniflora Loisel root structure and meiofaunal abundance. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 67:221–225.
Pfeiffer, W. J., and R. G. Wiegert 1981. Grazers onSpartina and their predators. p. 87–112.In L. R. Pomeroy and R. G. Wiegert (eds.) Ecology of a Salt Marsh. Ecological Studies (38). Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, USA.
Rader, D. N. 1984. Salt-marsh benthic invertebrates: small-scale patterns of distribution and abundance. Estuaries 7:413–420.
Rozas, L. P., and W. E. Odum. 1987. Use of tidal freshwater marshes by fishes and macrofaunal crustaceans along a marsh stream-order gradient. Estuaries 10:36–43.
Rozas, L.P., C. C. McIvor, and W. E. Odum 1988. Intertidal rivulets and creckbanks: corridors between tidal creeks and marshes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 47:303–307.
Sargent, W. B. and P. R. Carlson, Jr. 1987. The utility of Breder traps for sampling mangrove and high marsh fish assemblages. p. 194–205.In F. J. Webb (ed.) Proceedings of the Fourteenth Annual Conference on Wetlands Restoration and Creation. Hillsborough Community College, Tampa, FL, USA.
Southwood, T. R. E. 1978. Ecological Methods with Particular Reference to the Study of Insect Populations. 2nd ed. Chapman and Hall, London, UK.
Steel, R. G. D. and J. H. Torrie 1960. Principles and Procedures of Statistics with Special Reference to the Biological Sciences. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, NY, USA.
Subrahmanyam, C. B., W. L. Kruczynski, and S. H. Drake 1976. Studies on the animal communities in two north Florida salt marshes. Part II. Macroinvertebrate communities. Bulletin Marine Sciences 26:172–195.
Teal, J. M. 1958. Distribution of fiddler crabs in Georgia salt marshes. Ecology 39:185–193.
Teal, J. M. 1962. Energy flow in the salt marsh ecosystem of Georgia. Ecology 43:214–224.
Tumer, R. E. 1976. Geographic variations in salt marsh macrophyte production: a review. Contributions in Marine Science 20:47–68.
Schubauer, J. P., and C. S. Hopkinson. 1984. Above- and belowground emergent macrophyte production and tumover in a coastal marsh ecosystem, Georgia. Limnology and Oceanography 29:1052–1065.
Wenner, E. L., and H. R. Beatty. 1988. Macrobenthic communities from wetland impoundments and adjacent open marsh habitats in South Carolina. Estuaries 11:29–44.
Zar, J. H. 1984. Biostatistical Analysis. 2nd ed. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LaSalle, M.W., Landin, M.C. & Sims, J.G. Evaluation of the flora and fauna of aSpartina alterniflora marsh established on dredged material in Winyah Bay, South Carolina. Wetlands 11, 191–208 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160849
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160849