Abstract
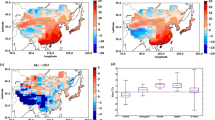
Climate change detection, attribution, and prediction were studied for the surface temperature in the Northeast Asian region using NCEP/NCAR reanalysis data and three coupled-model simulations from ECHAM4/OPYC3, HadCM3, and CCCma GCMs (Canadian Centre for Climate Modeling and Analysis general circulation model). The Bayesian fingerprint approach was used to perform the detection and attribution test for the anthropogenic climate change signal associated with changes in anthropogenic carbon dioxide (CO2) and sulfate aerosol (SO 2−4 ) concentrations for the Northeast Asian temperature. It was shown that there was a weak anthropogenic climate change signal in the Northeast Asian temperature change. The relative contribution of CO2 and SO 2−4 effects to total temperature change in Northeast Asia was quantified from ECHAM4/OPYC3 and CCCma GCM simulations using analysis of variance. For the observed temperature change for the period of 1959–1998, the CO2 effect contributed 10%–21% of the total variance and the direct cooling effect of SO 2−4 played a less important role (0%–7%) than the CO2 effect. The prediction of surface temperature change was estimated from the second CO2+SO 2−4 scenario run of ECHAM4/OPYC3 which has the least error in the simulation of the present-day temperature field near the Korean Peninsula. The result shows that the area-mean surface temperature near the Korean Peninsula will increase by about 1.1° by the 2040s relative to the 1990s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiguo Dai, G. A. Meehl, W. M. Washington, and T. M. L. Wigley, 2001: Climate change in the 21st Century over the Asia-Pacific region simulated by the NCAR CSM and PCM.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,18, 639–658.
Berger, J. O., 1985:Statistical Decision Theory and Bayesian Analysis. 2nd ed., Springer-Verlag, 617pp.
Berliner, L. M., R. A. Levine, and D. J. Shea, 2000: Bayesian climate change assessment.J. Climate,13, 3805–3820.
Bernardo, J. M., and A. F. M. Smith, 1994:Bayesian Theory. Wiley & Sons, 586pp.
Cubasch, U., and Coauthors, 2001:Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 525–582.
Deutsches KlimaRechenzentrum (DKRZ), 1992: The ECHAM3 general circulation model.DKRZ Technical Report,6, ISSN 0940-9327, Modellbetreuungsgruppe Hamburg, 184pp.
Epstein, E. S., 1985:Statistical Inference and Prediction in Climatology: A Bayesian Approach. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 199pp.
Gao, X., Z. Zhao, Y. Ding, R. Huang, and F. Giorgi, 2001; Climate change due to greenhouse effects in China as simulated by a regional climate model.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,18, 1224–1230.
Giorgi, F., B. Hewitson, J. Christensen, M. Hulme, H. von Storch, P. Whetton, R. Jones, and L. Fu C. Mearns, 2001:Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 583–638.
Gordon, C., C. Cooper, C. A. Senior, H. Banks, J. M. Gregory, T. C. Johns, J. F. B. Mitchell, and R. A. Wood, 2000: The simulation of SST, sea ice extents and ocean heat transports in a version of the Hadley Centre coupled model without flux adjustments.Climate Dyn.,16, 147–168.
Graybill, F. A., 1976:Theory and Application of the Linear Model. Duxbury Press, 704pp.
Guo, Y., Y. Yu, X. Liu, and X. Zhang, 2001; Simulation of climate change induced by CO2 increasing for East Asia with IAP/LASG GOALS model.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,18, 53–66.
Hasselmann, K., 1997: Multi-pattern fingerprint method for detection and attribution of climate change.Climate Dyn.,13, 601–611.
Kattenberg, A., and Coauthors, 1996:Climate Change 1995: The Science of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group I to the Second Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 285–327.
Kistler, R. E., and Coauthors, 2001: The NCEP/NCAR 50-year reanalysis: Monthly means CD-ROM and documentation.Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc.,82, 247–267.
Lee, J. H., K. T. Sohn, and B. Kim, 2001: Detection of anthropogenic climate change signal in East Asian region.Journal of the Korean Data Analysis Society,3, 217–225. (in Korean)
Levine, R. A., and L. M. Berliner, 1999: Statistical principles for climate change studies.J. Climate,12, 565–574.
Lohmann, U., and J. Feichter, 1997: Impact of sulfate aerosols on albedo and lifetime of clouds.J. Geophys. Res.,102, 13685–13700.
Lohmann, U., K. von Salzen, N. McFarlane, H. G. Leighton, and J. Feichter, 1999a: Tropospheric sulphur cycle in the Canadian general circulation model.J. Geophys. Res.,104, 26833–26858.
Lohmann, U., N. McFarlane, L. Levkov, K. Abdella, and F. Albers, 1999b: Comparing different cloud schemes of a single column model by using mesoscale forcing and nudging technique.J. Climate,12, 438–461.
Mearns, L. O., M. Hulme, T. R. Carter, R. Leemans, M. Lal, and P. Whetton, 2001:Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change IPCC, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 739–768.
Mitchell, J. F. B., T. C. Johns, and J. M. Gregory, and S. F. B. Tett, 1995: Climate response to increasing levels of greenhouse gases and sulfate aerosols.Nature,376, 501–504.
North, G, R., and M. J. Stevens, 1998: Detecting climate signals in the surface temperature record.J. Climate,11, 563–577.
Oberhuber, J. M., 1993a: Simulation of the Atlantic circulation with a coupled sea-ice-mixed layer-isopycnical general circulation model. Part I: Model description.J. Phys. Oceanogr.,23, 808–829.
Oberhuber, J. M., 1993b: Simulation of the Atlantic circulation with a coupled sea-ice-mixed layer-isopycnical general circulation model. Part II: Model experiment.J. Phys. Oceanogr.,23, 830–845.
Pope, V. D., M. L. Gallani, P. R. Rowntree, and R. A. Stratton, 2000: The impact of new physical parameterizations in the Hadley Centre climate model HadAM3.Climate Dyn.,16, 123–146.
Roeckner, E., and Coauthors, 1992: Simulation of the present-day climate with the ECHAM model: Impact of model physics and resolution. Max-Planck Institute for Meteorology, Report No.93, Hamburg, 171pp.
Santer, B. D., and Coauthors, 1996: A search for human influences on the thermal structure of the atmosphere.Nature,382, 616–619.
Shine, K. P., and P. M. de F. Forster, 1999: The effect of human activity on radiative forcing of climate change: A review of recent developments.Global Planet Change,20, 205–225.
von Storch, H., and F. W. Zwiers, 1999:Statistical Analysis in Climate Research. Cambridge University Press, 484pp.
Zeng Zhaomei, Yan Zhongwei, and Ye Duzheng, 2001; The regions with the most significant temperature trends during the last century.Adv. Atmos. Sci.,18, 481–496.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JH., Kim, B., Sohn, KT. et al. Climate change signal analysis for Northeast Asian surface temperature. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 22, 159–171 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02918506
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02918506