Abstract
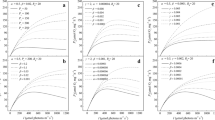
A simple diagnostic simulation of the annual cycling of the surface specific photosynthesis rate (SPR) in Jiaozhou Bay is described in this paper. Light intensity, temperature and nutrients (nitrate+ammonia, phosphate) were considered as main factors controlling photosynthesis of phytoplankton and were introduced into the model by different function equations. The simulated variation of specific photosynthesis rate coincided with the measured data. Analysis of the effect of every factor on photosynthesis indicated that the variation of photosynthesis rate was controlled by all these three factors, while temperature showed good correlation with SPR as measurement showed. This diagnostic simulation yielded the values of some parameter relating with the photosynthesis in Jiaozhou Bay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T., 1997. Pelagic nutrient cycles, herbivores as sources and sinks. Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 280p.
Baumert, H., 1996. On the theory of photosynthesis and growth in phytoplankton. Part 1. Light limitation and constant temperature.Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 81(1): 109–139.
Burmaster, D. E., 1979. The continuous culture of phytoplankton: mathematical equivalence among three unsteady state models.Am. Nat. 113: 123–134.
Campbell, E. E., Bate, G. C., 1988. The photosynthesis response of surf. phytoplankton to temperature.Botanica Marina 31: 251–255.
Chapelle, A., Lazure, P., Menesguen, A., 1994. Modeling eutrophication events in a coastal ecosystem: sensitiity analysis.Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 39: 529–548.
Chen, C. W., Orlob, G. T., 1975. Ecological simulation of aquatic environments.In: Patten B. C. ed., System Analysis and Simulation in Ecology, Vol. 3, Academic Press, New York, p. 476–588.
Droop, M. R., 1983. 25 years of algal growth kinetics, a personal review.Botanic Marina (XXVI): 99–112.
Dugdale, R. C., Goering, J. J., 1967. Uptake of new and regenerated forms of nitrogen in primary production.Limnol. Oceanogr. 12: 196–206.
Eppley, R. W., 1972. Temperature and phytoplankton growth in the sea.Fish. Bull. U. S. 70(4): 1063–1085.
Fransz, H. G., Verhagen, J. H. G., 1985. Modelling research on the productioncycle of phytoplankton in the southern bight of the North Sea in relation to riverborne nutrient loads.Neth. J. Sea Res. 19: 142–250.
Jπrgensen, S. E., 1994. Fundamentals of ecological modelling (2nd edition). Elsevier, Amsterdam, p. 65.
Kinney E. H., Vharles, T. R., 1998. Response of primary producers to nutrient enrichment, in a shallow estuary.Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 163: 89–98.
Lalli, C. M., Parsons, T. R., ed., 1993. Biological Oceanography, an Introduction. Pergamon Press, Oxford. p25.
Mitchell, B. G., Brody, E. A., 1991. Light limitation of phytoplankton biomass and macronutrients utilization in the Southem Ocean.Limnol. Oceanol. 36 (8): 1662–1677.
Nielsen, E. S., 1975. Marine Photosynthesis, with Special Emphasis on the Ecological Aspects. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company. Amsterdam, London, New York, p. 435.
Pan Youlian, Zen Chengkui, Guo Yujie. 1992. Assimilation number of phytoplanktonIn: Liu Ruiyu ed., Ecological and Living Resources of Jiaozhou Bay, Science Press, Beijing. p. 72. (in Chinese)
Platt, T., Jassby, A. D., 1976. The relationship between photosynthesis rate and light for natural assemblages of coastal marine phytoplankton.J. Phycol. 12(4): 421–430.
Riley, G. A., 1947. Factors controlling phytoplankton populations on Geoges Bank.J. Mar. Res. 5–6: 55–72.
Schroeder, F., 1997. Water quality in the Elbe estuary: significance of different processes for the oxygen deficit at Hamburg.Emiron. Model. and Assess. 2: 73–82.
Shen Zhiliang, 1995. The variation of nutrients in Jiaozhou Bay.In: Jiao Nianzhi ed., Ecology in Jiaozhou Bay, Science Press, Beijing, p. 55. (in Chinese)
Steele, J. H., 1962. Environmental control of photosynthesis in the sea.Limnol Oceanol. 7(2): 137–150
Tett, P., Edward, A., 1986. A model for the growth of shelf—sea phytoplankton in summer.Esturaine, Coast and Shelf Science 23: 641–672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Project 49876022 supported by NSFC.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ling, R., Man-ping, Z., Xian-kun, L. et al. Simple simulation of the annual variation of the specific photosynthesis rate in Jiaozhou Bay. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 19, 63–72 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842791
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02842791