Abstract
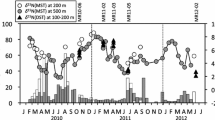
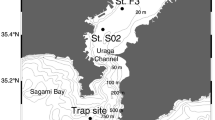
Organic carbon, total nitrogen, amino acids, sugars, and chlorophyll were determined in < 1 mm fractions of the samples collected by successive large aperture time-series sediment traps (Honjo-Mark M) in northern South China Sea during September 1987 to October 1988. The ratio of C/N and the relative abundance of amino acids and sugars show that organic matter in the settling particles from northern South China Sea is derived mainly from marine plantkon (especially phytoplankton). The organic carbon fluxes in our sediment traps are lower than those in other sediment traps. But the relative contents of Corg/total particulate matter are generally similar to those in the Panama Basin, Arabian Sea and Subarctic Pacific. It is suggested that monsoon-caused changes of physical and chemical conditions in the upper euphotic layer would control the fluxes of organic matter as well as its composition and transport in northern South China Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alldredge, A.L. and M.W. Silver, 1988, Characteristics of dynamics and significance of marine snow: Progress in Oceanography, v. 20, p. 41–80.
Chen Jianfang and Zheng Lianfu, 1996, Sediment trap and global change studies: Marine Sciences Bulletin, v. 15, n. 1, p. 41–47 (in Chinese).
Chen Wenbin and Xu Luqiang, 1993, A preliminary study of particle flux in the South China Sea, in Zheng Lianfu and Chen Wenbin, eds., Marine sedimentation processes and geochemistry in the South China Sea: Beijing, China Ocean Press, p. 191–201 (in Chinese).
Hakke, B., V. Ittekkot, and R. R. Nair, 1992, Fluxes of amino acids and hexosamine to the deep Arabian Sea: Marine Chemistry, v. 40, p. 291–314.
Hakke, B., V. Ittekkot, and S. Honjo, 1993, Amino acid and carbohydrate fluxes to the deep Subarctic Pacific: Deep Sea Research, v. 40, p. 547–560.
Hechy, E., K. Mopper, and E. T. Degens, 1973, The amino acids and sugar composition of diatom cell walls: Marine Biology, v. 19, p. 323–331.
IGBP Report No. 23 (JGOFS Report No. 9), 1992, Joint Global Ocean Flux Study Implementation Plan. Stockholm: [s. n.], p. 45.
Ittekkot, V., E.T. Degens, and S. Honjo, 1984, Seasonally in the fluxes of sugars, amino acids, and amino sugars to the deep ocean: Panama Basin: Deep Sea Research, v. 31, p. 1017–1083.
Ittekkot, V., W.G. Deuser, and E. T. Degens, 1984, Seasonality in the fluxes of sugars, amino acids, and amino sugars to the deep ocean: Sargasso Sea: Deep Sea Research, v. 31, p. 1057–1069.
Jennerjahn, T.C., S. Kempe, and L. Q. Xu, 1992, Particle flux in the northern South China Sea, in X.L. Jin., H.R. Kudrass and G. Pautot, eds., Marine geology and geophysics of the South China Sea: Beijing, China Ocean Press, p. 228–235.
Michaelis, W. and V. Ittekkot, 1982, Biogeochemistry of river: field and analytical techniques, in E.T. Degens, ed., Transport of carbon and minerals in major world rivers: Hamburg, Mitt Geol. Palaont Inst. Univ. Hamburg, SCOPE/UNEP Sonderband 52, p. 69–89.
Parsons, T.R., 1984, Biological oceanographic processes (3rd ed.): New York, Pergamon Press, p. 37–114.
State Oceanic Administration, 1988, Report on a comprehensive investigation of the environmental resources in central South China Sea: Beijing, China Ocean Press, 419p. (in Chinese)
Stevenson, F.J. and C. N. Cheng, 1970, Amino acids in sediments: recovery by acid hydrolysis and quantitative estimation by a colorimetric procedure: Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta, v. 34, n. 1, p. 77–88.
Wakeham, S.G. and C. Lee, 1989, Organic geochemistry of particulate matter in the ocean: The role of particles in oceanic sedimentary cycles: Organic Geochemistry, v. 14, p. 83–89.
Wang Jiangke, Chen Shuijia, and Zhong Yueming, 1991, Biogeochemistry of amino acid: Beijing, China Sciences Press, 308p. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was financially supported by both Sino-German Scientific Cooperation Program and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 49070269, 49776297).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jianfang, C., Luqiang, X., Lianfu, Z. et al. Organic geochemical characteristics of time-series settling particles in northern South China Sea and their implications. Chin. J. Geochem. 17, 275–283 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02834604
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02834604