Abstract
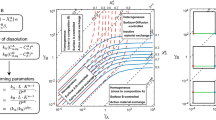
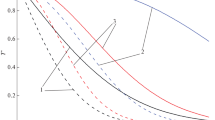
Minerals that react with each other during the progressive evolution of metamorphic terranes are not always in physical contact. As such, an “intergranular fluid” could play a major role in element transfer and chemical evolution. However, the nature of this fluid and its specific role remains somewhat elusive. Recent experiments in our laboratory shed some light on the behavior of such a fluid. Here we present a simple mathematical model which accounts for diffusion within crystals and fluid, solubility in the fluid and mass balance between the various reservoirs. The model elucidates the nature of element exchange between two minerals via the mediation of an intergranular fluid. It is shown that a coupling of thermodynamics and kinetics controls the evolution of the system and the concentration of an element in the intergranular fluid is a key parameter of interest.
The results have important implications for standard tools of metamorphic petrology such as geothermometers and barometers, geospeedometry and the closure of isotopic systems. For example, homogeneity of mineral grains may be a poor criterion for equilibrium and the rim compositions of minerals showing diffusion zoning may be out of equilibrium with distant exchange partners, even in the presence of a fluid in which transport is fast.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman R G 1988 Internally consistent thermodynamic data for minerals in the system Na2O-K2O-CaO-MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2-H2O-CO2;J. Petrol. 29 445–522
Brady J B 1983 Intergranular diffusion in metamorphic rocks;Am. J. Sci. 283 181–200
Chakraborty S, Lasaga A C and Bolton E W 1997 Diffusion controlled fractionation of trace elements in magmatic systems. AGU Fall Meeting;EOS 78 F833
Chakraborty S, Farver J R, Yund R A and Rubie D C 1994 Mg tracer diffusion in synthetic forsterite and San Carlos Olivine as a function of P,T and fO2;Phys. Chem. Min. 21 489–500
Dempster T J and Tanner P W G 1997 The biotite isograd, Central Pyrenees: a deformation-controlled reaction;J. Metamorphic Geol. 15 531–548
Dohmen R, Chakraborty S, Palme H and Rammensee W 2001 The role of element solubility on the kinetics of element partitioning:in situ observations and a thermodynamic kinetic model;J. Geophys. Res., in review.
Dohmen R, Chakraborty S, Palme H and Rammensee W 1998 Solid-solid reactions mediated by a gas phase: An experimental study of reaction progress and the role of surfaces in the system Olivine + Fe-metal;Am. Min. 83 970–984
Eiler J M, Baumgartner L P and Valley J W 1992 Intercrystalline stable isotope diffusion: a fast grain boundary model;Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 112 543–557
Farver J R, Yund R A and Rubie D C 1994 Magnesium grain boundary diffusion in forsterite aggregates at 1000‡C—1300‡ C and 0.1 MPa to 10 GPa;J. Geophys. Res. 99 19809–19819
Fletcher R C and Hofmann A W 1974 Simple models of diffusion and combined diffusion-infiltration metasomatism; InGeochemical Transport and Kinetics (eds) A W Hofmann, B J Giletti, H S Yoder Jr, and R A Yund, (D C Washington, Carnegie Inst. Washington) p. 243–259
Florence F P and Spear F S 1995 Intergranular diffusion kinetics of Fe and Mg during retrograde metamorphism of a pelitic gneiss from the Adirondack Mountains;Earth and Planet. Sci. Lett. 134 329–340
Ganguly J, Cheng W and Chakraborty S 1998 Cation diffusion in aluminosilicate garnets: experimental determination in pyrope almandine diffusion couples;Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 131 171–180
Jamtveit B, Bucher-Nurminen K and Austrheim H 1990 Fluid controlled eclogitization of granulites in deep crustal shear zones, Bergen Arcs, Western Norway;Contrib Mineral. Petrol. 104 184–193
Knudsen M 1909 Die Molekularströmung der gase durch Offnungen und die Effusion;Ann. Phys. 28 999–1016
Lasaga A C 1986 Metamorphic reaction rate laws and development of isograds;Min. Mag. 50 359–373
Mueller R F 1967 Mobility of the elements in metamorphism;J. Geol. 75 565–582
O’Brien P J 1999 Asymmetric zoning profiles in garnet from HP-HT granulite and implications for volume and grainboundary diffusion;Min. Mag. 63 227–238
Oelkers E H, Helgesson H C, Shock E L, Sverjensky D A, Johnson J W and Pokrovskii V A 1995 Summary of the apparent standard partial molal Gibbs Free Energies of formation of aqueous species, minerals, and gases at pressures 1 to 5000 bars and temperatures 25 to 1000‡ C;J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 24 1401–1553
Rammensee W and Fraser D 1981 Activities in solid and liquid Fe-Ni and Fe-Co alloys determined by Knudsen cell mass spectrometry;Ber. Bunsen. Phys. Chem. 85 588–592
Rubie D C 1986 The catalysis of mineral reactions by water and restrictions on the presence of aqueous fluid during metamorphism;Min. Mag. 50 399–415
Watson E B 1999 Lithologic partitioning of fluids and melts;Am. Min. 84 1693–1710
Watson E B and Wark D A 1997 Diffusion of dissolved SiO2 in H2O at 1 GPa, with implications for mass transport in the crust and upper mantle.Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 130 66–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, S., Dohmen, R. Some aspects of the role of intergranular fluids in the compositional evolution of metamorphic rocks. J Earth Syst Sci 110, 293–303 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702896
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702896