Abstract
Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) is one of the new techniques which will probably dominate geodesy and geophysics in the near future. Its main advantage lies in the fact that it brings the accuracy of direction measurements to a level previously possible only for range measurements. This closes the gap between powerful range determination techniques such as laser ranging and the much less accurate determination of directions through photographic tracking of artificial earth satellites.
The technique is geometric in the sense that the relevant observations are independent of the gravity field of the earth. However, the “orbits” of the observed extragalactic radio sources with respect to an earth-fixed system are dominated and perturbed by the rotation of the earth with respect to inertial frame. This allows the determination of polar motion, precession-nutation and length-of-the-day variations, and the technique becomes also “dynamic” in this respect.
The capability of determining the geometry of a network of stations within a short time interval and with a centimeter level accuracy also allows the study of the variation of network geometry with time caused by earth tides and other periodic or secular station drifts.
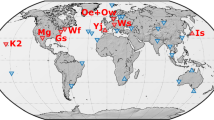
The main objective of the present work is the exploration of the capabilities of VLBI for the recovery of earth rotation and network geometry parameters. For this purpose, a number of characteristic experimental designs based on present and candidate for the near future station locations is chosen. The results from the analysis of simulated observations for each particular design are presented in the paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. ARNOLD, (1974): “Geodetic Aspects of Laser Distance Measurements to the Moon and Radio-Interference Measurements to Quasars”,Gerlands Beiträge zur Geophysik, 83, 4, 249–269.
G. BLAHA, (1971): “Inner Adjustment Constraints with Emphasis on Range Observations”, Reports of the Department of Geodetic Science, No. 148, The Ohio State University, Columbus.
A. DERMANIS, (1977): “Design of Experiment for Earth Rotation and Baseline Parameter Determination from Very Long Baseline Interferometry”, Reports of the Department of Geodetic Science, No. 245, The Ohio State University, Columbus.
E. GRAFAREND, (1974): “Optimization of Geodetic Networks”,The Canadian Surveyor, 28, 5, 716–723.
L.H. KOOPMANS, (1974):The Spectral Analysis of Time Series. Academic Press, New York.
I.I. MUELLER, (1969):Spherical and Practical Astronomy as Applied to Geodesy Frederick Ungar Publishing Co., New York.
A.J. POPE, (1971): “Transformation of Covariance Matrices Due to Changes in Minimal Control”. Paper presented at the AGU Annual Fall Meeting, San Francisco.
I.I. SHAPIRO and C.A. KNIGHT, (1970): “Geophysical Applications of Long-Baseline Radio Interferometry”. In: L. Mansinha et al. (eds.),Earthquake Dispalacement Fields and the Rotation of the Earth, pp. 284–301. D. Reidel Publishing Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
J.B. THOMAS, (1972a): “An Analysis of Long Baseline Radio Interferometry”,JPL Technical Report 32-1526, VII, pp. 37–50.
J.B. THOMAS, (1972b): “An Analysis of Long Baseline Radio Interferometry, Part II”.JPL Technical Report 32-1526, VIII, pp. 29–38.
J.B. THOMAS, (1973): “An Analysis of Long Baseline Radio Interfermetry, Part III”.JPL Technical Report 32-1526, XVI, p. 47.
U.A. UOTILA, (1967): “Introduction to Adjustment Computations with Matrices”. Lecture Notes, Department of Geodetic Science, The Ohio State University, Columbus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dermanis, A., Mueller, I.I. Earth rotation and network geometry optimization for very long baseline interferometers. Bull. Geodesique 52, 131–158 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02521695
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02521695