Abstract
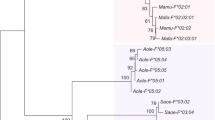
The human Rh blood-group system is encoded by two homologous genes,RhD andRhCE. TheRH genes in gorillas and chimpanzees were investigated to delineate the phylogeny of the humanRH genes. Southern blot analysis with an exon 7-specific probe suggested that gorillas have more than twoRH genes, as has recently been reported for chimpanzees. Exon 7 was well conserved between humans, gorillas, and chimpanzees, although the exon 7 nucleotide sequences from gorillas were more similar to the humanD gene, whereas the nucleotide sequences of this exon in chimpanzees were more similar to the humanCE gene.
The intron between exon 4 and exon 5 is polymorphic and can be used to distinguish the humanD gene from theCE gene. Nucleotide sequencing revealed that the basis for the intron polymorphism is anAlu element inCE which is not present in theD gene. Examination of gorilla and chimpanzee genomic DNA for this intron polymorphism demonstrated that theD intron was present in all the chimpanzees and in all but one gorilla. TheCE intron was found in three of six gorillas, but in none of the seven chimpanzees. Sequence data suggested that theAlu element might have previously been present in the chimpanzeeRH genes but was eliminated by excision or recombination.
Conservation of theRhD gene was also apparent from the complete identity between the 3′-noncoding region of the human D cDNA and a gorilla genomic clone, including anAlu element which is present in both species.
The data suggest that at least twoRH genes were present in a common ancestor of humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas, and that additionalRH gene duplication has taken place in gorillas and chimpanzees. TheRhCE gene appears to have diverged more thanRhD among primates. In addition, theRhD gene deletion associated with the Rh-negative phenotype in humans seems to have occurred after speciation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arce MA, Thompson ES, Wagner S, Coyne KE, Ferdman BA, Lublin DM (1993) Molecular cloning of RhD cDNA derived from a gene present in RhD-positive, but not Rh-negative individuals. Blood 82:651–655
Avent ND, Ridgwell K, Tanner MJA, Anstee DJ (1990) cDNA cloning of a 30 kDa erythrocyte membrane protein associated with Rh (Rhesus)-blood-group-antigen expression. Biochem J 271:821–825
Batzer MA, Stoneking M, Alegria-Hartman M, Bazan H, Kass DH, Shaikh TH, Novick GE, Ioannou PA, Scheer WD, Herrera RJ, Deininger PL (1994) African origin of human-specific polymorphicAlu insertions. Proc Nall Acad Sci USA 91:12288–12292
Blancher A, Socha WW, Ruffie J (1992) Diversity of human anti-D monoclonal antibodies revealed by reactions with chimpanzee red blood cells. Vox Sang 63:112–118
Calabretta B, Robberson DL, Barrera-Saldana HA, Lambrou TP, Saunders GF (1982) Genome instability in a region of human DNA enriched inAlu repeat sequences. Nature 296:219–225
Cherif-Zahar B, Bloy C, Le Van Kim C, Blanchard D, Bailly P, Hermand P, Salmon C, Cartron J-P, Colin Y (1990) Molecular cloning and protein structure of a human blood group Rh polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6243–6247
Cherif-Zahar B, Ryanal V, Le Van Kim C, D'Ambrosio AM, Bailly P, Cartron J-P, Colin Y (1993) Structure and expression of the RH locus in the Rh-deficiency syndrome. Blood 82:656–662
Cherif-Zahar B, Le Van Kim C, Rouillac C, Raynal V, Cartron J-P, Colin Y (1994a) Organization of the gene (RHCE) encoding the human blood group RhCcEe antigens and characterization of the promoter region. Genomics 19:68–74
Cherif-Zahar B, Raynal V, D'Ambrosio AM, Cartron JP, Colin Y (1994b) Molecular analysis of the structure and expression of the RH locus in individuals with D-, Dc-, and Dcw-gene complexes. Blood 84:4354–4360
Colin Y, Cherif-Zahar B, Le Van Kim C, Raynal V, Van Huffel V, Cartron J-P (1991) Genetic basis of the RhD-positive and RhD-negative blood group polymorphism as determined by Southern analysis. Blood 78:2747–2752
Feng D, Doolittle RF (1987) Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol 25:351–360
Hyland CA, Wolter LC, Saul A (1994) Three unrelated Rh D gene polymorphisms identified among blood donors with Rhesus CCee (r′r′) phenotypes. Blood 84:321–324
Jurka J, Milosavljevic A (1991) Reconstruction and analysis of humanAlu genes. J Mol Evol 32:105–121
Le Van Kim C, Muro I, Cherif-Zahar B, Raynal V, Cherrier C, Cartron J-P, Colin Y (1992) Molecular cloning and primary structure of the human blood group RhD polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10925–10929
Miller KA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Muro I, Le Van Kim C, Cherif-Zahar B, Salvignol I, Blancher A, Cartron J-P, Colin Y (1994a) Molecular characterization of the Rh-like locus and gene transcripts from the Rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). J Mol Evol 38:169–176
Moro I, Le Van Kim C, Rouillac C, van Rhenen DJ, LePennec P, Bailly P, Cartron J-P, Colin Y (1994b) Rearrangements of the blood group RhD gene associated with the DVI category phenotype. Blood 83: 1129–1135
Race RR, Sanger R (1975) Blood groups in man, 6th ed. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Rouillac C, Le Van Kim C, Blancher A, Roubinet F, Cartron J-P, Colin Y (1995) Lack of G blood group antigen in DIIIb erythrocytes is associated with segmental DNA exchange betweenRH genes. Br Haematol 89:424–426
Rychlik W, Rhoads RE (1989) A computer program for choosing optimal oligonucleodde for filter hybridization, sequencing and in vitro amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 17:8543–8551
Salvignol I, Blancher A, Calvas P, Socha WW, Colin Y, Cartron J-P, Ruffié J (1993) Relationship between chimpanzee Rh-like genes and the R-C-E-F blood group system. J Med Primatol 22:19–28
Salvignol I, Calvas P, Socha WW, Colin Y, Le Van Kim C, Bailly P, Ruffié J, Carton J-P, Blancher A (1995) Structural analysis of the RH-like blood group gene products in nonhuman primates. Immunogenetics 41:271–281
Socha WW, Moor-Jankowski J (1980) Chimpanzee R-C-E-F blood group system. A counterpart of the human RH-Hr blood groups. Folia Primatol (Basel) 33:172–188
Socha WW, Ruffié J (1990) Monoclonal antibodies directed against human Rh antigens in tests with the red cells of nonhuman primates. Rev Fr Tranfus Hemobiol 33:39–48
Schmid CW, Jelinek WR (1982) TheAlu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science 216:1065–1070
Wiener AS, Moor-Jankowski J, Gordon EB (1964) Blood groups of apes and monkeys. IV. The Rh-Hr blood types of anthropoid apes. Am J Hum Genet 16:246–253
Wiener AS, Moor-Jankowski J, Gordon EB, Riopelle AL Shell WF (1966) Human-type blood factors in gibbons, with special reference to the multiplicity of serological specificities of human type M blood. Transfusion 6:311–318
Westhoff CM, Wylie DE (1994) Investigation of the human Rh blood group system in nonhuman primates and other species with serologic and Southern blot analysis. J Mol Evol 39:87–92
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: C.M. Westhoff
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westhoff, C.M., Wylie, D.E. Investigation of the RH locus in gorillas and chimpanzees. J Mol Evol 42, 658–668 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02338799
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02338799