Abstract
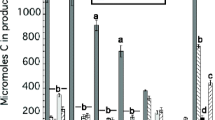
Hemicellulose-degrading enzymes were detected in cell-free extracts of protozoa representing ten genera of rumen entodiniomorphid and holotrich ciliates. The enzyme preparations released monosaccharides, disaccharides, and oligomers fromLolium perenne hemicellulose B and oat spelt xylan; the activity was present both in cells isolated directly from rumen contents and in those cultured in vitro. The specific activities were higher in the cellulolytic entodiniomorphid genera (Polyplastron, Diploplastron, Eremoplastron, Epidinium, Ophryoscolex, Eudiplodinium) than in the holotrich ciliates (Dasytrichia ruminantium, Isotricha intestinalis/I. prostoma) and the entodinia examined (Entodinium bursa, E. simplex, E. caudatum). The rate of hemicellulose-B degradation to alcohol-soluble products was approximately 5–10 times higher than the rate of reducing sugar accumulation; this indicates an initial depolymerization to intermediate oligosaccharide fragments. Examination of the hemicellulose degradation products by thin-layer and gas-liquid chromatography confirmed oligosaccharide formation, revealed markedly different rates of arabinose and xylose release, and indicated that the mode of polysaccharide degradation was similar in the protozoal preparations examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Aboud Akkada AR (1965) The metabolism of ciliate protozoa in relation to rumen function. In: Dougherty RW, Allen RS, Burroughs W, Jacobson NL, McGilliard AD (eds), Physiology of digestion in the ruminant. Washington: Butterworth's, pp 335–343.
Abou Akkada AR, Eadie JM, Howard BH (1963) The biochemistry of rumen protozoa. 7. The carbohydrases ofPolyplastron multivesiculatum (Dogiel and Fedorowa). Biochem J 89:268–272
Abou Akkada AR, Howard BH (1960) The biochemistry of rumen protozoa. 3. The carbohydrate metabolism ofEntodinium. Biochem J 76:445–451
Abou Akkada AR, Howard BH (1961) The biochemistry of rumen protozoa. 4. The decomposition of pectic substances. Biochem J 78:512–517
Akin DE, Amos HE (1979) Mode of attack on orchardgrass leaf blades by rumen protozoa. Appl Environ Microbiol 37:332–338
Amos HE, Akin DE (1978) Rumen protozoal degradation of structurally intact forge tissues. Appl Environ Microbiol 36:513–522
Bailey RW, Clarke RTJ (1963) Carbohydrase activity of rumenEntodinium species from sheep on a starch-free diet. Nature (Lond) 198:787
Bailey RW, Clarke RTJ (1963) Carbohydrases of the rumen oligotrichEremoplastron bovis. Nature (Lond) 199:1291–1292
Bailey RW, Clarke RTJ, Wright DE (1962) Carbohydrases of the rumen ciliateEpidinium ecaudatum (Crawley): action on plant hemicellulose. Biochem J 83:517–523
Bailey RW, Gaillard BDE (1965) Carbohydrases of the rumen ciliateEpidinium ecaudatum (Crawley): hydrolysis of plant hemimcellulose fractions and β-linked glucose polymers. Biochem J 95:758–766
Bauchop T (1979) The rumen ciliateEpidinium in primary degradation of plant tissues. Appl Environ Microbiol 37:1217–1223
Bauchop T, Clarke RTJ (1976) Attachment of the ciliateEpidinium (Crawley) to plant fragments in the sheep rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 32:417–422
Coleman GS (1978) Rumen entodiniomorphid protozoa. In: Taylor AE, Baker JR (eds) Methods of cultivating parasites in vitro. London: Academic Press, pp 39–54
Coleman GS (1983) The cellulolytic activity of thirteen species of rumen entodiniomorphid protozoa. J Protozool 30:36A
Coleman GS, Sandford DC, Beahon S (1980) The degradation of polygalacturonic acid by rumen ciliate protozoa. J Gen Microbiol 120:295–300
Dekker RFH (1976) Hemicellulose degradation in the ruminant: Misc Pap Landbouwhogeschool Wageningen Netherlands 12:43–54
Hansen SA (1975) Thin-layer chromatographic method for identification of oligosaccharides in starch hydrolysates. J Chromatogr 105:388–390
Hayer GS, Punj ML, Bhatia IS (1976) Studies on hemicellulase of rumen protozoa from buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Indian J Anim Sci 46:587–592
Lever, M (1977) Carbohydrate determination with 4-hydroxybenzoic acid hydrazide (PAHBAH): effect of bismuth on the reaction. Anal Biochem 81:21–27
Lowry OH, Rosebrough WJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Morrison IM (1974) Changes in the hemicellulosic polysaccharide of rye-grass with increasing maturity. Carbohydr Res 36:45–51
Morrison IM (1979) Changes in the cell wall components of laboratory silages and the effect of various additives on these changes. J Agric Sci (Cambridge) 93:581–586
Naga MA, El-Shazly KJ (1968) The metabolic characterization of the ciliate protozoonEudiplodinium medium from the rumen of buffalo. J Gen Microbiol 53:305–315
Orpin CG (1983) The role of ciliate protozoa and fungi in the rumen digestion of plant cell walls. Anim Feed Sci Technol 10:121–143
Rao AM, Punj ML, Bhatia IS (1977) Studies on epidinial hemicellulase from the rumen of goat. Indian J Anim Sci 47:539–544
Williams AG (1979) Exocellular carbohydrase formation by rumen holotrich ciliates. J Protozool 26:665–672
Williams AG, Harfoot CG (1976) Factors affecting the uptake and metabolism of soluble carbohydrates by the rumen ciliateDasytricha ruminantium isolated from ovine rumen contents by filtration. J Gen Microbiol 96:125–136
Williams AG, Strachan NH (1984) The distribution of polysaccharide-degrading enzymes in the bovine rumen digesta ecosystem. Curr Microbiol 10:215–220
Williams AG, Withers SE (1981) Hemicellulose degrading enzymes synthesized by rumen bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol 51:375–385
Williams AG, Withers SE, Coleman GS (1984) Glycoside hydrolases of rumen bacteria and protozoa. Curr Microbiol 10:287–293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, A.G., Coleman, G.S. Hemicellulose-degrading enzymes in rumen ciliate protozoa. Current Microbiology 12, 85–90 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567397
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01567397