Abstract
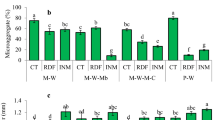
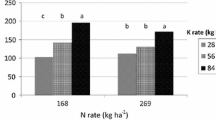
The effect of continuous application of rates of N (40, 80 and 120 kg N ha−1), P (0, 17.5, and 35 kg P ha−1) and K (0 and 33.2 kg K ha−1) to a maize-wheat annual sequence on the changes in soil fertility after harvest of maize and wheat in their 11th cycle are reported. The organic carbon (O.C.), available nutrients and micronutrients tended to decline with cropping. Application of N or P significantly increased O.C. status of the soil both after harvest of maize and wheat. Potassium addition also increased the O.C. status but significant differences were observed only after wheat harvest (22nd crop). The available N status of the soil increased significantly with N application whereas a declining trend occurred with P dressings. Potassium application did not affect the soil available N content. The maximum decline in available P status was observed under N120 P0 K33.2 treatment whereas a significant increase occurred in P treated plots. The available K status continued to decline in plots receiving increasing rates of N and NP fertilizers. The soil available K status was maintained to its initial content in plots receiving fertilizer K with increasing rates of N with or without P. Continuous application of increasing levels of N (averaged over PK) depleted the soil of DTPA-extractable Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu content. The addition of P also resulted in a decline in the status of Mn and Cu whereas the Fe and Mn content of the soil was increased. The available micronutrients content was least affected by K additions. The contents of organic carbon, available N and K in differentially fertilized plots were higher after harvest of 22 crops (wheat) than 21 crops (maize) while the reverse occurred in respect of available P and micronutrients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (1992) Agronomic research for sustained crop and soil productivity. Tech Bull Dept Agron (PAU), Ludhiana, Punjab, India. 32p
Arora CL, Nayyar VK and Randhawa NS (1975) Note on secondary and micro-element contents in fertilizers and manures. Indian J Agric Sci 45: 80–85
Bhangu SS and Sidhu PS (1993) Potassium mineralogy of five benchmark soils of central Punjab. J Potassium Res 9: 105–112
Biswas CR and Benbi DK (1989) Long-term effects of manure and fertilizer on wheat based cropping systems in semi-arid alluvial soils. Fert News 34: 33–38
Biswas CR, Sekhon GS and Singh R (1977) Accumulation and decline of available phosphorus and potassium in a soil under multiple cropping. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 25: 23–27
Cope JT Jr (1981) Effect of 50 years of fertilization with phosphorus and potassium on soil test levels and yield at six locations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45: 342–347
Dalal RC and Mayer RJ (1986) Long-term trends in fertility of soil under continuous cultivation and cereal cropping in Southern Queensland. II. Total organic carbon and its rate of loss from soil profile. Aust J Soil Res 24: 281–292
Harjit Singh (1992) Influence of continuous fertilization to a maize-wheat sequence on the changes in soil properties and kinetics of P and K release. M.Sc. Thesis, Punjab Agric Univ, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. pp 151 + XVII
Jackson ML (1967) Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice Hall of India Pvt Ltd., New Delhi, India. 485p
Kapur ML, Talukdar NC and Rana DS (1986) Influence of continuous application of inorganic fertilizers in a fixed maize-wheat rotation on soil chemical properties. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 34: 198–199
Lindsay WL and Norvell WA (1978) Development of DTPA soil test for Zn, Fe, Mn, and Cu. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42: 421–428
Minhas RS and Mehta RL (1984) Effect of continuous application of fertilizers on crop yield and some soil chemical properties under wheat-maize rotation. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 32: 749–751
Muthuswamy P, Santhy P and Ramanathan G (1990) Long-term use of fertilizer on soil fertility and yield of crops in irrigated inceptisol. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 38: 541–542
Odell TR, Melsted SW and Walker WM (1984) Changes in organic carbon and N of Morrow plots soil under different treatments (1904–1973). Soil Sci 137: 160–171
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS and Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available P in soils by extraction with NaHCO3, USDA Circ No. 939
Sharma KN, Singh B, Sodhi JS, Kapur ML and Rana DS (1984) Changes in soil fertility status as influenced by continuous cropping and fertilizer application. J. Agric Sci (Camb) 102: 215–218
Sharma KN, Rana DS and Bhandari AL (1987) Influence of growing various crops in five fixed cropping sequences on the changes in phosphorus and potassium content of soil. J Agric Sci (Camb) 109: 281–284
Sharma KN, Bhandari AL, Rana DS, Kapur ML and Sodhi JS (1990) Crop yield, nutrient uptake and soil properties as influenced by components of crop technology in a pigeonpea-wheat sequence. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 38: 520–523
Singh L, Verma RNS and Lohia SS (1980) Effect of continuous application of FYM and chemical fertilizers on some soil properties. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 28: 170–172
Snedecor GW and Cochran GW (1967) Statistical Methods. Sixth edition. Oxford and IBH Publishing Co. New Delhi, India. 593p
Subbiah BV and Asija GL (1956) A rapid procedure for the estimation of available nitrogen in soils. Curr Sci 25: 259–260
Thind GS, Meelu OP and Sharma KN (1979) Effect of crop rotation on soil fertility status. Indian J Agric Sci 49: 276–280
Walkley A and Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 38: 29–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, H., Sharma, K.N. & Arora, B.S. Influence of continuous fertilization to a maize-wheat system on the changes in soil fertility. Fertilizer Research 40, 7–19 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749858
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749858