Summary
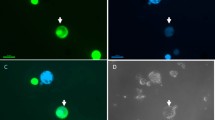
Protoplasts of Vicia hajastana Grossh. obtained from suspension-culture cells and Pisum sativum L. obtained from leaves adhered tightly to each other in concentrated solutions of high-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol (PEG). The adhesion occurred non-specifically between the free protoplasts from the same species as well as from the different species and genus. It was enhanced by enrichment of the PEG solution with calcium. Very few heteroplasmic fusions occurred during the period when the protoplasts were incubated in the PEG solution. However, many heterokaryons (up to 10%) were formed soon after the PEG solution was diluted out. The same phenomena were also observed in protoplasts from suspension-culture cells of Glycine max L. and from leaves of Hordeum vulgare L. Vicia and soybean protoplasts obtained from cultured cells regenerated cell walls and underwent sustained cell division after such treatment. Some Vicia-pea heterokaryons divided once. Over 10% of the soybean-barley hybrids divided in 7 days. Some divided 4–5 times and formed small clusters of cells in 10 days. The hybrids were recognizable because they contained chloroplasts from the leaf protoplast and exhibited morphological characters typical of the chlorophyll-less cells. None of the protoplasts from pea and barley leaves, either with or without PEG treatment, underwent cell division during the period of observation. The mechanism of adhesion and fusion of the protoplasts has been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carlson, P. S.: Induction and isolation of auxotrophic mutants in somatic cell cultures of Nicotiana tabacum. Science 168, 487–489 (1970)
Carlson, P. S., Smith, H. H., Dearing, R. D.: Parasexual interspecific plant hybridization. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 69, 2292–2294 (1972)
Eriksson, T.: Studies on the growth requirements and growth measurements of cell cultures of Haplopappus gracilis. Physiol. Plantarum (Cph.) 18, 976–993 (1965)
Eriksson, T.: Isolation and fusion of plant protoplasts. In: Les cultures de tissue de plantes, p. 297–301. Paris: CNRS 1971
Gamborg, O. L., Miller, R. A., Ojima, K.: Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp. Cell Res. 50, 151–158 (1968)
Giles, K. L.: An interspecific aggregate cell capable of cell wall regeneration. Plant and Cell Physiol. 13, 207–209 (1972)
Hartmann, J. X., Kao, K. N., Gamborg, O. L., Miller, R. A.: Immunological methods for the agglutination of protoplasts from cell suspension cultures of different genera. Planta (Berl.) 112, 45–56 (1973)
Kao, K. N., Gamborg, O. L., Michayluk, M. R., Keller, W. A., Miller, R. A.: The effects of sugars and inorganic salts on cell regeneration and sustained division in plant protoplasts. In: Protoplastes et fusion de cellules somatiques végétales, p. 207–213. Paris: CNRS 1973
Kao, K. N., Gamborg, O. L., Miller, R. A., Keller, W. A.: Cell divisions in cells regenerated from protoplasts of soybean and Haplopappus gracilis. Nature (Lond.) New Biol. 232, 124 (1971)
Keller, W. A., Harvey, B. L., Kao, K. N., Miller, R. A., Gamborg, O. L.: Determination of the frequency of interspecific protoplast fusion by differential staining. In: Protoplastes et fusion de cellules somatiques végétales, p. 456–463. Paris: CNRS 1973
Merck Index, 6th ed. Rahway, N. J., USA: Merck & Co. 1952
Meyer, K. H.: Natural and synthetic high polymers. New York: Interscience 1952
Nickell, L. G., Torrey, J. G.: Crop improvement through plant cell and tissue culture. Science 166, 1068–1069 (1969)
Potrykus, I.: Intra and interspecific fusion of protoplasts from petals of Torenia baillonii and Torenia fournieri. Nature (Lond.) New Biol. 231, 51–58 (1971)
Power, J. B., Cummins, S. E., Cocking, E. C.: Fusion of isolated plant protoplasts. Nature (Lond.) 225, 1016–1018 (1970)
Schenk, R. U., Hildebrandt, A. C.: Somatic hybridization: a new approach to genetic change. Amer. J. Bot. 55, 731 (1968)
Takebe, I., Otsuki, Y., Aoki, S.: Isolation of tobacco mesophyll cells in intact and active state. Plant and Cell Physiol. 9, 115–124 (1968)
Wallin, A., Eriksson, T.: Plating of protoplasts from cell suspension cultures of Daucus carota. In: Protoplastes et fusion de cellules somatiques végétales, p. 301–307. Paris: CNRS 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
National Research Council (Canada) No. 13732.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kao, K.N., Michayluk, M.R. A method for high-frequency intergeneric fusion of plant protoplasts. Planta 115, 355–367 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388618
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388618