Summary
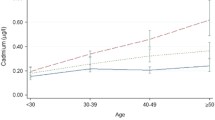
The cadmium body burden of the occupationally non-burdened population in the southern Bavarian area was estimated from the cadmium concentrations in liver and renal cortex, determined by ET-AAS of 263 autopsy cases. A mean value of 17.9 mg cadmium was calculated for all cases and 21.9 mg cadmium for all adults. The body burdens found do not depend on sex but greatly on smoking habits. Mean values for non-smokers are 13.5 mg, for moderate smokers 22.5 mg and for heavy smokers 33.2 mg. The dependence on age is similar to that of the cadmium concentration in the kidney cortex: an increase up to an age of approximately 50 years and a decrease at higher ages. Between the average value we found and the critical body burden calculated by Roels et al. (1983) is a safety factor of 8 to 10, but in some of our cases of middle-aged, heavy smokers this safety factor drops to a value lower than 1. It is concluded that it seems to be imperative to control the further trend of the cadmium body burden in occupationally non-burdened populations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brockhaus A, Freier I, Ewers U, Jermann E, Dolgner R (1983) Levels of cadmium and lead in blood in relation to smoking, sex, occupation, and other factors in an adult population of the FRG. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 52:167–175
Ciba-Geigy AG (1979) Wissenschaftliche Tabellen, Basel (own publication)
Dornemann A, Kleist H (1978) Bestimmung von Cadmium im Vollblut. Zbl Arbeitsmed 6:165–168
Drasch G (1982) Kadmiumbelastung im Südbayerischen Raum. Münchn Med Wochenschr 124:1129–1132
Drasch G (1983) Die anthropogene Blei- und Cadmiumbelastung des Menschen - Untersuchungen an Skelett- and Organmaterial. Habil.-Schrift, München
Elinder GC, Kjellström T, Lind B, Linnman L, Piscator M, Sundstedt K (1983) Cadmium exposure from smoking cigarettes: variations with time and country where purchased. Environm Res 32:220–227
Ellis KJ, Vartsky D, Zanzi J, Cohn SH, pYasumura S (1979) Cadmium: in vivo measurements in smokers and non-smokers. Science, NY 205:323–325
Ellis KJ, Morgan WD, Zanzi I, Yasumura S, Vartsky D, Cohn SH (1981) Critical concentrations of cadmium in human renal cortex: dose-effect studies in cadmium smelter workers. J Toxicol Environ Health 7:691–703
Friberg L (1982) The critical concentration concept and reference levels for cadmium in indicator media for the general population. International Workshop on Biological Indicators on Cadmium Exposure Diagnostic and Analytical Reliability, Luxembourg
Friberg L, Piscator M, Nordberg GF, Kjellström T (1974) Cadmium in the environment, 2nd edn. CRC Press Inc., Cleveland, Ohio
Haddock AG, Travis CC (1979) Age dependent biological half-time of cadmium in the human renal cortex. In: Hemphill DD (ed) Proceedings of trace substances in environmental health XIII. University of Missouri, Columbia, pp 190–194
Hasegawa Y (1982) “Normal” levels of cadmium in blood and kidney cortex in the general population. International Workshop on Biological Indicators on Cadmium Exposure Diagnostic and Analytical Reliability, Luxembourg
IARC — International Agency for Research on Cancer (1976) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk of chemicals to man. Lyon 1976/11, pp 39–74
Jessen H, Kruse H, Piechotowski I (1984) Cadmiumkonzentrationen im Blut von Stadt- und Inselbewohnern in Schleswig-Holstein. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 54:45–54
Kemper FH, Bertram HP (1979) Data presented at the first meeting of the Scientific Advisory Committee to Examine the Toxicity and Ecotoxicity of Chemical Compounds. Luxembourg, 12–13 Dec. 1979
Kinkeldey G (1978) Ermittlung eines Verteilungsmusters für Cadmium in der menschlichen Leber. Z Ges Hyg 24:927–929
Kjellström T (1979) Exposure and accumulation of cadmium in populations from Japan, the United States, and Sweden. Report on a 3 year cooperative research project. Environ Health Persp 28:169
Kjellström T, Nordberg GF (1978) A kinetic model of cadmium metabolism in the human being. Environ Res 16:248–269
Kjellström T, Friberg L, Nordberg G, Piscator M (1971) Further considerations on uptake and retention of cadmium in human kidney cortex. In: Friberg L, Piscator M, Nordberg GF, Kjellström T (eds) Cadmium in the environment. CRC Press, Cleveland, pp 140–148
Kjellström T, Elinder CG, Friberg L (1984) Conceptual problems in establishing the critical concentration of cadmium in human kidney cortex. Environ Res 33:284–295
Lauwerys RR (1978) Criteria (dose/effect relationships) for cadmium. Commission of the European Communities, Pergamon Press, Oxford
Lauwerys RR (ed) (1982) The toxicology of cadmium. Commission of the European Communities, Luxembourg
Lauwerys RR, Buchet JP, Roels HA (1976) The relationship between cadmium exposure or body-burden and the concentration of cadmium in blood and urine in man. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 36:275–285
Lauwerys RR, Roels H, Bernard A, Buchet JP (1980) Renal responses to cadmium in a population living in a nonferrous smelter area in Belgium. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 45:271
Lauwerys RR, Bernard A, Roels H, Buchet JP (1982) Health surveillance of workers exposed to cadmium: biological monitoring of exposure and early detection of health effects. International Workshop on Biological Indicators on Cadmium Exposure Diagnostic and Analytical Reliability, Luxembourg
Lewis GP, Jusko WJ, Coughlin LL (1972) Cadmium accumulation in man: influence of smoking, occupation, alcoholic habit and disease. J Chron Dis 25:717–726
McLellan JS, Thomas BJ, Fremlin HH, Harvey TC (1975) Cadmium - its in vivo detection in man. Phys Med Biol 20:88–95
Nordberg GF (ed) (1976) Effects and dose-response, relationships of toxic metals. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Östergaard K (1977) The concentration of cadmium in renal tissue from smokers and nonsmokers. Acta Med Scand 202:193–195
Roels HA, Bernard A, Buchet JP, Goret A, Lauwerys R, Chettle DR, Harvey TC, Haddad IA (1979) Critical concentration of cadmium in renal cortex and urine. Lancet 1979:221
Roels HA, Lauwerys RR, Buchet JP, Bernard A, Chattle DR, Harvey TC, Al-Haddad IK (1981) In vivo measurement of liver and kidney cadmium in workers exposed to this metal: its significance with respect to cadmium in blood and urine. Environ Res 26: 217–240
Roels HA, Lauwerys RR, Dardenne AN (1983) The critical level of cadmium in human renal cortex: a re-evaluation. Toxicol Lett 15: 357–360
Schaller KH, Schneider L, Hall G, Valentin H (1984) Cadmium-Gehalt im Vollblut bei Bewohnern verschiedener Regionen des Freistaates Bayern. Zbl Bakt Hyg I [Abt Org B] 178:446–463
Scherer G, Barkemeyer H (1983) Cadmium concentrations in tobacco and tobacco smoke. Ecotox Environ Safety 7:71–78
Shuman MS, Voors AW, Gallagher PN (1974) Contribution of cigarette smoking to cadmium accumulation in man. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 12:570–576
Stöppler M (1984) Cadmium. In: Merian E (ed) Metalle in der Umwelt. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 527–560
Syversen TLM, Stray TK, Syversen GB, Ofstad J (1976) Cadmium and zinc in human liver and kidney. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 36:251–256
Thürauf J, Schaller KH, Valentin H, Weltke D (1981) Zur gegenwärtigen Belastung der Bevölkerung mit Cadmium. Fortschr Med 99:1312–1317
UBA, Umweltbundesamt (1977) Luftqualitätskriterien für Cadmium. Berichte 4/77, Berlin
Vahter M (ed) (1982) Assessment of human exposure to lead and cadmium through biological monitoring. Report prepared for United Nations Environment Programme and World Health Organization. National Swedish Institute of Environmental Medicine and Karolinska Institute [Department of Environmental Hygiene] Stockholm, Sweden
Vartsky D, Ellis KJ, Chen NS, Cohn SH (1977) A facility for in vivo measurement of kidney and liver cadmium by neutron capture prompt gamma ray analysis. Phys Med Biol 22:1085–1096
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Drasch, G., Kauert, G. & von Meyer, L. Cadmium body burden of an occupationally non burdened population in southern Bavaria (FRG). Int Arch Occup Environ Health 55, 141–148 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378376
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378376