Summary
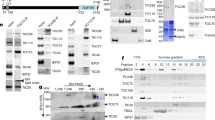
The ADP/ATP translocator is an abundant protein of the mitochondrial inner membrane, which in fungi and mammals is synthesized without a presequence. Here we report that the translocator from potato has an amino-terminal extension which may function in mitochondrial targeting. Several cDNA clones encoding the nucleotide sequence of the ADP/ATP translocator have been isolated from potato leaf and tuber cDNA libraries constructed in lambda phages. Only one class of cDNA clones was found but possibly different translocator genes are expressed in other tissues. High levels of transcripts for the translocator are found in all tissues analysed. Sequence determination of the complete insert of one of the clones reveals a long open reading frame of 1158 bp encoding a protein of 386 amino acids corresponding to a calculated molecular weight of 42 kDa. In contrast, the ADP/ATP translocator proteins from fungi and mammals are significantly smaller. Comparison of the Neurospora translocator with the potato protein shows about 75% sequence homology, being confined to the region after amino acid 85 of the potato polypeptide. Antibodies directed against the fungal translocator recognize a protein of 30 kDa in the inner membrane of potato mitochondria, suggesting that the mature protein has a similar size as the translocators from fungi and mammals. Thus, the additional segment of the potato ADP/ATP translocator forms an amino-terminal extension which may be involved in the import of the protein into plant mitochondria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian GS, McCammon MT, Montgomery DL, Douglas MG (1986) Mol Cel Biol 6:626–634
Amasino RM (1986) Anal Biochem 152:304–307
Arends H, Sebald W (1984) EMBO J 3:377–382
Aquila H, Misra D, Eulitz M, Klingenberg M (1982) Hoppe-Seyler's Physiol Chem 363:345–349
Baker A, Leaver CJ, (1985) Nucleic Acids Res 13:5857–5867
Bathgate B, Baker A, Leaver CJ (1989) Eur J Biochem 183:303–310
Battini R, Ferrari S, Kaczmarek L, Calabretta B, Chen S, Baserga R (1987) J Biol Chem 262:4355–4359
Boutry M, Chua NH (1985) EMBO J 4:2159–2165
Braun HP, Emmermann M, Schmitz UK (1991) Mol Gen Genet (in press)
Conzens AL, Runswick MJ, Walker JE (1989) J Mol Biol 206:261–280
Dale RMK, McClure BA, Houchins JP (1985) Plasmid 13:31–40
Dean C, Tamaki S, Dunsmuir P, Mitchell F, Katayama C, Dooner H, Bedbrook J (1986) Nucleic Acids Res 14:2229–2240
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Gietl C, Lehnerer M, Olsen O (1990) Plant Mol Biol 14:1019–1030
Hackenberg H, Klingenberg M (1980) Biochem 19:548–555
Hackenberg H, Riccio P, Klingenberg M (1978) Eur J Biochem 88:373–378
Hartl FU, Pfanner N, Nicholson DW, Neupert W (1989) Biochim Biophys Acta 988:1–45
Huynh TV, Young RA, Davis RW (1985) In: Glover DM (ed) DNA cloning, vol 1. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 49–78
Jones JDG, Dunsmuir P, Bedbrook J (1985) EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Joshi CP (1987) Nucleic Acids Res 15:9627–9640
Klingenberg M (1979) Trends Biochem Sci 4:249–252
Klingenberg M (1981) Nature 290:449–454
Ku D-H, Kagan J, Chen S-T, Chang C-D, Baserga R, Wurzel J (1990) J Biol Chem 265:16060–16063
Laemmli UK (1970) Nature 227:680–685
Lawson JE, Douglas MG (1988) J Biol Chem 263:14812–14818
Nakagawa T, Maeshima M, Nakamura K, Asahi T (1990) Eur J Biochem 191:557–561
Neckelmann N, Li K, Wade RP, Shuster R, Wallace DC (1987) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:7580–7584
Pfanner N, Hoeben P, Tropschug M, Neupert W (1987) J Biol Chem 262:14851–14854
Runswick MJ, Powell SJ, Nyren P, Walker JE (1987) EMBO J 6:1367–1373
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular Cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson A (1977) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5470
Saraste M, Walker JE (1982) FEBS Lett 144:250–254
Schmitz UK, Lonsdale DM (1989) Plant Cell 1:783–791
Sebald W, Graf T, Lukins HB (1979) Eur J Biochem 93:587–599
Söllner T, Pfaller R, Griffiths G, Pfanner N, Neupert W (1990) Cell 62:107–115
Verner K, Schatz G (1988) Science 241:1307–1313
Vestweber D, Schatz G (1988) J Cell Biol 107:2037–2043
Zimmermann R, Paluch U, Sprinzl M, Neupert W (1979) Eur J Biochem 99:247–252
Zimmermann R, Neupert W (1980) Eur J Biochem 109:217–229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by B. B. Sears
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emmermann, M., Braun, H.P. & Schmitz, U.K. The ADP/ATP translocator from potato has a long amino-terminal extension. Curr Genet 20, 405–410 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317069
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317069