Summary
-
1.
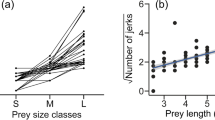
The prey capture efficiency of each individual in a Cyrtophora citricola colony is dependent on time (Fig. 1), total colony size (Fig. 1), and the spider's position within the colony (Fig. 2).
-
2.
Aggressive approaches by orbless individuals within the colony appear to concentrate on the positions within the matrix of webs that have the highest capture efficiency (compare Figs. 2 and 5).
-
3.
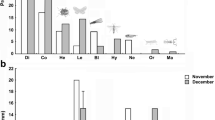
The incidence of avian attempts at predation and/or cleptoparasitism increases directly with colony size (Fig. 4), which indicates that the conspicuousness of the colonies is a disadvantage to the spiders.
-
4.
Resource division is evident in the one mixed-species aggregation observed. Sticky-orb spiders (Leucauge spp.) take the same size prey as C. citricola (Fig. 3), but forage during the day when C. citricola is least active. Tangle-web spiders (Argyrodes spp.) capture prey in significantly smaller size classes than C. citricola capture (Fig. 3).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott, C.G.: Birds caught in spider webs. Condor 33, 169 (1931)
Blanke, R.: Untersuchungen zur Ökophysiologie und Ökethologie von Cyrtophora citricola Forskål (Araneae, Araneidae) in Andalusien. Forma Functio 5, 125–206 (1972)
Brach, V.: Anelosimus studiosus (Araneae: Theridiidae) and the evolution of quasisociality in theridiid spiders. Evolution 31, 154–161 (1977)
Bradoo, B.L.: Life history and bionomics of Idris sp. (Scelionidae: Hymenoptera), egg parasite of Uloborus, a commensal on the web of social spider Stegodyphus sarasinorum Karsch. Zool. Anz. 188, 43–52 (1972)
Bristowe, W.S.: The comity of spiders, Vol. II. London: The Ray Society, Publ. 128, 1941
Burtt, E.H., Jr., Sustare, D., Hailman, J.P.: Cedar waxwing feeding from spider's web. Wilson Bull. 88, 157 (1976)
Buskirk, R.E.: Coloniality, activity patterns and feeding in a tropical orb-weaving spider. Ecology 56, 1314–28 (1975)
Buskirk, R.E.: Sociality in the Arachnida. In: Social insects. Hermann, H.R. (ed.), Vol. II, Chap. 7. New York: Academic (in press) 1979)
Charnov, E.L., Orians, G.H., Hyatt, K.: Ecological implications of resource depression. Am. Nat. 110, 247–59 (1976)
Darchen, R.: Ethologie des quelques araignées sociales l'interattraction, la construction et la chasse. Actes V. Congr. UIEIS, Toulouse 1967, 333–345 (1967)
Exline, H.: A new group, Conopista Karsch 1881 (Theridiidae, Conopisthinae) and three new species from Ecuador and Peru. Trans. Conn. Acad. Arts Sci. 36, 177–189 (1945)
Gibbons, J.D.: Non-parametric methods for quantitative analysis. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston 1976
Kaston, B.J.: Some little known aspects of spider behaviour. Am. Midl. Nat. 73, 336–56 (1965)
Krebs, J.R.: Social learning and the significance of mixed species flocks of chickadees (Parus spp.). Can. J. Zool. 51, 1275–88 (1973)
Kullmann, E.: Beobachtung des Netzbaues und Beiträge zur Biologie von Cyrtophora citricola Forskål (Araneae: Araneidae). Zool. Jahrb. Abt. Syst. Oekol. Geogr. Tiere 86, 181–216 (1958)
Kullmann, E.: Beobachtungen und Betrachtungen zum Verhalten der Theridiide Conopistha argyrodes Walck. (Araneae). Mitt. Zool. Mus. Berlin 35, 275–92 (1959)
Kullmann, E.: Evolution of social behavior in spiders (Araneae; Eresidae and Theridiidae). Am. Zool. 12, 419–26 (1972)
Lubin, Y.D.: Behavioral ecology of tropical tent spiders of the genus Cyrtophora (Araneae: Araneidae), Ph. D. Dissertation, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL (1972)
Lubin, Y.D.: Web structure and function: The non-adhesive orb-web of Cyrtophora moluccensis (Doleschall) (Araneae: Araneidae). Forma Funtio 6, 337–58 (1973)
Lubin, Y.D.: Adaptive advantages and the evolution of colony formation in Cyrtophora (Araneae: Araneidae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 54, 321–39 (1974)
MacKay, G.H.: A spider (Argiope aurantia) and a bird (Astraglinus tristis; Goldfinch). Auk 46, 123–4 (1929)
Morse, D.H.: Ecological aspects of some mixed-species foraging flocks of birds. Ecol. Monogr. 40, 119–68 (1970)
Pearson, D.L.: A pantropical comparison of bird community structure on six lowland forest sites. Condor 79, 232–44 (1977)
Rovner, J.S.: Territoriality in the sheet-web spider Linyphia triangularis (Clerck) (Araneae: Linyphiidae). Z. Tierpsychol. 25, 232–42 (1968)
Schear, W.A.: The evolution of social phenomena in spiders. Bull. Br. Arachnol. Soc. 1, 65–76 (1970)
Vollrath, F.: Konkurrenzvermeidung bei tropischen kleptoparasitischen Haubennetzspinnen der Gattung Argyrodes (Arachnida: Araneae: Theridiidae). Entomol. Germ. 3, 104–108 (1976)
Wallace, G.J.: Winter studies of color-banded chickadees. Bird Banding 12, 49–67 (1941)
Willis, E.O.: Local distribution of mixed flocks in Puerto Rico. Wilson Bull. 85, 75–77 (1973)
Wilson, E.O.: The insect societies. Cambridge: Belknap 1971
Wilson, E.O.: Sociobiology, the new synthesis. Cambridge: Belknap 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rypstra, A.L. Foraging flocks of spiders. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 5, 291–300 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293677
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293677