Abstract
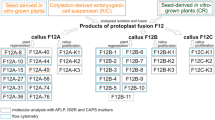
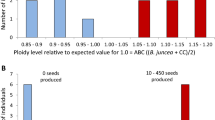
Most of the alloplasmic cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) systems are known to be associated with a number of floral abnormalities that result from nuclear-cytoplasmic incompatibilities. One such system, ‘tour’, which is derived from Brassica tournefortii, induces additional floral abnormalities and causes chlorosis in Brassica spp. While the restorer for this CMS has been reported to be present in B. napus, in B. juncea, where the abnormalities are more pronounced, no restorer has yet been identified. Rectification of these floral abnormalities through mitochondrial recombinations and chloroplast replacement might result in the improvement of this CMS system. As organelle recombinations can possibly be achieved only by somatic cell hybridization, fusion experiments were carried out between hygromycin-resistant B. juncea AABB carrying ‘tour’ cytoplasm and phosphinotricin-resistant, normal B. oleracea CC to generate AABBCC hexaploid somatic hybrids. The presence of selectable marker genes facilitated the selection of hybrids in large numbers. The resulting hybrids showed wide variation in floral morphology and organelle composition. Regenerants with normal, male-sterile flowers having recombinant ‘tour’-or ‘oleracea’-type mitochondria and ‘oleracea’-type chloroplasts were obtained. Hybrids with male-fertile flowers were also obtained that had recombined ‘tour’ mitochondria. The AABBCC hexaploid hybrids synthesized in the present study were successfully utilized as a bridging material for transferring variability in the organelle genome simultaneously to all the digenomic Brassica species, and all of these hybrids are now being stabilized through repeated backcrosses to the allopolyploid crop brassicas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berbec A (1994) Variation among offspring of alloplasmic tobacco Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. ‘Zamojska 4’ with the cytoplasm of N. knightiana Goodspeed. Theor Appl Genet 89:127–132
Bonnett HT, Kofer W, Hakansson G, Glimelius K (1991) Mitochondrial involvement in petal and stamen development studied by sexual and somatic hybridization of Nicotiana species. Plant Sci 80:119–130
Brown GG, Bussey H, Des Rosiers LJ (1986) Analysis of mitochondrial DNA, chloroplast DNA, and double-stranded RNA in fertile and cytoplasmic male-sterile sunflower (Helianthus annuus). Can J Genet Cytol 28:121–129
Crouzillat D, de la Canal L, Perrault A, Ledoigt G, Vear F, Serieys H (1991) Cytoplasmic male sterility in sunflower: comparison of molecular biology and genetic studies. Plant Mol Biol 16:415–426
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant molecular DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Edwardson JR (1970) Cytoplasmic male sterility. Bot Rev 36:341–420
Hanson MR, Pruitt KD, Nivision HT (1989) Male sterility loci in plant mitochondrial genomes. Oxford Surv Plant Mol Cell Biol 6:61–85
Kaul MLH (1988) Male sterility in higher plants. In: Monographs on theoretical and applied genetics, vol. 10. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1005
Kofer W, Glimelius K, Bonnett HT (1991) Modifications of mitochondrial DNA cause changes in floral development in homeotic-like mutants of tobacco. Plant Cell 3:759–769
Kyozuka, J, Kaneda T, Shimamoto K (1989) Production of cytoplasmic male sterile rice (Oryza sativa L.) by cell fusion. Biotechnology 7:1171–1174
Leclercq P (1969) Une sterlite male cytoplasmique chez le tournesol. Ann Amel Plant 19:99–106
Leclercq P (1984) Identification de genes de restauration de fertilite sur cytoplasmes sterilisants chez le tournesol. Agronomie 4:573–576
Mekiyanon S, Kaneko Y, Matsuzawa Y (1994) A new petaloid-type male sterility in alloplasmic Brassica campestris L. Cruciferae Newsl 16:91
Moneger F, Smart CJ, Leaver CJ (1994) Nuclear restoration of cytoplasmic male sterility in sunflower is associated with the tissue-specific regulation of a novel mitochondrial gene. EMBO J 13:8–17
Mukhopadhyay A, Topfer R, Pradhan AK, Sodhi YS, Steinbiss HH, Schell J, Pental D (1991) Efficient regeneration of Brassica oleracea hypocotyl protoplasts and high frequency genetic transformation by direct DNA uptake. Plant Cell Rep 10:375–379
Mukhopadhyay A, Arumugam N, Pradhan AK, Murthy HN, Yadav BS, Sodhi YS, Pental D (1994) Somatic hybrids with substitution type genomic configuration TCBB for the transfer of nuclear and organelle genes from Brassica tournefortii TT to allotetraploid oil seed crop B. carinata BBCC. Theor Appl Genet 89:19–25
Nagy JJ, Maliga P (1976) Callus induction and plant regeneration from mesophyll protoplasts of Nicotiana sylvestris. Z Pflanzenphysiol 78:453–455
Pelletier G, Primard C, Vedel F, Chetrit P, Remy R, Rousselle P, Renard M (1983) Intergeneric cytoplasmic hybridization in Cruciferae by protoplast fusion. Mol Gen Genet 191:244–250
Pelletier G, Primard C, Ferault M, Vedal F, Chetrit P, Renard M, Delourme R (1988) Use of protoplasts in plant breeding: cytoplasmic aspects. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 12:173–180
Pental D, Pradhan AK, Sodhi YS, Mukhopadhyay A (1993) Variation amongst Brassica juncea for regeneration from hypocotyl and optimization of conditions for Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. Plant Cell Rep 12:462–467
Pradhan AK, Mukhopadhyay A, Pental D (1991) Identification of putative cytoplasmic donor of a CMS system in Brassica juncea. Plant Breed 106: 204–208
Pradhan AK, Prakash S, Mukhopadhyay A, Pental D (1992) Phylogeny of Brassica and allied genera based on variation in chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA patterns: molecular and taxonomic classifications are incongruous. Theor Appl Genet 85:331–340
Prakash S, Chopra VL (1988) Synthesis of alloplasmic Brassica campestris as a new source of cytoplasmic male sterility. Plant Breed 101:253–255
Prakash S, Chopra VL (1990) Male sterility caused by cytoplasm of Brassica oxyrrhina in B. campestris and B. juncea. Theor Appl Genet 79:285–287
Rao GU, Batra-Sarup V, Prakash S, Shivanna KR (1994) Development of a new cytoplasmic male sterility system in Brassica juncea through wide hybridization. Plant Breed 112:171–174.
Sand SA, Christoff GT (1973) Cytoplasmic-chromosomal interactions and altered differentiation in tobacco. J Hered 64: 24–30
Siculella L, Palmer JD (1988) Physical and gene organization of mitochondrial DNA in fertile and male sterile sunflower, cms-associated alterations in structure and transcription of the atpA gene. Nucleic Acids Res 16:3787–3799
Sodhi YS, Pradhan AK, Verma JK, Arumugam N, Mukhopadhyay A, Pental D (1994) Identification and inheritance of fertility restorer genes for ‘tour’ CMS in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Plant Breed 112:223–227
Stiewe G, Robbelen G (1994) Establishing cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica napus by mitochondrial recombination with B. tournefortii. Plant Breed 113: 294–304
Vedel F, Pla M, Vitart, V, Gutierres S, Chetrit P, De Paepe R (1994) Molecular basis of nuclear and cytoplasmic male sterility in higher plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 32:601–618
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by D. R. Pring
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugam, N., Mukhopadhyay, A., Gupta, V. et al. Synthesis of hexaploid (AABBCC) somatic hybrids: a bridging material for transfer of ‘tour’ cytoplasmic male sterility to different Brassica species. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 92, 762–768 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226099
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226099