Abstract
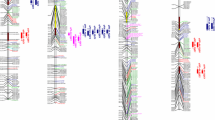
A linkage map of the rapeseed genome comprising 204 RFLP markers, 2 RAPD markers, and 1 phenotypic marker was constructed using a F1 derived doubled haploid population obtained from a cross between the winter rapeseed varieties ‘Mansholt's Hamburger Raps’ and ‘Samourai’. The mapped markers were distributed on 19 linkage groups covering 1441 cM. About 43% of these markers proved to be of dominant nature; 36% of the mapped marker loci were duplicated, and conserved linkage arrangements indicated duplicated regions in the rapeseed genome. Deviation from Mendelian segregation ratios was observed for 27.8% of the markers. Most of these markers were clustered in 7 large blocks on 7 linkage groups, indicating an equal number of effective factors responsible for the skewed segregations. Using cDNA probes for the genes of acyl-carrier-protein (ACP) and β-ketoacyl-ACP-synthase I (KASI) we were able to map three and two loci, respectively, for these genes. The linkage map was used to localize QTLs for seed glucosinolate content by interval mapping. Four QTLs could be mapped on four linkage groups, giving a minimum number of factors involved in the genetic control of this trait. The estimated effects of the mapped QTLs explain about 74% of the difference between both parental lines and about 61.7 % of the phenotypic variance observed in the doubled haploid mapping population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arondel V, Lemieux B, Hwang I, Gibson S, Goodman HM, Somervill CR (1992) Map-based cloning of a gene controlling omega-3 fatty acid desaturation in Arabidopsis. Science 258:1353–1355
Ashikawa I, Kurata N, Nagamura Y, Minobe Y (1993) Cloning of telomere-associated sequences from rice. In: Caligari P, Bond E (eds) Seventeenth Int Congr Genet, abstr. pp 184, the Quadgraphics Partnership, Thatchans, UK
Attia T, Röbbelen G (1986) Cytogenetic relationship within cultivated Brassica analyzed in amphihaploids from the three diploid ancestors. Can J Genet Cytol 28:323–329
Barone A, Ritter E, Schachtschabel U, Debener T, Salamini F, Gebhardt C (1990) Localization by restriction fragment length polymorphism mapping in potato of a major dominant gene conferring resistance to the potato cyst nematode Globodera rostochiensis. Mol Gen Genet 224:177–182
Bernatzky R, Tanksley SD (1986) Toward a saturated linkage map in tomato based on isozymes and random cDNA sequences. Genetics 112:887–898
Bonierbale MW, Plaisted RL, Tanksley SD (1988) RFLP maps based on a common set of clones reveal modes of chromosomal evolution in potato and tomato. Genetics 120:1095–1103
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RV (1980) Construction of a genetic map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Chew FS (1988) Biological effects of glucosinolates. In: Cutler HG (ed). Biologically active natural products — potential use in agriculture. ACS Symposium Series, Washington D.C. 380, pp 155–181
Chyi Y-S, Hoenecke ME, Sernyk JL (1992) A genetic linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci for Brassica rape (syn. campestris). Genome 35:746–757
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:266–267
Figdore SS, Kennard WC, Song KM, Slocum MK, Osborn TC (1988) Assessment of the degree of restriction fragment length polymorphism in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 75:833–840
Foisset N, Delourme R, Lucas MO, Renard M (1993) Segregation analysis of isozyme markers on isolated microspore-derived embryos in Brassica napus L. Plant Breeding 110:315–322
Giovannoni JJ, Wing RA, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD (1991) Isolation of molecular markers from specific chromosomal intervals using DNA pools from existing mapping populations. Nucleic Acids Res 19:6553–6558
Gland A (1985) Inheritance of content and pattern of glucosinolates in combinations of resynthesized rapeseedxrapeseed cultivars. In: Sorensen H (ed) Advances in the production and utilization of cruciferous crops. Proc Sem CEC Programme Res Plant Protein Improve. Copenhagen, pp 278–285
Guiderdoni E, Glazsmann JC, Courtois B (1991) Gametic selection in anther culture of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 81:406–412
Haley CS, Knott SA (1992) A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69:315–324
Heun M (1992) Mapping quantitative powdery mildew resistance of barley using a restriction fragment length polymorphism map. Genome 35:1019–1025
Hosaka K, Kianian SF, McGrath JM, Quiros CF (1990) Development and chromosomal localization of genome-specific DNA markers of Brassica and the evolution of amphidiploids and n=9 diploid species. Genome 33:131–142
Jung C, Kleine M, Fischer F, Herrmann RG (1990) Analysis of DNA from a Beta procumbens chromosome fragment in sugar beet carrying a gene for nematode resistance. Theor Appl Genet 79:663–672
Kianian SF, Quiros CF (1992) Generation of a Brassica oleracea composite RFLP map: linkage arrangements among various populations and evolutionary implications. Theor Appl Genet 84:544–554
Kishimoto N, Foolad MR, Shimosaka E, Matsuura S, Saito A (1993) Alignment of molecular and classical linkage maps of rice, Oryza sativa. Plant Cell Rep 12:457–461
Kleinhofs A, Kilian A, Maroof MAS, Biyashev RM, Hayes P, Chen FQ, Lapitan N, Fenwick A, Blake TK, Kanazin V, Ananiev E, Dahleen L, Kudrna D, Bollinger J, Knapp SJ, Liu B, Sorrells M, Heun M, Franckowiak JD, Hoffman D, Skadsen R, Steffenson BJ (1993) A molecular, isozyme and morphological map of the barley (Hordeum vulgare) genome. Theor Appl Genet 86:705–712
Klein-Lankhorst R, Rietveld P, Machiels B, Verkerk R, Weide R, Gebhardt C, Koornneef M, Zabel P (1991) RFLP markers linked to the root knot nematode resistance gene Mi in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 81:661–667
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Landry BS (1992) A genetic map for Brassica oleracea based on RFLP markers detected with expressed DNA sequences and mapping of resistance genes to race 2 of Plasmodiophora brassicae (Woronin). Genome 35:409–420
Landry BS, Hubert N, Etoh T, Harada JJ, Lincoln SE (1991) A genetic map for Brassica napus based on restriction fragment length polymorphisms detected with expressed DNA sequences. Genome 34:543–552
Lein K-A (1972) Genetische und physiologische Untersuchungen zur Bildung von Glucosinolaten in Rapssamen I. Zur Vererbung der Glucosinolatarmut. Z Pflanzenzuecht 67:243–256
Lukaszewski AJ (1992) A comparison of physical distribution of recombination in chromosome 1R in diploid rye and in hexaploid triticale. Theor Appl Genet 83:1048–1053
Lukaszewski AJ, Curtis CA (1993) Physical distribution of recombination in B-genome chromosomes of tetraploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 86:121–127
Martin GB, Williams JGK, Tanksley SD (1991) Rapid identification of markers linked to a Pseudomonas resistance gene in tomato by using random primers and near-isogenic lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:2336–2340
Martin GB, Brommonschenkel SH, Chunwongse J, Frary A, Ganal MW, Spivey R, Wu T, Earle ED, Tanksley SD (1993) Map-based cloning of a protein kinase gene conferring disease resistance in tomato. Science 262:1432–1436
Mather K The measurement of linkage in heredity, 2nd edn. Methuen and Co, London
Mithen RF, Lewis BG, Fenwick GR (1986) In vitro activity of glucosinolates and their products against Leptosphaeria maculans. Trans Br Mycol Soc. 87:433–440
Mou T, Liu H (1988) Genetic studies on the total glucosinolate content in seeds of rape (Brassica napus L.). Cruci. Newsl 13:52–53
Orton TJ, Browers MA (1985) Segregation of genetic markers among plants regenerated from cultured anthers of broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. ‘italica’). Theor Appl Genet 69:637–643
Paterson AH, Damon S, Hewitt JD, Zamir D, Rabinowitch HD, Lincoln SE, Lander ES, Tanksley SD (1991) Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits in tomato: comparison across species, generations, and environments. Genetics 127:181–197
Pillen K, Steinrücken G, Wricke G, Herrmann RG, Jung C (1992) A linkage map of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 84:129–135
Prakash S, Hinata K (1980) Taxonomy, cytogenetics and origin of crop Brassica, a review. Opera Bot 55:1–57
Quiros CF, Hu J, This P, Chevre AM, Delseny M (1991) Development and chromosomal localization of genome-specific markers by polymerase chain reaction in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 82:627–632
Reinhardt T-C (1992) Entwicklung und Anwendung von Nah-Infrarot-spektroskopischen Methoden für die Bestimmung von Öl-, Protein-, Glucosinolat-, Feuchte- und Fettsäure-Gehalten in intakter Rapssaat. PhD thesis, University of Göttingen. Cuvillier Verlag, Göttingen
Richards EJ, Ausubel FM (1988) Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 53:127–136
Röbbelen G (1960) Beiträge zur Analyse des Brassica-Genoms. Chromosoma 11:205–228
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1988): Extraction of DNA from plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol Manual A6:1–10.
Rücker B (1993) Genetische Analyse von Qualitäts- und Ertragsmerkmalen bei Winterraps (Brassica napus L.) unter besonderer Berücksichtigung des Glucosinolatgehalts der Samen. PhD thesis, University of Göttingen. Cuvillier Verlag, Göttingen
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Slocum MK, Figdore SS, Kennard WC, Suzuki JY, Osborn TC (1990) Linkage arrangement of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci in Brassica oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 80:57–64
Song K, Osborn TC (1992) Polyphyletic origins of Brassica napus. New evidence based on organelle and nuclear RFLP analyses. Genome 35:992–1001
Song KM, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1988a) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). 1. Genome evolution of diploid and amphidiploid species. Theor Appl Genet 75:784–794
Song KM, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1988b) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). 2. Preliminary analysis of subspecies within B. rapa (syn. campestris) and B. oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 76:593–600
Song K, Osborn TC, Williams PH (1990) Brassica taxonomy based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). 3. Genome relationships in Brassica and related genera and the origin of B. oleracea and B. rapa (syn. campestris). Theor Appl Genet 79:497–506
Song KM, Suzuki JY, Slocum MK, Williams PH, Osborn TC (1991) A linkage map of Brassica rapa (syn. campestris) based on restriction fragment length polymorphism loci. Theor Appl Genet 82:296–304
Tanksley SD, Bernatzky R, Lapitan NL, Prince JP (1988) Conservation of gene repertoire but not gene order in pepper and tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:6419–6423
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB, Messeguer R, Miller JC, Miller L, Paterson AH, Pineda O, Röder MS, Wing RA, Wu W, Young ND (1992) High-density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Thompson DM, Chalmers K, Waugh R, Forster BP, Thomas WTB, Caligari PDS, Powell W (1991) The inheritance of genetic markers in microspore-derived plants of barley Hordeum vulgare L. Theor Appl Genet 81:487–492
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uzunova, M., Ecke, W., Weissleder, K. et al. Mapping the genome of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). I. Construction of an RFLP linkage map and localization of QTLs for seed glucosinolate content. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 90, 194–204 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222202
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00222202