Summary
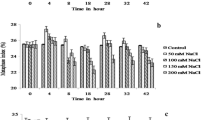
Roots of detopped tobacco plants (Nicotiana tabacum var. Virginia Gold) were exposed to Na, K, and Ca salts or to water, and cation transfer to xylem vessels was measured. In some cases plants had been exposed to Na in addition to regular nutrient solutions before detopping. Calcium in the external medium greatly depressed the transport of Na from the external medium to the xylem vessels and it often stimulated the transfer of K from the external medium to the xylem vessels. The K/Na ratio in the exudate thus was dependent upon the Ca content of the external medium under these conditions. In contrast, externally applied Ca or Ca deficiency had very little effect on the transfer of preaccumulated K and Na from compartments within roots to the xylem vessels. The K/Na ratio in the exudate under these conditions was not related to Ca levels nor to mild Ca deficiency. The ratios decreased with time after detopping regardless of Ca level. Intact plants accumulated more Na than did root systems of detopped plants in a 6-day period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ElZam, C. E., Interactions between sodium, potassium and calcium in their absorption by intact barley plants. Abstr. 6th Intern. Colloqium, Israel (1970).
Epstein, E., Mineral metabolism. In: Plant Biochemistry, edited by J. Bonner and J. E. Varner, New York, pp. 438–466 (1965).
Epstein, E., Dual pattern of ion absorption by plant cells and by plants. Nature 212, 1324–1327 (1966).
Jarvis, P. and House, C. R., Evidence for symplasmic ion transport in maize roots. J. Exp. Botany 21, 83–90 (1970).
Laties, G. G., Dual mechanisms of salt uptake in relation to compartmentation and long-distance transport. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 20, 89–166 (1969).
Leo, M. W. M., A.Wallace and Claricia B.Joven, Root pressure exudation in tobacco. Advances Frontier Plant Sci. 21, 45–90 (1968).
Pearson, G. A., Absorption and translocation of sodium in beans and cotton. Plant Physiol 42 1171–1175 (1967).
Vaadia, Y., Autonomic diurnal fluctuations in rate of exudation and root pressure of decapitated sunflower plants. Physiology 13, 701–717 (1960).
Wallace, A., Ashcroft, R. T., and Lunt, O. R., Root pressure exudation in tobacco. II. The osmometer theory of exudation. In: Current Topics in Plant Nutrition, edited by A. Wallace, Los Angeles pp. 136–143 (1966).
Wallace, A., Soufi, S. M., and Hemaidan, N., Day-night differences in accumulation and translocation of ions by tobacco plants. Plant Physiol. 41, 102–104 (1966).
Wallace, A., Ashcroft, R. T. and Lunt, O. R., Day-night periodicity of exudation in detopped tobacco. Plant Physiol. 42, 238–242 (1967).
Wallace, A. and Romney, E. M., Some interactions of Ca, Sr, and Ba in plants. Agron. J. 63, 245–248 (1971).
Wallace, Arthur, Effect of temperature on K and Ca transport from within the root to the xylem exudate of tobacco. Plant and Soil (in press).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Riverside University of CaliforniaSoil Science and Agricultural Engineering
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallace, A., Abou-Zamzam, A.M. & Cha, J.W. Effect of calcium on transport of cations to the xylem exudate of tobacco. Plant Soil 38, 41–48 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011216
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011216