Abstract
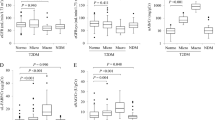
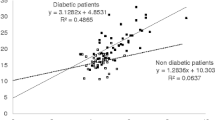
HbA1c and glycated albumin (GA) levels are affected not only by plasma glucose levels but also by hemoglobin metabolism and albumin metabolism, respectively. Thus, HbA1c and GA for patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN), with progression of DN stage, are assumed to be affected by renal anemia and proteinuria, respectively. In this investigation, the GA/HbA1c ratio (G/H ratio) was evaluated and compared for DN patients at different stages. This study included 286 patients with diabetes mellitus (DN stage 1, 149; stage 2, 81; stage 3, 30; stage 4, 19; stage 5, 7), for whom HbA1c and GA were measured simultaneously. Patients with malignant diseases, chronic liver diseases, or thyroid disorders, and those with systemic corticosteroid use were excluded. The G/H ratio for DN stage 3 patients was significantly lower than for DN stage 1 patients, and it was significantly higher for DN stage 5 patients than for DN stage 1 patients. For all DN stage 4 patients, the G/H ratio did not differ significantly from that for patients with DN stage 1 and stage 2, but it was significantly higher for patients with anemia and lower for patients with marked proteinuria. In conclusion, for assessment of glycemic control status, HbA1c might be preferable for DN stage 4 patients without severe anemia and for DN stage 3 patients, whereas GA might be preferable for DN stage 4 patients without massive proteinuria and for DN stage 5 patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen MP. Nonenzymatic glycation: a central mechanism in diabetic microvasculopathy? J Diabet Complications. 1998;2:214–7.
Koenig RJ, Peterson CM, Jones RL, Saudek C, Lehrman M, Cerami A. Correlation of glucose regulation and hemoglobin AIc in diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1976;295:417–20.
Bunn HF, Gabbay KH, Gallop PM. The glycosylation of hemoglobin: relevance to diabetes mellitus. Science. 1978;20:21–7.
Jeffcoate SL. Diabetes control and complications: the role of glycated haemoglobin, 25 years on. Diabet Med. 2004;21:657–65.
Bry L, Chen PC, Sacks DB. Effects of hemoglobin variants and chemically modified derivatives on assays for glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem. 2001;47:153–63.
Koga M, Kasayama S. Clinical impact of glycated albumin as another glycemic control marker. Endocr J. 2010;57:751–62.
Takahashi S, Uchino H, Shimizu T, Kanazawa A, Tamura Y, Sakai K, et al. Comparison of glycated albumin (GA) and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in type 2 diabetic patients: usefulness of GA for evaluation of short-term changes in glycemic control. Endocr J. 2007;54:139–44.
Guthrow CE, Morris MA, Day JF, Thorpe SR, Baynes JW. Enhanced nonenzymatic glucosylation of human serum albumin in diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1979;76:4258–61.
Okada T, Nakao T, Matsumoto H, Nagaoka Y, Tomaru R, Iwasawa H, Wada T. Influence of proteinuria on glycated albumin values in diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Intern Med. 2011;50:23–9.
Chujo K, Shima K, Tada H, Oohashi T, Minakuchi J, Kawashima S. Indicators for blood glucose control in diabetics with end-stage chronic renal disease: GHb vs. glycated albumin (GA). J Med Invest. 2006;53:223–8.
Inaba M, Okuno S, Kumeda Y, Yamada S, Imanishi Y, Tabata T, et al. Glycated albumin is a better glycemic indicator than glycated hemoglobin values in hemodialysis patients with diabetes: effect of anemia and erythropoietin injection. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:896–903.
Peacock TP, Shihabi ZK, Bleyer AJ, Dolbare EL, Byers JR, Knovich MA, et al. Comparison of glycated albumin and hemoglobin A1c levels in diabetic subjects on hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2008;7:1062–8.
Koga M, Otsuki M, Matsumoto S, Saito H, Mukai M, Kasayama S. Negative association of obesity and its related chronic inflammation with serum glycated albumin but not glycated hemoglobin levels. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;378:48–52.
Bando Y, Kanehara H, Toya D, Tanaka N, Kasayama S, Koga M. Association of serum glycated albumin to glycated haemoglobin A1c ratio with hepatic function tests in patients with chronic liver disease. Ann Clin Biochem. 2009;46:368–72.
Krolewski AS, Laffel LM, Krolewski M, Quinn M, Warram JH. Glycosylated hemoglobin and the risk of microalbuminuria in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1251–5.
Schnedl WJ, Lahousen T, Wallner SJ, Krause R, Lipp RW. Silent hemoglobin variants and determination of HbA1c with the high-resolution program of the HPLC HA-8160 hemoglobin analyzer. Clin Biochem. 2005;38:88–91.
The Committee of Japan Diabetes Society on the diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. Report of the Committee on the classification and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Invest. 2010;1:212–28.
Kouzuma T, Usami T, Yamakoshi M, Takahashi M, Imamura S. An enzymatic method for the measurement of glycated albumin in biological samples. Clin Chim Acta. 2002;324:61–71.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Koga, M., Murai, J., Saito, H. et al. Evaluation of the glycated albumin/HbA1c ratio by stage of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetol Int 2, 141–145 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-011-0033-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-011-0033-z