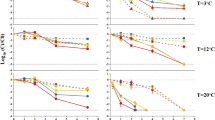
Abstract
Limestone aquifers provide the main drinking water resources of southern Italy. Due to cattle grazing and/or manure spreading, these aquifers are often characterized by microbial contamination of groundwater. The aim of this paper is to summarize the results obtained during a 10-year research carried out in experimental field sites in southern Italy, analyzing (1) the influence of the topsoil of pyroclastic origin on the migration of microbial cells from the ground towards the groundwater, and then on the groundwater vulnerability, (2) the influence of the rainfall regime on the breakthrough at the springs, (3) the reliability of thermotolerant coliforms and fecal enterococci as bacterial indicators of microbial contamination, and (4) the effectiveness of microorganisms as natural tracers for some hydrogeological purposes. The results obtained showed that fecal enterococci are a more reliable indicator than thermotolerant coliforms for detecting contamination and that the entity and distribution over time of microbial contamination of fecal origin are influenced by several factors, such as precipitation regime, thermal regime and existence and thickness of the topsoil of pyroclastic origin. Moreover, the migration of a significant amount of bacterial cells through the topsoil and the underlying carbonate rocks allows the utilization of microorganisms as effective natural tracers, to be coupled with other classic tracers to study the recharge and the flow processes. In a broader perspective, these results can be used to optimize the investigations in other hydrogeological scenarios, with emphasis on those where different water types coexist and interact in same aquifer systems.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott S, Caughley B, Scott G (1998) Evaluation of enterolert for the enumeration of enterococci in the marine environment. N Z J Mar Freshw Res 32:505–513
Agosta F, Aydin A (2006) Architecture and deformation mechanism of a basin-bounding normal fault in Mesozoic platform carbonates, central Italy. J Struct Geol 28:1445–1467
Allocca V, Celico F, Petrella E, Marzullo G, Naclerio G (2008) The role of land use and environmental factors on microbial pollution of mountainous limestone aquifers. Environ Geol 55:277–283
Andreo B, Liñán C, Carrasco F, Jiménez de Cisneros C, Caballero F, Mudry J (2004) Influence of rainfall quantity on the isotopic composition (18O and 2H) of water in mountainous areas. Application for groundwater research in the Yunquera-Nieves karst aquifers (S Spain). Appl Geochem 19:561–574
Antonellini M, Aydin A (1994) Effect of faulting on fluid flow in porous sandstones: petrophysical properties. AAPG Bull 78:355–377
Aquilina L, Ladouche B, Dorfliger N (2006) Water storage and transfer in the epikarst of karstic systems during high flow periods. J Hydrol 327:472–485
ASTM (2006) Standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (Unified Soil Classification System), ASTM D 2487, ASTM International
Barbosa TM, Serra CR, La Ragione RM, Woodward MJ, Henriques AO (2005) Screening for Bacillus isolates in the broiler gastrointestinal tract. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:968–978
Becker MW, Metge DW, Collins SA, Shapiro AM, Harvey RW (2003) Bacterial transport experiments in fractured crystalline bedrocks. Ground Water 41:682–689
Bense VF, Van den Berg EH, Van Balen RT (2003) Deformation mechanisms and hydraulic properties of fault zones in unconsolidated sediments; the Roer Valley Rift System, The Netherlands. Hydrogeol J 11:319–332
Billi A, Salvini F, Storti F (2003) The damage zone faultcore transition in carbonate rocks: implications for fault growth, structure and permeability. J Struct Geol 25:1779–1794
Briancesco R, Bonadonna L (2005) An italian study on Cryptosporidium and Giardia in wastewater, fresh water and treated water. Environ Monit Assess 104:445–457
Bucci A, Naclerio G, Allocca V, Celico P, Celico F (2011) Potential use of microbial community investigations to analyze hydrothermal systems behaviour: the case of Ischia island, southern Italy. Hydrol Process 25:1866–1873
Bucci A, Petrella E, Naclerio G, Gambatese S, Celico F (2014) Bacterial migration through low-permeability fault zones in compartmentalised aquifer systems: a case study in Southern Italy. Int J Speleol 43:273–281
Bucci A, Allocca V, Naclerio G, Capobianco G, Divino F, Fiorillo F, Celico F (2015) Winter survival of microbial contaminants in soil: an in situ verification. J Environ Sci 27:131–138
Caertman ST, La Ragione RM (2004) Spore probiotics as animal feed supplements. In: Ricca E, Henriques AO, Cutting SM (eds) Bacterial spore formers. Probiotics and emerging applications. Horizon Bioscience, Wymondham, pp 155–161
Caine JS, Evans JP, Forster CB (1996) Fault zone architecture and permeability structure. Geology 24:1025–1028
Celico F, Varcamonti M, Guida M, Naclerio G (2004) Influence of precipitation and soil on transport of fecal enterococci in limestone aquifers. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2843–2847
Celico F, Petrella E, Celico P (2006) Hydrogeological behaviour of some fault zones in a carbonate aquifer of Southern Italy: an experimentally based model. Terra Nova 18:308–313
Celico F, Capuano P, De Felice V, Naclerio G (2008) Hypersaline groundwater genesis assessment through a multidisciplinary approach: the case of Pozzo del Sale spring (southern Italy). Hydrogeol J 16:1441–1451
Celico F, Naclerio G, Bucci A, Nerone V, Capuano P, Carcione M, Allocca V, Celico P (2010) Influence of pyroclastic soil on epikarst formation: a test study in southern Italy. Terra Nova 22:110–115
Celle-Jeanton H, Emblanch C, Mudry J, Charmoille A (2003) Contribution of time tracers (Mg2+, TOC, δ13CTDIC, NO3 −) to understand the role of the unsaturated zone. A case study : karst aquifer in the Doubs valley, eastern France. Geophys Res Lett 30:1322
Chester FM, Logan JM (1987) Composite planar fabric of gouge from the Punchbowl fault, California. J Struct Geol 9:621–634
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Easton AD (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Cocolin L, Alessandria V, Dolci P, Gorra R, Rantsiou K (2013) Culture independent methods to assess the diversity and dynamics of microbiota during food fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 167:29–43
Cutting SM (2004) Commercial probiotic products containing Bacillus spores. In: Ricca E, Henriques AO, Cutting SM (eds) Bacterial spore formers. Probiotics and emerging applications. Horizon Bioscience, Wymondham, pp 217–219
Danielopol DL, Griebler C, Gunatilaka A, Notenboom J (2003) Present state and future prospects for groundwater ecosystems. Environ Conserv 30:104–130
Di Gennaro A, Aronne G, De Mascellis R, Vingiani S (2002) I sistemi di terre della Campania (1:250.000). SELCA ed., Firenze
Fairley JP, Hinds JJ (2004) Field observation of fluid circulation patterns in a normal fault system. Geophys Res Lett 31:L19502
FAO (1988) Soil map of the world, revised legend, World Soil Resources Report 60. FAO, Rome
FAO (2006) Guidelines for soil description. FAO, Rome
Farnleitner AH, Wilhartitz I, Ryzinska G, Kirschner AKT, Stadler H, Burtscher MM, Hornek R, Szewzyk U, Herndl G, Mach RL (2005) Bacterial dynamics in spring water of alpine karst aquifers indicates the presence of stable autochthonous microbial endokarst communities. Environ Microbiol 7:1248–1259
Geldenhuys JC, Pretorius PD (1989) The occurrence of enteric viruses in polluted water, correlation to indicator organisms and factors influencing their number. Water Sci Technol 21:105–109
Gleeson C, Gray N (1997) The coliform index and waterborne disease. Spon, London
Goddard JV, Evans JP (1995) Chemical changes and fluid-rock interaction in faults of crystalline thrust sheets, north-western Wyoming, USA. J Struct Geol 17:533–547
Goldscheider N, Hunkeler D, Rossi P (2006) Review: microbial biocenoses in pristine aquifers and an assessment of investigative methods. Hydrogeol J 14:926–941
Griebler C, Mösslacher F (2003) Grundwasser-Ökologie (Ground-water ecology). Facultas UTB, Vienna
Hancock PJ, Boulton AJ, Humphreys WF (2005) Aquifers and hyporheic zone: towards an ecological understanding of groundwater. Hydrogeol J 13:98–111
Harvey RW, Garabedian SP (1991) Use of colloid filtration theory in modeling movement of bacteria through a contaminated sandy aquifer. Environ Sci Technol 25:178–185
Jiang D, Huang Q, Cai P, Rong X, Chen W (2007) Adsorption of Pseudomonas putida on clay minerals and iron oxide. Colloid Surf B 54:217–221
Kani J, Mills D (2000) Recommended methods for the analysis of recreational marine water to comply with AB 411. California Department of Health Services, Environmental Laboratory Accreditation Program and Microbiological Disease Laboratory, Sacramento
Mollema PN, Antonellini M (1999) Development of strikeslip faults in the dolomites of the Sella Group, Northern Italy. J Struct Geol 21:273–292
Mösslacher F, Griebler C, Notenboom J (2001) Biomonitoring of groundwater systems: methods, applications and possible indicators among the groundwater biota. In: Griebler C, Danielopol DL, Gibert J, Nachtnebel HP, Notenboom J (eds) Groundwater ecology: a tool for management of water resources. Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxemburg, pp 132–170
Naclerio G, Petrella E, Nerone V, Allocca V, De Vita P, Celico F (2008) Influence of topsoil of pyroclastic origin on microbial contamination of groundwater in fractured carbonate aquifers. Hydrogeol J 16:1057–1064
Naclerio G, Fardella G, Marzullo G, Celico F (2009a) Filtration of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus cereus spores in a pyroclastic topsoil, carbonate Apennines, southern Italy. Colloid Sur B 70:25–28
Naclerio G, Nerone V, Bucci A, Allocca V, Celico F (2009b) Role of organic matter and clay fraction on migration of Escherichia coli cells through pyroclastic soils, southern Italy. Colloid Surf B 72:57–61
Newman J, Mitra G (1994) Fluid-influenced deformation and recrystallization of dolomite at low temperatures along a natural fault zone, Mountain City window, Tennessee. Geol Soc Am Bull 106:1267–1280
Osaka T, Yoshie S, Tsuneda S, Hirata A, Iwami N, Inamori Y (2006) Identification of acetate- or methanol-assimilating bacteria under nitrate reducing conditions by stable-isotope probing. Microb Ecol 52:253–266
Øvreås L, Forney L, Daae FL, Torsvik V (1997) Distribution of bacterioplankton in meromictic lake Saelenvannet, as determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of PCR-amplified gene fragments coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3367–3373
Petrella E, Celico F (2013) Mixing of water in a carbonate aquifer, southern Italy, analysed through stable isotope investigations. Int J Speleol 42:25–33
Petrella E, Capuano P, Celico F (2007) Unusual behaviour of epikarst in the Acqua dei Faggi carbonate aquifer (Southern Italy). Terra Nova 19:82–88
Petrella E, Falasca A, Celico F (2008) Natural-gradient tracer experiments in epikarst: a test study in the Acqua dei Faggi experimental site, southern Italy. Geofluids 8:159–166
Petrella E, Naclerio G, Falasca A, Bucci A, Capuano P, De Felice V, Celico F (2009a) Non-permanent shallow halocline in a fractured carbonate aquifer, southern Italy. J Hydrol 373:267–272
Petrella E, Capuano P, Carcione M, Celico F (2009b) A high-altitude temporary spring in a compartmentalized carbonate aquifer: the role of low-permeability faults and karst conduits. Hydrol Process 23:3354–3364
Petrella E, Aquino D, Fiorillo F, Celico F (2014) The effect of low-permeability fault zones on groundwater flow in a compartmentalized system. Experimental evidence from a carbonate aquifer (Southern Italy). Hydrol Process, in press
Pronk M, Goldscheider N, Zopfi J (2006) Dynamics and interaction of organic carbon, turbidity and bacteria in a karst aquifer system. Hydrogeol J 14:473–484
Pronk M, Goldscheider N, Zopfi J (2009) Microbial communities in karst groundwater and their potential use for biomonitoring. Hydrogeol J 17:37–48
Rose JB, Darbin H, Gerba CP (1988) Correlation of protozoa, Cryptosporidium and Giardia, with water quality variables in a watershed. Water Sci Technol 20:271–276
Salvini F, Billi A, Wise DU (1999) Strike-slip fault propagation cleavage in carbonate rocks: the Mattinata Fault Zone, Southern Apennines, Italy. J Struct Geol 21:1731–1749
Segadelli S (2014) Hydrogeological behaviour of peridotitic aquifers: the case of Mount Prinzera (northern Apennines, Italy). PhD Thesis, University of Parma, (in Italian)
Shangkuan YH, Yang JF, Lin HC, Shaio MF (2000) Comparison of PCR–RFLP, ribotyping and ERIC–PCR for typing Bacillus anthracis and Bacillus cereus strains. J Appl Microbiol 89:452–462
Storti F, Balsamo F (2010) Impact of ephemeral cataclastic fabrics on laser diffraction particle size distribution analysis in loose carbonate fault breccia. J Struct Geol 32:507–522
Tam NKM, Uyen NQ, Hong HA, Duc LH, Hoa TT, Serra CR, Henriques AO, Cutting SM (2006) The intestinal life cycle of Bacillus subtilis and close relatives. J Bacteriol 188:2692–2700
USDA (1979) Soil conservation service, Engineering Field Manual USDA, SCS
WHO (2006) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 1st Addendum to, 3rd edn. World Health Organization, New York
Wu X-Y, Walker M, Vanselow B, Chao R-L, Chin J (2007) Characterization of mesophilic bacilli in faeces of feedlot cattle. J Appl Microbiol 102:872–879
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bucci, A., Petrella, E., Naclerio, G. et al. Microorganisms as contaminants and natural tracers: a 10-year research in some carbonate aquifers (southern Italy). Environ Earth Sci 74, 173–184 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4043-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4043-1