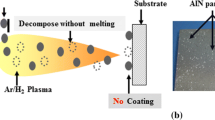
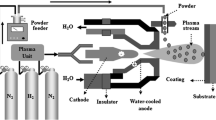
Abstract
Feedstock powder characteristics (size distribution, morphology, shape, specific mass, and injection rate) are considered to be one of the key factors in controlling plasma-sprayed coatings microstructure and properties. The influence of feedstock powder characteristics to control the reaction and coatings microstructure in reactive plasma spraying process (RPS) is still unclear. This study, investigated the influence of feedstock particle size in RPS of aluminum nitride (AlN) coatings, through plasma nitriding of aluminum (Al) feedstock powders. It was possible to fabricate AlN-based coatings through plasma nitriding of all kinds of Al powders in atmospheric plasma spray (APS) process. The nitriding ratio was improved with decreasing the particle size of feedstock powder, due to improving the nitriding reaction during flight. However, decreasing the particle size of feedstock powder suppressed the coatings thickness. Due to the loss of the powder during the injection, the excessive vaporization of fine Al particles and the completing nitriding reaction of some fine Al particles during flight. The feedstock particle size directly affects on the nitriding, melting, flowability, and the vaporization behaviors of Al powders during spraying. It concluded that using smaller particle size powders is useful for improving the nitriding ratio and not suitable for fabrication thick AlN coatings in reactive plasma spray process. To fabricate thick AlN coatings through RPS, enhancing the nitriding reaction of Al powders with large particle size during spraying is required.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.M. Ingo, S. Kaciulis, A. Mezzi, T. Valente, F. Casadei, and G. Gusmano, Characterization of Composite Titanium Nitride Coatings Prepared by Reactive Plasma Spraying, Electrochim. Acta, 2005, 50, p 4531-4537
W. Feng, D. Yan, J. He, X. Li, and Y. Dong, Reactive Plasma Sprayed TiN Coating and its Tribological Properties, Wear, 2005, 258, p 806-811
D.T. Gawne, Y. Bao, and T. Zhang, Plasma-Spray Deposition of Silicon Nitride-Based Coatings, Proc. of the International Thermal Spray Conf., 2001, CD.
S. Thiele, R.B. Heimann, L.-M. Berger, M. Herrmann, M. Nebelung, T. Schnick, B. Wielage, and P. Vuoristo, Microstructure and Properties of Thermally Sprayed Silicon Nitride-Based Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2002, 11(2), p 218-225
M. Yamada, T. Inamoto, M. Fukumoto, and T. Yasui, Fabrication of Silicon Nitride Thick Coatings by Reactive RF Plasma Spraying, Mater. Trans., 2004, 45, p 3304-3308
F. Kassabji, F. Tourenne, A. Derradji, and P. Fauchais, Aluminium and Aluminium Nitride Deposition by Low Pressure Nitrogen Arc Plasma Spraying, Proc. 10th Int. Therm. Spray Conf., 1983, 80, p 82-84
M. Fukumoto, M. Yamada, T. Yasui, and K. Takahashi, Fabrication of Aluminum Nitride Coating by Reactive RF Plasma Spray Process, Proc. of the International Thermal Spray Conf. (ITSC), 2004, CD.
M. Yamada, T. Yasui, M. Fukumoto, and K. Takahashi, Nitridation of Aluminum Particles and Formation Process of Aluminum Nitride Coatings by Reactive RF Plasma Spraying, Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(9), p 4166-4171
M. Yamada, M. Shahien, T. Yasui, and M. Fukumoto, Fabrication of Aluminum Nitride Coating by Atmospheric Plasma Spray, Proc. of the 19th International Symposium on Plasma Chemistry (ISPC19), Bochum, Germany, July 26-31, 2009, USB (P2.11.35).
M. Shahien, M. Yamada, T. Yasui, and M. Fukumoto, Cubic Aluminum Nitride Coating Through Atmospheric Reactive Plasma Nitriding, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(3), p 635-641
M. Yamada, Y. Kouzaki, T. Yasui, and M. Fukumoto, Fabrication of Iron Nitride Coatings by Reactive RF Plasma Spraying, Surf. Coat. Technol, 2006, 201, p 1745-1751
A.W. Wemer, Carbide, Nitride and Boride Materials Synthesis and Processing, Chapman & Hall, London, 1997, p 6-68
H.O. Pierson, Handbook of Refractory Carbides and Nitrides, Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, NJ, 1996, p 237-239
A.W. Weimer, G.A. Cochran, G.A. Eisman, J.P. Henley, B.D. Hook, L.K. Mills, T.A. Guiton, A.K. Knudsen, N.R. Nicholas, J.E. Volmering, and W.G. Moore, Rapid Process for Manufacturing Aluminum Nitride Powder, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1994, 77(3), p 3-18
S. Nakamura, The Roles of Structural Imperfections in InGaN-Based Blue Light-Emitting Diodes and Laser Diodes, Science, 1998, 281, p 956-961
L.R. Krishna, D. Sen, Y.S. Rao, G.V.N. Rao, and G. Sundararajan, Thermal Spray Coating of Aluminum Nitride Utilizing the Detonation Spray Technique, J. Mater. Res., 2002, 17(10), p 2514-2523
B. Kolman, J. Forman, J. Dubsky, and P. Chraska, Homogeneity Studies of Powders and Plasma Sprayed Deposits, Mikrochim. Acta, 1994, 114-115, p 335-342
P. Fauchais, A. Vardelle, and B. Dussoubs, Quo Vadis Thermal Spraying?, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2001, 10(1), p 44-66
A.J. Allen, G.G. Long, H. Boukari, J. Ilavsky, A. Kulkarni, S. Sampath, H. Herman, and A.N. Goland, Microstructure Characterization Studies to Relate the Properties of Thermal-Spray Coatings to Feedstock and Spray Conditions, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2001, 146-147, p 544-552
P. Fauchais, G. Montavan, and G. Bertrand, Influence of Powders on Thermal Spray Coating Structures: Recent Developments in Nano or Finely Structured Coatings and Some Safety Issues, Proc. of the International Thermal Spray Conf. (ITSC), 2009, p 799-817.
P. Fauchais, G. Montavan, and G. Bertrand, From Powders to Thermally Sprayed Coatings, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2010, 19(1-2), p 56-80
M. Wang and L.L. Shaw, Effect of the Powder Manufacturing Method on Microstructure and Wear Performance of Plasma Sprayed Alumina-Titania Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2007, 202, p 34-44
M. Vardelle, A. Vardelle, P. Fauchais, K.-I. Li, B. Dussoubs, and N.J. Themelis, Controlling Particle Injection in Plasma Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2001, 10(2), p 267-284
F.B. Ettouil, O. Mazhorova, B. Pateyron, H. Ageorges, M. El Ganaoui, and P. Fauchais, Predicting Dynamic and Thermal Histories of Agglomerated Particles Injected within a d. C. Plasma Jet, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2008, 202, p 4491-4495
C. Lin and S. Chung, Combustion synthesis of aluminum nitride powder using additives, J. Mater. Res., 2001, 16(8), p 2200-2208
S. Sampath, X.Y. Jiang, J. Matejicek, A.C. Leger, and A. Vardelle, Substrate Temperature Effects on Splat Formation, Microstructure Development and Properties of Plasma Sprayed Coatings Part I: Case Study for Partially Stabilized Zirconia, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, 272, p 181-188
S. Sampath and X. Jiang, Splat Formation and Microstructure Development During Plasma Spraying: Deposition Temperature Effects, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 304-306, p 144-150
H.R. Salimijazi, L. Pershin, T.W. Coyle, J. Mostaghimi, S. Chandra, Y.C. Lau, L. Rosenzweig, and E. Moran, Effect of Droplet Characteristics and Substrate Surface Topography on the Final Morphology of Plasma-Sprayed Zirconia Single Splats, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2007, 16(2), p 291-299
H. Zhang, X.Y. Wang, L.L. Zheng, and S. Sampath, Numerical Simulation of Nucleation, Solidification, and Microstructure Formation in Thermal Spraying, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2004, 47, p 2191-2203
T. Chraska and A.H. King, Transmission Electron Microscopy Study of Rapid Solidification of Plasma Sprayed Zirconia Part I. First Splat Solidification, Thin Solid Films, 2001, 397, p 30-39
P. Duwez, R.H. Willen, and W. Klement, Continuous Series of Metastable Solid Solutions in Silver-Copper Alloys, J. Appl. Phys., 1960, 31, p 1136-1137
D.J. Tilly, J.P.A. Lofvander, and C.G. Levi, Solidification Paths and Carbide Morphologies in Melt Processed MoSi2-SiC In Situ Composites, Metall. Mater. Trans., 1996, 28A, p 1889-1900
M.J. Kramer, H. Mecco, K.W. Dennis, E. Vargonova, R.W. McCallum, and R.E. Napolitano, Rapid Solidification and Metallic Glass Formation—Experimental and Theoretical Limits, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2007, 353, p 3633-3639
J. Kong, Z. Ye, and F. Lv, Non-Equilibrium Solidification Character of Zr56.2Ti13.8Nb5.0Cu6.9Ni5.6Be12.5 Bulk Metallic Glass Composites Containing Ductile Dendrite Phase, J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 478, p 202-205
R.A. Rodriguez-Diaz, L. Banos, O. Novelo, C. Flores, J. Colin, J. Arenas-Alatorre, and J.A. Juarez-Islas, Microstructural Characterization of Fe40Al15Cr (% at.) Intermetallic Alloy Produced by Rapid Solidification, Acta Microsc., 2009, 18(2), p 169-173
I. Kimura, K. Ichiya, M. Ishii, N. Hotta, and T. Kitamura, Synthesis of Fine AlN Powder by a Floating Nitridation Technique Using an N2/NH3 Gas Mixture, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1989, 8, p 303-304
T. Fujii, K. Yoshida, K. Suzuki, and S. Ito, Direct Nitriding of Large Grains of Aluminum with 2 mm Size, Solid State Ionics, 2001, 141-142, p 593-598
M. Radwan and Y. Miyamoto, Growth of Quasi-Aligned AlN Nanofibers by Nitriding Combustion Synthesis, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2007, 90(8), p 2347-2351
M. Vardelle, A. Vardelle, and P. Fauchais, Spray Parameter and Particle Behavior Relationships During Plasma Spraying, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 1993, 2(1), p 79-91
K. Remesh, H.W. Ng, and S.C.M. Yu, Influence of Process Parameters on the Deposition Footprint in Plasma-Spray Coating, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2003, 12(3), p 377-392
Z. Salhi, S. Guessasma, and N. Fenineche, Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia In-flight Particle characteristics Under Vacuum Plasma Spray Conditions, Vacuum, 2009, 83, p 1382-1387
M. Varadelle, C. Trassy, A. Vardelle, and P. Fauchais, Experimental Investigation of Powder Vaporization in Thermal Plasma Jets, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process, 1991, 11(2), p 185-201
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by MEXT KAKENHI (21760583). M. Shahien would like to thank NGK foundation in Aichi, Japan for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahien, M., Yamada, M., Yasui, T. et al. Reactive Atmospheric Plasma Spraying of AlN Coatings: Influence of Aluminum Feedstock Particle Size. J Therm Spray Tech 20, 580–589 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-010-9582-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-010-9582-0