Abstract
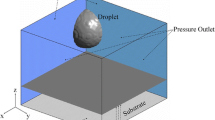
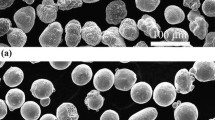
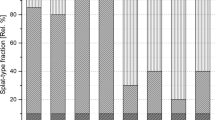
NiCr single splats were plasma-sprayed on aluminum and stainless steel substrates, which were modified by immersion in boiling water, to grow specific types of oxide/oxyhydroxide on the surface. It was observed that there was no splat formation on aluminum substrate. In contrast, a significant number of splats were formed on stainless steel substrate. The differences in splat formation on aluminum and stainless steel surfaces corresponded to the variations of thickness and proportions of the oxide/oxyhydroxide layer on the surfaces. A three-dimensional numerical model was developed to simulate the impact of a droplet onto the substrate. The simulation illustrated good agreement with experimental observations. The effect of the oxide layer on the splat morphology was also examined. It was suggested that the splat morphology was more strongly influenced by water release from the dehydration of oxyhydroxide to oxide rather than by simple presence of the oxide layer on the substrate surface.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B :
-
body force
- C p :
-
specific heat capacity
- f :
-
mass fraction
- F :
-
volume of fraction of the droplet
- k :
-
thermal conductivity
- L :
-
latent heat of fusion
- n :
-
interface normal vector pointing from the droplet to air
- R c :
-
thermal contact resistance at the droplet-substrate interface
- T :
-
temperature
- T 0 :
-
substrate initial temperature
- T m :
-
equilibrium melting temperature
- p :
-
pressure
- t :
-
time
- u :
-
velocity vector
- α:
-
thermal diffusivity
- ρ:
-
density
- μ:
-
effective viscosity
- σ:
-
surface tension coefficient
- κ:
-
surface curvature
- δ:
-
interface delta function
- l:
-
liquid phase
- m:
-
equilibrium melting temperature
- ox:
-
oxide
- s:
-
solid
- sub:
-
substrate
- α:
-
droplet
- β:
-
air
References
S. Chandra and P. Fauchais, Formation of Solid Splats during Thermal Spray Deposition, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2009, 18(2), p 148-180
P. Fauchais, M. Fukumoto, A. Vardella, and M. Vardella, Knowledge Concerning Splat Formation: An Invited Review, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2004, 13(3), p 337-360
S. Dallaire, Influence of Temperature on the Bonding Mechanism of Plasma-Sprayed Coatings, Thin Solid Films, 1982, 95(3), p 237-244
R.C. Dykhuizen, Review of Impact and Solidification of Molten Thermal Spray Droplets, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 1994, 3(4), p 351-361
M. Fukumoto, H. Nagai, and T. Yasui, Influence of Surface Character Change of Substrate due to Heating on Flattening Behavior of Thermal Spray Particle, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2006, 15(4), p 759-764
M. Fukumoto, I. Ohgitani, M. Shiiba, and T. Yasui, Effect of Substrate Surface Change by Heating on Transition in Flattening Behavior of Thermal Sprayed Particles, Mater. Trans., 2004, 45(6), p 1869-1873
X. Jiang, W. Yuepeng, H. Herbert, and S. Sanjay, Role of Condensates and Adsorbates on Substrate Surface on Fragmentation of Impinging Molten Droplets During Thermal Spray, Thin Solid Films, 2001, 385(1-2), p 132-141
C.J. Li and J.L. Li, Evaporated-Gas-Induced Splashing Model for Splat Formation During Plasma Spraying, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 184(1), p 13-23
M. Fukumoto and Y. Huang, Flattening Mechanism in Thermal Sprayed Ni Particles Impinging on Flat Substrate Surface, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 1999, 8(3), p 427-432
M. Fukumoto, T. Yamaguchi, M. Yamada, and T. Yasui, Splash Splat to Disk Splat Transition Behavior in Plasma-Sprayed Metallic Materials, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2007, 16(5-6), p 905-912
A. McDonald, M. Lamontagne, C. Moreau, and S. Chandra, Impact of Plasma-Sprayed Metal Particles on Hot and Cold Glass Surfaces, Thin Solid Films, 2006, 514(4), p 212-222
V. Pershin, M. Lufitha, S. Chandra, and J. Mostaghimi, Effect of Substrate Temperature on Adhesion Strength of Plasma-Sprayed Nickel Coatings, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2003, 12, p 370-376
M. Pasandideh-Fard, V. Pershin, S. Chandra, and J. Mostaghimi, Splat Shapes in a Thermal Spray Coating Process: Simulations and Experiments, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2001, 11, p 206-217
A.T.T. Tran, M.M. Hyland, T. Qiu, B. Withy, and B.J. James, Effects of Surface Chemistry on Splat Formation during Plasma Spraying, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2008, 17(5-6), p 637-645
J. Mostaghimi, S. Chandra, R. Ghafouri-Azar, and A. Dolatabadi, Modeling Thermal Spray Coating Processes: A Powerful Tool in Design and Optimization, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2003, 163-164, p 1-11
M.F. Bahbou and P. Nylen, On-line Measurement of Plasma-Sprayed Ni-Particles During Impact on a Ti-Surface: Influence of Surface Oxidation, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2007, 16(4), p 506-511
M. Pasandideh-Fard, S. Chandra, and J. Mostaghimi, A Three-Dimensional Model of Droplet Impact and Solidification, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2002, 45, p 2229-2242
A. McDonald, M. Xue, S. Chandra, J. Mostaghimi, and C. Moreau, Modeling Fragmentation of Plasma-Sprayed Particles Impacting on a Solid Surface at Room Temperature, Comptes Rendus Mecanique, 2007, 335, p 351-356
H.R. Salimijazi, M. Raessi, J. Mostaghimi, and T.W. Coyle, Study of Solidification Behavior and Splat Morphology of Vacuum Plasma Sprayed Ti Alloy by Computational Modeling and Experimental Results, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2007, 201(18), p 7924-7931
M. Bussmann, J. Mostaghimi, and S. Chandra, On a Three-Dimensional Volume Tracking Model of Droplet Impact, Phys. Fluids, 1999, 11, p 1406-1417
M. Bussmann, S. Chandra, and J. Mostaghimi, Modeling the Splash of a Droplet Impacting a Solid Surface, Phys. Fluids, 2000, 12, p 3121-3132
J. Cedelle, M. Vardelle, and P. Fauchais, Influence of Stainless Steel Substrate Preheating on Surface Topography and on Millimeter- and Micrometer-sized Splat Formation, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 201, p 1373-1382
A. McDonald, C. Moreau, and S. Chandra, Effect of Substrate Oxidation on Spreading of Plasma-Sprayed Nickel on Stainless Steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2007, 202, p 23-33
A. McDonald, S. Chandra, and C. Moreau, Photographing Impact of Plasma-Sprayed Particles on Rough Substrates, J. Mater. Sci., 2008, 43, p 4631-4643
H.B. Parizi, L. Rosenzweig, J. Mostaghimi, S. Chandra, T. Coyle, H. Salimi, L. Pershin, A. McDonald, and C. Moreau, Numerical Simulation of Droplet Impact on Patterned Surfaces, J. Thermal Spray Technol., 2007, 16(5-6), p 713-721
J.U. Brackbill, D.B. Kothe, and C. Zemach, A Continuum Method for Modeling Surface Tension, J. Comput. Phys., 1992, 100, p 335-354
S.-P. Wang, G.-X. Wang, and E.F. Matthys, Melting and Resolidification of a Substrate in Contact with a Molten Metal: Operational Maps, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1998, 41(10), p 1177-1188
W.D. Bennon and F.P. Incropera, A Continuum Model for Momentum, Heat and Species Transport in Binary Solid-Liquid Phase Change Systems—I. Model Formulation, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1987, 30(10), p 2161-2170
C. Prakash and V. Voller, On the Numerical Solution of Continuum Mixture Model Equations Describing Binary Solid-Liquid Phase Change, Numer. Heat Transfer B, 1989, 15(2), p 171-189
C.W. Hirt and B.D. Nichols, Volume of Fluid (VOF) Methods for the Dynamics of Free Boundaries, J. Comput. Phys., 1981, 39, p 201-225
H.K. Versteeg and W. Malalasekera, An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite Volume Method, 2nd ed., Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 2007
Ansys Inc., Ansys CFX Documentation, 2007, USA
S. Brossard, P.R. Munroe, A.T.T. Tran, and M.M. Hyland, Study of the Splat-Substrate Interface for a NiCr Coating Plasma Sprayed on to Polished Aluminum and Stainless Steel Substrates, in International Thermal Spray Coating: Expanding Thermal Spray Performance to New Markets and Applications, 2009, Las Vegas, US
W.J. Trompetter, Splat-Substrate Interactions in High Velocity Thermal Spray Coatings, PhD thesis, University of Auckland, 2008
A.P. Grosvenor, B.A. Kobe, and N.S. McIntyre, Examination of the Oxidation of Iron by Oxygen using X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and QUASES, Surf. Sci., 2004, 565(2-3), p 151-162
M.R. Alexander, G.E. Thompson, and G. Beamson, Characterization of the Oxide/Hydroxide Surface of Aluminum Using X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: A Procedure for Curve Fitting the O 1 s Core Level, Surf. Interface Anal., 2000, 29(7), p 468-477
R. Dhiman and S. Chandra, Freezing-Induced Splashing During Impact of Molten Metal Droplets with High Weber Numbers, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2005, 48(25-26), p 5625-5638
A. McDonald, C. Moreau, and S. Chandra, Thermal Contact Resistance Between Plasma-Sprayed Particles and Flat Surfaces, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2007, 50, p 1737-1749
R. Dhiman, A.G. McDonald, and S. Chandra, Predicting Splat Morphology in a Thermal Spray Process, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2007, 201, p 7789-7801
A. McDonald, C. Moreau, and S. Chandra, Thermal Contact Resistance Between Plasma-Sprayed Particles and Flat Surfaces, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 2006, 50, p 1737-1749
D.R. Lide, CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 86th Edition (CDROM Version 2006), Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, 2006
Acknowledgments
The author would like to acknowledge Tertiary Education Commission of New Zealand for Top Achiever Doctoral scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is an invited paper selected from presentations at the 2009 International Thermal Spray Conference and has been expanded from the original presentation. It is simultaneously published in Expanding Thermal Spray Performance to New Markets and Applications: Proceedings of the 2009 International Thermal Spray Conference, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, May 4-7, 2009, Basil R. Marple, Margaret M. Hyland, Yuk-Chiu Lau, Chang-Jiu Li, Rogerio S. Lima, and Ghislain Montavon, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tran, A.T.T., Hyland, M.M. The Role of Substrate Surface Chemistry on Splat Formation During Plasma Spray Deposition by Experiments and Simulations. J Therm Spray Tech 19, 11–23 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-009-9414-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-009-9414-2