Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to investigate the dosimetric effect of various hip prostheses on pelvis lateral fields treated by a 9-MV photon beam using Monte Carlo (MC) and effective path-length (EPL) methods.
Material and methods
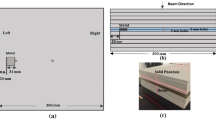
The head of the Neptun 10 pc linac was simulated using the MCNP4C MC code. The accuracy of the MC model was evaluated using measured dosimetric features including depth dose values and dose profiles in a water phantom. The Alfard treatment planning system (TPS) was used for EPL calculations. A virtual water phantom with dimensions of 30 × 30 × 30 cm3 and a cube with dimensions of 4 × 4 × 4 cm3 made of various metals centered in 12 cm depth was used for MC and EPL calculations. Various materials including titanium, Co-Cr-Mo, and steel alloys were used as hip prostheses.
Results
Our results showed significant attenuation in absorbed dose for points after and inside the prostheses. Attenuations of 32%, 54% and 55% were seen for titanium, Co-Cr-Mo, and steel alloys, respectively, at a distance of 5 cm from the prosthesis. Considerable dose increase (up to 18%) was found at the water–prosthesis interface due to back-scattered electrons using the MC method. The results of EPL calculations for the titanium implant were comparable to the MC calculations. This method, however, was not able to predict the interface effect or calculate accurately the absorbed dose in the presence of the Co-Cr-Mo and steel prostheses.
Conclusion
The dose perturbation effect of hip prostheses is significant and cannot be predicted accurately by the EPL method for Co-Cr-Mo or steel prostheses. The use of MC-based TPS is recommended for treatments requiring fields passing through hip prostheses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
PJ Biggs MD Russell (1988) ArticleTitleEffect of a femoral head prosthesis on megavoltage beam radiotherapy In J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 14 581–6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c7jvV2hsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0360-3016(88)90279-9
M Carolan P Dao C Fox P Metcalfe (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of hip prostheses on radiotherapy dose Australas Radiol 44 290–5 Occurrence Handle10974722 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1440-1673.2000.00816.x Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvmt1SlsA%3D%3D
M Erlanson L Franzen R Henriksson B Littbrand PO Lofroth (1991) ArticleTitlePlanning of radiotherapy for patients with hip prosthesis Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 20 1093–8 Occurrence Handle2022511 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M3hs1yjtw%3D%3D
MB Hazuka GS Ibbott JJ Kinzie (1988) ArticleTitleHip prostheses during pelvic irradiation: effects and corrections Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 14 1311–7 Occurrence Handle3133330 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c3ls1Oqug%3D%3D
WD Burleson CD Stutzman JA Stitt UL Karlsson TA Mian (1991) ArticleTitleIn vivo isocenter dose in two hip prosthesis patients Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 20 1347–52 Occurrence Handle2045308 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M3lvVWkuw%3D%3D
PJ Keall JV Siebers R Jeraj R Mohan (2003) ArticleTitleRadiotherapy dose calculations in the presence of hip prostheses Med Dosim 28 107–12 Occurrence Handle12804709 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0958-3947(02)00245-5
JH Kung H Reft W Jackson I Abdalla (2001) ArticleTitleIntensity-modulated radiotherapy for a prostate patient with a metal prosthesis Med Dosim 26 305–8 Occurrence Handle11747995 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0958-3947(01)00079-6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FmvV2mtQ%3D%3D
WU Laub F Nusslin (2003) ArticleTitleMonte Carlo dose calculations in the treatment of a pelvis with implant and comparison with pencil-beam calculations Med Dosim 28 229–33 Occurrence Handle14684187 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.meddos.2003.05.001
C Reft R Alecu IJ Das BJ Gerbi P Keall E Lief et al. (2003) ArticleTitleDosimetric considerations for patients with HIP prostheses undergoing pelvic irradiation: report of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 63 Med Phys 30 1162–82 Occurrence Handle12852541 Occurrence Handle10.1118/1.1565113
R Roberts (2001) ArticleTitleHow accurate is a CT-based dose calculation on a pencil beam TPS for a patient with a metallic prosthesis? Phys Med Biol 46 N227–34 Occurrence Handle11580187 Occurrence Handle10.1088/0031-9155/46/9/402 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrjtlKkug%3D%3D
E Wieslander T Knoos (2003) ArticleTitleDose perturbation in the presence of metallic implants: treatment planning system versus Monte Carlo simulations Phys Med Biol 48 3295–305 Occurrence Handle14620059 Occurrence Handle10.1088/0031-9155/48/20/003
GX Ding CW Yu (2001) ArticleTitleA study on beams passing through hip prosthesis for pelvic radiation treatment Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51 1167–75 Occurrence Handle11704342 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0360-3016(01)02592-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3Mnlt1CltQ%3D%3D
CM Ma T Pawlicki SB Jiang et al. (2000) ArticleTitleMonte Carlo verification of IMRT dose distributions from a commercial treatment planning optimization system Phys Med Biol 45 2483–95 Occurrence Handle11008950 Occurrence Handle10.1088/0031-9155/45/9/303 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvlt1Gluw%3D%3D
A Farajollahi A Mesbahi (2006) ArticleTitleMonte Carlo dose calculations for a 6-MV photon beam in a thorax phantom Radiat Med 24 269–76 Occurrence Handle16958400 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s11604-005-1493-5
A Mesbahi M Allahverdi H Gheraati (2005) ArticleTitleMonte Carlo dose calculations in conventional thorax fields for 60Co photons Radiat Med 23 341–50 Occurrence Handle16342907
A Mesbahi D Thwaites A Reilly (2006) ArticleTitleExperimental and Monte Carlo evaluation of Eclipse treatment planning system for lung dose calculations Rep Pract Oncol Radiother 3 1–11
TD Solberg JJ DeMarco IJ Chetty AV Mesa CH Cagnon AN Li et al. (2001) ArticleTitleA review of radiation dosimetry application using the MCNP Monte Carlo code Radiochim Acta 89 337–55 Occurrence Handle10.1524/ract.2001.89.4-5.337 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXksFChsb0%3D
SY Lin TC Chu JP Lin MT Liu (2002) ArticleTitleThe effect of a metal hip prosthesis on the radiation dose in therapeutic photon beam irradiations Appl Radiat Isot 57 17–23 Occurrence Handle12137022 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0969-8043(02)00078-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvVGhsL8%3D
Briesmeister JF. MCNP—a general Monte Carlo N-particle transport code, version 4C. Report LA-13709-M. Los Alamos National Laboratory, NM, 2000
A Mesbahi M Fix M Allahverdi E Grein H Garaati (2005) ArticleTitleMonte Carlo calculation of Varian 2300C/D Linac photon beam characteristics: a comparison between MCNP4C, GEANT3 and measurements Appl Radiat Isot 62 469–77 Occurrence Handle15607926 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.apradiso.2004.07.008 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXhtFWqsrnL
A Mesbahi AJ Reilly DI Thwaites (2006) ArticleTitleDevelopment and commissioning of a Monte Carlo photon beam model for Varian Clinac 2100EX linear accelerator Appl Radiat Isot 64 656–62 Occurrence Handle16455264 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.apradiso.2005.12.012 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD28Xjs1WksL4%3D
J Venselaar H Welleweerd B Mijnheer (2001) ArticleTitleTolerances for the accuracy of photon beam dose calculations of treatment planning systems Radiother Oncol 60 191–201 Occurrence Handle11439214 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0167-8140(01)00377-2 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MzosFertQ%3D%3D
PJ Gullane (1991) ArticleTitlePrimary mandibular reconstruction: analysis of 64 cases and evaluation of interface radiation dosimetry on bridging plates Laryngoscope 101 IssueID6 Pt 2 suppl 54 1–24 Occurrence Handle2041453 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M3ltFOjuw%3D%3D
MR Sontag JR Cunninghum (1997) ArticleTitleCorrections to absorbed dose calculations for tissue inhomogeneities Med Phys 4 431–8 Occurrence Handle10.1118/1.594329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mesbahi, A., Nejad, F. Dose attenuation effect of hip prostheses in a 9-MV photon beam: commercial treatment planning system versus Monte Carlo calculations. Radiat Med 25, 529–535 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-007-0181-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-007-0181-z