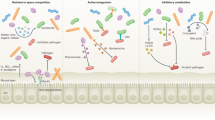
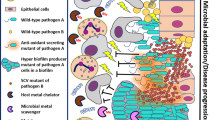
Abstract
Renewed studies of chronic infection have shifted the focus from single pathogens to multi-microbial communities as culture-independent techniques reveal complex consortia of microbes associated with chronic disease. Despite a general acceptance that some chronic diseases are caused by mixed microbial communities, areas of research exploring community interactions as they relate to the alteration of virulence are still in the early stages. Members of the NIH Human Microbiome Project have been actively characterizing the microbial communities of the skin, nasal, oral, gastrointestinal, and urogenital cavities of healthy adults. Concomitantly, several independent studies have begun to characterize the oral, nasal, sinus, upper and lower respiratory microbiomes in healthy and diseased human tissue. The interactions among the members of these polymicrobial communities have not been thoroughly explored and it is clear there is a need to identify the functional interactions that drive population-level virulence if new therapeutic approaches to chronic disease are to be developed. For example, multiple studies have examined the role of quorum sensing (QS) in microbial virulence, and QS antagonists are being developed and tested as novel therapeutics. Other potential targets include the Gram-negative type III signaling system (T3SS), type IV pili, and two component regulatory systems (TCRS). Initial results from these studies indicate limited efficacy in vivo, further suggesting that the interactions in a heterogeneous community are complex and poorly understood. If progress is to be made in the development of more effective treatments for chronic diseases, a better understanding of the composition and functional interactions that occur within multi-microbial communities must be developed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anzaudo M M, Busquets N P, Ronchi S, Mayoral C (2005). Isolated pathogen microorganisms in respiratory samples from children with cystic fibrosis. Rev Argent Microbiol, 37(3): 129–134
Armbruster C E, Hong W, Pang B, Weimer K E, Juneau R A, Turner J, Swords W E (2010). Indirect pathogenicity of Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis in polymicrobial otitis media occurs via interspecies quorum signaling. MBio, 1(3): e00102-10–e00102-19
Arthur M, Molinas C, Courvalin P (1992). The VanS-VanR twocomponent regulatory system controls synthesis of depsipeptide peptidoglycan precursors in Enterococcus faecium BM4147. J Bacteriol, 174(8): 2582–2591
Baddour LM, Christensen G D (1987). Prosthetic valve endocarditis due to small-colony staphylococcal variants. Rev Infect Dis, 9(6): 1168–1174
Bader M S (2008). Diabetic foot infection. Am Fam Physician, 78(1): 71–79
Bakaletz L O (2010). Immunopathogenesis of polymicrobial otitis media. J Leukoc Biol, 87(2): 213–22
Bala A, Kumar R, Harjai K(2011). Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosaby azithromycin and its effectiveness in urinary tract infections. J Med Microbiol, 60(Pt 3): 300–306
Bassler B L (1999). How bacteria talk to each other: regulation of gene expression by quorum sensing. Curr Opin Microbiol, 2(6): 582–587
Bassler B L, Wright M, Silverman M R (1994). Multiple signaling systems controlling expression of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes encoding a second sensory pathway. Mol Microbiol, 13(2): 273–286
Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M(2007). Quorum-sensing blockade as a strategy for enhancing host defences against bacterial pathogens. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci, 362(1483): 1213–22
Bjarnsholt T, Jensen P O, Jakobsen T H, Phipps R, Nielsen A K, Rybtke M T, Tolker-Nielsen T, Givskov M, Høiby N, Ciofu O, the Scandinavian Cystic Fibrosis Study Consortium (2010). Quorum sensing and virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa during lung infection of cystic fibrosis patients. PLoS One, 5(4): e10115
Boles B R, Thoendel M, Singh P K (2005). Genetic variation in biofilms and the insurance effects of diversity. Microbiology, 151(Pt 9: 2816–2818
Brown S M (2010). Multiple strains of non-tuberculous mycobacteria in a patient with cystic fibrosis. J R Soc Med, 103(Suppl 1): 34–43
Burmolle M, Thomsen T R, Fazli M, Dige I, Christensen L, Homoe P, Tvede M, Nyvad B, Tolker-Nielsen T, Givskov M, Moser C, Kirketerp-Moller K, Johansen H K, Hoiby N, Jensen P O, Sorensen S J, Bjarnsholt T (2010). Biofilms in chronic infections—a matter of opportunity—monospecies biofilms in multispecies infections. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, 59(3), 324–336
Burns J L, Emerson J, Stapp J R, Yim D L, Krzewinski J, Louden L, Ramsey B W, Clausen C R (1998). Microbiology of sputum from patients at cystic fibrosis centers in the United States. Clin Infect Dis, 27(1): 158–163
Chan J, Hadley J (2001). The microbiology of chronic rhinosinusitis: results of a community surveillance study. Ear Nose Throat J, 80(3): 143–145
Charlson E S, Chen J, Custers-Allen R, Bittinger K, Li H, Sinha R, Hwang J, Bushman F D, Collman R G (2010). Disordered microbial communities in the upper respiratory tract of cigarette smokers. PLoS ONE, 5(12): e15216
Chen P B, Davern L B, Katz J, Eldridge J H, Michalek S M (1996). Host responses induced by co-infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in a murine model. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 11(4): 274–281
Cherry D K, Woodwell D A (2002). National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2000 summary. Adv Data, 328: 1–32
Deng D M, Liu M J, ten Cate J M, Crielaard W (2007). The VicRK system of Streptococcus mutans responds to oxidative stress. J Dent Res, 86(7): 606–610
Dewhirst F E, Chen T, Izard J, Paster B J, Tanner A C, Yu W H, Lakshmanan A, Wade W G (2010). The human oral microbiome. J Bacteriol, 192(19): 5002–5017
Duque C, Stipp R N, Wang B, Smith D J, Hofling J F, Kuramitsu H K, Duncan M J, Mattos-Graner R O (2011). Downregulation of GbpB, a component of the VicRK regulon, affects biofilm formation and cell surface characteristics of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun, 79(2): 786–796
Ebersole J L, Feuille F, Kesavalu L, Holt S C (1997). Host modulation of tissue destruction caused by periodontopathogens: effects on a mixed microbial infection composed of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum. Microb Pathog, 23(1): 23–32
Ehrlich G D, Ahmed A, Earl J, Hiller N L, Costerton J W, Stoodley P, Post J C, Demeo P, Hu F Z (2010). The distributed genome hypothesis as a rubric for understanding evolution in situ during chronic bacterial biofilm infectious processes. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, 59(3): 269–279
Ehrlich G D, Hiller N L, Hu F Z (2008). What makes pathogens pathogenic. Genome Biol, 9(6): 225
Ehrlich G D, Hu F Z, Shen K, Stoodley P, Post J C (2005). Bacterial plurality as a general mechanism driving persistence in chronic infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res, (437):20–24
Evers S, Courvalin P (1996). Regulation of VanB-type vancomycin resistance gene expression by the VanS(B)-VanR (B) two-component regulatory system in Enterococcus faecalis V583. J Bacteriol, 178(5): 1302–1309
Falleiros de Padua R A, Norman Negri M F, Svidzinski A E, Nakamura C V, Svidzinski T I (2008). Adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candida albicans to urinary catheters. Rev Iberoam Micol, 25(3): 173–175
Feuille F, Ebersole J L, Kesavalu L, Stepfen M J, Holt S C (1996). Mixed infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum in a murine lesion model: potential synergistic effects on virulence. Infect Immun, 64(6): 2094–2100
Foreman A, Psaltis A J, Tan L W, Wormald P J (2009). Characterization of bacterial and fungal biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 23(6): 556–561
Foreman A, Wormald P J (2010). Different biofilms, different disease? A clinical outcomes study. Laryngoscope, 120(8): 1701–1706
Galperin M Y (2006). Structural classification of bacterial response regulators: diversity of output domains and domain combinations. J Bacteriol, 188(12): 4169–4182
Geske G D, O’Neill J C, Blackwell H E (2007). N-phenylacetanoyl-L-homoserine lactones can strongly antagonize or superagonize quorum sensing in Vibrio fischeri. ACS Chem Biol, 2(5): 315–319
Geske G D, O’Neill J C, Miller D M, Mattmann M E, Blackwell H E (2007). Modulation of bacterial quorum sensing with synthetic ligands: systematic evaluation of N-acylated homoserine lactones in multiple species and new insights into their mechanisms of action. J Am Chem Soc, 129(44): 13613–13625
Gotoh Y, Doi A, Furuta E, Dubrac S, Ishizaki Y, Okada M, Igarashi M, Misawa N, Yoshikawa H, Okajima T, Msadek T, Utsumi R (2010). Novel antibacterial compounds specifically targeting the essential WalR response regulator. J Antibiot (Tokyo), 63(3): 127–134
Guggenheim B, Gmur R, Galicia J C, Stathopoulou P G, Benakanakere M R, Meier A, Thurnheer T, Kinane D F (2009). In vitro modeling of host-parasite interactions: the ’subgingival’ biofilm challenge of primary human epithelial cells. BMC Microbiol, 9: 280
Hall-Stoodley L, Hu F Z, Gieseke A, Nistico L, Nguyen D, Hayes J, Forbes M, Greenberg D P, Dice B, Burrows A, Wackym P A, Stoodley P, Post J C, Ehrlich G D, Kerschner J E (2006). Direct detection of bacterial biofilms on the middle-ear mucosa of children with chronic otitis media. JAMA, 296(2): 202–211
Healy D Y, Leid J G, Sanderson A R, Hunsaker D H (2008). Biofilms with fungi in chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 138(5): 641–647
Hemady R K (1995). Microbial keratitis in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Ophthalmology, 102(7): 1026–1030
Hentzer M, Eberl L, Nielsen J, Givskov M (2003). Quorum sensing: a novel target for the treatment of biofilm infections. BioDrugs, 17(4): 241–250
Hentzer M, Wu H, Andersen J B, Riedel K, Rasmussen T B, Bagge N, Kumar N, Schembri M A, Song Z, Kristoffersen P, Manefield M, Costerton JW, Molin S, Eberl L, Steinberg P, Kjelleberg S, Høiby N, Givskov M (2003). Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J, 22(15): 3803–3815
Hermann C, Hermann J, Munzel U, Røchel R (1999). Bacterial flora accompanying Candida yeasts in clinical specimens. Mycoses, 42(11–12): 619–627
Higgins D A, Pomianek M E, Kraml C M, Taylor R K, Semmelhack M F, Bassler B L (2007). The major Vibrio cholerae autoinducer and its role in virulence factor production. Nature, 450(7171): 883–886
HoffmanL R, Deziel E, D’Argenio D A, Lepine F, Emerson J, McNamara S, Gibson R L, Ramsey B W, Miller S I (2006). Selection for Staphylococcus aureus small-colony variants due to growth in the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 103(52): 19890–19895
Hogan D A, Kolter R (2002). Pseudomonas-Candida interactions: an ecological role for virulence factors. Science, 296(5576): 2229–22232
Hoiby N (1974). Epidemiological investigations of the respiratory tract bacteriology in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol, 82(4): 541–550
Høiby N, Ciofu O, Bjarnsholt T (2010). Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in cystic fibrosis. Future Microbiol, 5(11): 1663–1674
Holcombe L J, McAlester G, Munro C A, Enjalbert B, Brown A J, Gow N A, Ding C, Butle G R, O’Gara F, Morrissey J P (2010). Pseudomonas aeruginosa secreted factors impair biofilm development in Candida albicans. Microbiology, 156(Pt 5): 1476–1486
Hong H J, Hutchings M I, Buttner M J, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, UK (2008). Vancomycin resistance VanS/VanR two-component systems. Adv Exp Med Biol, 631: 200–213
Hu F Z, Ehrlich G D (2008). Population-level virulence factors amongst pathogenic bacteria: relation to infection outcome. Future Microbiol, 3(1): 31–42
Ito R, Ishihara K, Shoji M, Nakayama K, Okuda K (2010). Hemagglutinin/adhesin domains of Porphyromonas gingivalis play key roles in coaggregation with Treponema denticola. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, 60(3): 251–260
Jakubovics N S, Kolenbrander P E (2010). The road to ruin: the formation of disease-associated oral biofilms. Oral Dis, 16(8): 729–739
Jenkinson H F, Lamont R J (2005). Oral microbial communities in sickness and in health. Trends Microbiol, 13(12): 589–595
Jesaitis A J, Franklin MJ, Berglund D, Sasaki M, Lord C I, Bleazard J B, Duffy J E, Beyenal H, Lewandowski Z (2003). Compromised host defense on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms: characterization of neutrophil and biofilm interactions. J Immunol, 171(8): 4329–4339
Jones M B, Peterson S N, Benn R, Braisted J C, Jarrahi B, Shatzkes K, Ren D, Wood T K, Blaser M J (2010). Role of luxS in Bacillus anthracis growth and virulence factor expression. Virulence, 1(2): 72–83
Kahl B, Herrmann M, Everding A S, Koch H G, Becker K, Harms E, Proctor R A, Peters G (1998). Persistent infection with small colony variant strains of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis, 177(4): 1023–1029
Keren I, Kaldalu N, Spoering A, Wang Y, Lewis K (2004a). Persister cells and tolerance to antimicrobials. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 230(1): 13–18
Keren I, Shah D, Spoering A, Kaldalu N, Lewis K (2004b). Specialized persister cells and the mechanism of multidrug tolerance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol, 186(24): 8172–8180
Kesavalu L, Holt S C, Ebersole J L (1998). Virulence of a polymicrobic complex, Treponema denticola and Porphyromonas gingivalis, in a murine model. Oral Microbiol Immunol, 13(6): 373–377
Klinger J D, Thomassen M J (1985). Occurrence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Gram-negative nonfermentative bacilli in cystic fibrosis patients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis, 3(2): 149–158
Kolenbrander P E (2000). Oral microbial communities: biofilms, interactions, and genetic systems. Annu Rev Microbiol, 54: 413–437
Kolenbrander P E, Andersen R N, Blehert D S, Egland P G, Foster J S, Palmer R J Jr (2002). Communication among oral bacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev, 66(3): 486–505
Kolenbrander P E, Palmer R J Jr, Rickard A H, Jakubovics N S, Chalmers N I, Diaz P I (2006). Bacterial interactions and successions during plaque development. Periodontol 2000, 42: 47–79
Krishnamurthy A, McGrath J, Cripps A W, Kyd J M (2009). The incidence of Streptococcus pneumoniae otitis media is affected by the polymicrobial environment particularly Moraxella catarrhalis in a mouse nasal colonisation model. Microbes Infect, 11(5): 545–553
Lambiase A, Catania M R, Del Pezzo M, Rossano F, Terlizzi V, Sepe A, Raia V (2011). Achromobacter xylosoxidans respiratory tract infection in cystic fibrosis patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis
Lanza D C, Kennedy D W (1997). Adult rhinosinusitis defined. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 117(Suppl 3): 1–7
Lattar S M, Tuchscherr L P, Caccuri R L, Centron D, Becker K, Alonso C A, Barberis C, Miranda G, Buzzola F R, von Eiff C, Sordelli D O (2009). Capsule expression and genotypic differences among Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with chronic or acute osteomyelitis. Infect Immun, 77(5): 1968–1975
Lee B, Haagensen J A, Ciofu O, Andersen J B, Hoiby N, Molin S (2005). Heterogeneity of biofilms formed by nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol, 43(10): 5247–5255
Leid J G, Costerton J W, Shirtliff M E, Gilmore M S, Engelbert M (2002). Immunology of Staphylococcal biofilm infections in the eye: new tools to study biofilm endophthalmitis. DNA Cell Biol, 21(5–6): 405–413
Leid J G, Kerr M, Selgado C, Johnson C, Moreno G, Smith A, Shirtliff M E, O’Toole G A, Cope E K (2009). Flagellar-mediated biofilm defense mechanisms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa against host derived lactoferrin. Infect Immun, 77(10): 4559–4566
Leid J G, Willson C J, Shirtliff ME, Hassett D J, Parsek MR, Jeffers A K (2005). The exopolysaccharide alginate protects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria from IFN-gamma-mediated macrophage killing. J Immunol, 175(11): 7512–7518
Li J, Helmerhorst E J, Leone CW, Troxler R F, Yaskell T, Haffajee A D, Socransky S S, Oppenheim F G (2004). Identification of early microbial colonizers in human dental biofilm. J Appl Microbiol, 97(6): 1311–1318
Li M, Villaruz A E, Vadyvaloo V, Sturdevant D E, Otto M (2008). AI-2-dependent gene regulation in Staphylococcus epidermidis. BMC Microbiol, 8: 4
Ly N, McCaig L F (2002). National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2000 outpatient department summary. Adv Data, (327): 1–27
Maeda S, Ito M, Ando T, Ishimoto Y, Fujisawa Y, Takahashi H, Matsuda A, Sawamura A, Kato S (2006). Horizontal transfer of nonconjugative plasmids in a colony biofilm of Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 255(1): 115–120
Moore J E, Reid A, Millar B C, Jiru X, Mccaughan J, Goldsmith C E, Collins J, Murphy P G, Elborn J S (2002). Pandoraea apista isolated from a patient with cystic fibrosis: problems associated with laboratory identification. Br J Biomed Sci, 59(3): 164–166
Nadel D M, Lanza D C, Kennedy D W (1999). Endoscopically guided sinus cultures in normal subjects. Am J Rhinol, 13(2): 87–90
Nyvad B, Kilian M (1987). Microbiology of the early colonization of human enamel and root surfaces in vivo. Scand J Dent Res, 95(5): 369–380
Palmer R J Jr, Gordon S M, Cisar J O, Kolenbrander P E (2003). Coaggregation-mediated interactions of streptococci and actinomyces detected in initial human dental plaque. J Bacteriol, 185(11): 3400–3409
Palmer R J Jr, Kazmerzak K, Hansen M C, Kolenbrander P E (2001). Mutualism versus independence: strategies of mixed-species oral biofilms in vitro using saliva as the sole nutrient source. Infect Immun, 69(9): 5794–5804
Park J E, Yung R, Stefanowicz D, Shumansky K, Akhabir L, Durie P R, Corey M, Zielenski J, Dorfman R, Daley D, Sandford A J (2011). Cystic fibrosis modifier genes related to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Genes Immun
Periasamy S, Kolenbrander P E (2009). Mutualistic biofilm communities develop with Porphyromonas gingivalis and initial, early, and late colonizers of enamel. J Bacteriol, 191(22): 6804–6411
Perloff J R, Palmer J N (2004). Evidence of bacterial biofilms on frontal recess stents in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol, 18(6): 377–380
Peters B M, Jabra-Rizk M A, Scheper M A, Leid J G, Costerton J W, Shirtliff M E (2010). Microbial interactions and differential protein expre ssion in Staphylococcus aureus-Candida albicans dual-species biofilms. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol, 59(3): 493–503
Prince A A, Steiger J D, Khalid A N, Dogrhamji L, Reger C, Eau Claire S, Chiu A G, Kennedy D W, Palmer J N, Cohen N A (2008). Prevalence of biofilm-forming bacteria in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol, 22(3): 239–245
Proctor R A, Von Eiff C, Kahl B C, Becker K, McNamara P, Herrmann M, Peters G (2006). Small colony variants: a pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections. Nat Rev Microbiol, 4(4): 295–305
Ramsey M M, Whiteley M (2009). Polymicrobial interactions stimulate resistance to host innate immunity through metabolite perception. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 106(5): 1578–1583
Rickard A H, Palmer R J Jr, Blehert D S, Campagna S R, Semmelhack M F, Egland P G, Bassler B L, Kolenbrander P E (2006). Autoinducer 2: a concentration-dependent signal for mutualistic bacterial biofilm growth. Mol Microbiol, 60(6): 1446–1456
Roberts M E, Stewart P S (2004). Modeling antibiotic tolerance in biofilms by accounting for nutrient limitation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother, 48(1): 48–52
Rolauffs B, Bernhardt T M, von Eiff C, Hart M L, Bettin D (2002). Osteopetrosis, femoral fracture, and chronic osteomyelitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus small colony variants (SCV) treated by girdlestone resection—6-year follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 122(9–10): 547–550
Romano J D, Kolter R (2005). Pseudomonas-Saccharomyces interactions: influence of fungal metabolism on bacterial physiology and survival. J Bacteriol, 187(3): 940–948
Ryan R P, Dow J M (2008). Diffusible signals and interspecies communication in bacteria. Microbiology, 154(7): 1845–1858
Sanderson A R, Leid J G, Hunsaker D (2006). Bacterial biofilms on the sinus mucosa of human subjects with chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope, 116(7): 1121–1126
Schauder S, Shokat K, Surette M G, Bassler B L (2001). The LuxS family of bacterial autoinducers: biosynthesis of a novel quorumsensing signal molecule. Mol Microbiol, 41(2): 463–476
Shirtliff M E, Peters B M, Jabra-Rizk M A (2009). Cross-kingdom interactions: Candida albicans and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 299(1): 1–8
Soni K A, Lu L, Jesudhasan P R, Hume ME, Pillai S D (2008). Influence of autoinducer-2 (AI-2) and beef sample extracts on E. coli O157:H7 survival and gene expression of virulence genes yadK and hhA. J Food Sci, 73(3): M135–M139
Soni K, Jesudhasan P, Cepeda M, Williams B, Hume M, Russell W K, Jayaraman A, Pillai S D (2007). Proteomic analysis to identify the role of LuxS/AI-2 mediated protein expression in Escherichia coli O157:H7. Foodborne Pathog Dis, 4(4): 463–471
Stelzmueller I, Biebl M, Wiesmayr S, Eller M, Hoeller E, Fille M, Weiss G, Lass-Floerl C, Bonatti H (2006). Ralstonia pickettii—innocent bystander or a potential threat? Clin Microbiol Infect, 12(2): 99–101
Stephenson M F, Mfuna L, Dowd S E, Wolcott R D, Barbeau J, Poisson M, James G, Desrosiers M (2010). Molecular characterization of the polymicrobial flora in chronic rhinosinusitis. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 39(2): 182–187
Stone A, Saiman L (2007). Update on the epidemiology and management of Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, in patients with cystic fibrosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med, 13(6): 515–521
Surette M G, Miller M B, Bassler B L (1999). Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Vibrio harveyi: a new family of genes responsible for autoinducer production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 96(4): 1639–1644
Swem L R, Swem D L, O’Loughlin C T, Gatmaitan R, Zhao B, Ulrich S M, Bassler B L (2009). A quorum-sensing antagonist targets both membrane-bound and cytoplasmic receptors and controls bacterial pathogenicity. Mol Cell, 35(2): 143–153
Taga M E, Semmelhack J L, Bassler B L (2001). The LuxS-dependent autoinducer AI-2 controls the expression of an ABC transporter that functions in AI-2 uptake in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Microbiol, 42(3): 777–793
Tribble G D, Lamont G J, Progulske-Fox A, Lamont R J (2007). Conjugal transfer of chromosomal DNA contributes to genetic variation in the oral pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis. J Bacteriol, 189(17): 6382–6388
Ulrich L E, Zhulin I B (2007). MiST: a microbial signal transduction database. Nucleic Acids Res, 35(Database issue): D386–D390
Waters C M, Bassler B L (2005). Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol, 21(1): 319–346
Weimer K E, Armbruster C E, Juneau R A, Hong W, Pang B, Swords W E (2010). Coinfection with Haemophilus influenzae promotes pneumococcal biofilm formation during experimental otitis media and impedes the progression of pneumococcal disease. J Infect Dis, 202(7): 1068–1075
Wellinghausen N, Essig A, Sommerburg O (2005). Inquilinus limosus in patients with cystic fibrosis, Germany. Emerg Infect Dis, 11(3): 457–459
Wolcott R, Dowd S (2011). The role of biofilms: are we hitting the right target? Plast Reconstr Surg, 127(Suppl 1): 28–35
Xavier K B, Bassler B L (2005). Interference with AI-2-mediated bacterial cell-cell communication. Nature, 437(7059): 750–753
Xu K D, Stewart P S, Xia F, Huang C T, McFeters G A (1998). Spatial physiological heterogeneity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm is determined by oxygen availability. Appl Environ Microbiol, 64(10): 4035–4039
Zhao L, Xue T, Shang F, Sun H, Sun B (2010). Staphylococcus aureus AI-2 quorum sensing associates with the KdpDE two-component system to regulate capsular polysaccharide synthesis and virulence. Infect Immun, 78(8): 3506–3815
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leid, J.G., Cope, E. Population level virulence in polymicrobial communities associated with chronic disease. Front. Biol. 6, 435–445 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-011-1153-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-011-1153-3