Abstract
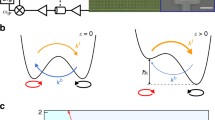
Based on the rapid experimental developments of circuit QED, we propose a feasible scheme to simulate the spin-boson model with superconducting circuits, which can be used to detect quantum Kosterlitz-Thouless (KT) phase transition. We design the spinboson model by using a superconducting phase qubit coupled to a semi-infinite transmission line, which is regarded as a bosonic reservoir with a continuum spectrum. By tuning the bias current or the coupling capacitance, the quantum KT transition can be directly detected through tomography measurement on the states of the phase qubit. We also estimate the experimental parameters using the numerical renormalization group method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feynman R P. Simulating physics with computers. Int J Theor Phys, 1982, 21 (6-7): 467–488
Sachdev S. Quantum Phase Transitions. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999
Leggett A J, Chakravarty S, Dorsey A T, et al. Dynamics of the dissipative two-state system. Rev Mod Phys, 1987, 59 (1): 1–85
Weiss U. Quantum Dissipative Systems. 2nd ed. Singapore: World Scientific, 1999
Bulla R, Costi T A, Pruschke T. Numerical renormalization group method for quantum impurity systems. Rev Mod Phys, 2008, 80 (2): 395–450
Bulla R, Lee H J, Tong N H, et al. Numerical renormalization group for quantum impurities in a bosonic bath. Phys Rev B, 2005, 71(4): 045122
Tong N H, Vojta M. Signatures of a noise-induced quantum phase transition in a mesoscopic metal ring. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97 (1): 016802
Hur K L. Coulomb blockade of a noisy metallic box: A realization of Bose-Fermi kondo models. Phys Rev Lett, 2004, 92 (19): 196804
Furusaki A, Matveev K A. Occupation of a resonant level coupled to a chiral luttinger liquid. Phys Rev Lett, 2002, 88 (22): 226404
Orth P P, Stanic I, Hur K L. Dissipative quantum Ising model in a coldatom spin-boson mixture. Phys Rev A, 2008, 77 (5): 051601
Kopp A, Hur K L. Universal and measurable entanglement entropy in the spin-boson model. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 98(22): 220401; Hur K L, Doucet-Beaupré P, Hofstetter W. Entanglement and criticality in quantum impurity systems. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 99 (12): 126801
Makhlin Y, Schön G, Shnirman A. Quantum-state engineering with Josephson-junction devices. Rev Mod Phys, 2001, 73 (2): 357–400
You J Q, Nori F. Superconducting circuits and quantum information. Phys Tod, 2005, 58 (11): 42–47
Yu Y, Han S Y, Chu X, et al. Coherent temporal oscillations of macroscopic quantum states in a Josephson junction. Science, 2002, 296: 889–892; Yu Y, Zhu S L, Sun G, et al. Quantum jumps between macroscopic quantum states of a superconducting qubit coupled to a microscopic two-level system. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 101 (15): 157001
Blais A, Huang R S, Wallraff A, et al. Cavity quantum electrodynamics for superconducting electrical circuits: An architecture for quantum computation. Phys Rev A, 2004, 69 (6): 062320
Wallraff A, Schuster D I, Blais A, et al. Strong coupling of a single photon to a superconducting qubit using circuit quantum electrodynamics. Nature, 2004, 431: 162–167; Blais A, Gambetta J, Wallraff A, et al. Quantum-information processing with circuit quantum electrodynamics. Phys Rev A, 2007, 75(3): 032329; Hu Y, Xiao Y F, Zhou ZW, et al. Controllable coupling of superconducting transmission-line resonators. Phys Rev A, 2007, 75 (1): 012314
Hofheinz M, Weig E M, Ansmann M, et al. Generation of Fock states in a superconducting quantum circuit. Nature, 2008, 454: 310–314; Hofheinz M, Wang H, Ansmann M, et al. Synthesizing arbitrary quantum states in a superconducting resonator. Nature, 2009, 459: 546–549
Zhou L, Gong Z R, Liu Y X, et al. Controllable scattering of a single photon inside a one-dimensional resonator waveguide. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 101(10): 100501
Martinis J M, Nam S, Aumentado J, et al. Decoherence of a superconducting qubit due to bias noise. Phys Rev B, 2003, 67 (9): 094510
Steffen M, Ansmann M, McDermott R, et al. State tomography of capacitively shunted phase qubits with high fidelity. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 97 (5): 050502
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, L., Tong, N., Xue, Z. et al. Simulation of the spin-boson model with superconducting phase qubit coupled to a transmission line. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 55, 1557–1561 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-012-4863-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-012-4863-x