Abstract
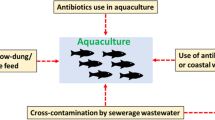
In this study, antibiotic resistance and major phenol and genotypes of non-typhoid Salmonella spp. from riversheds in Taiwan were examined. In 236 water samples tested, 54 (22.9 %) contained Salmonella spp. Fifteen Salmonella serovars were identified from the Salmonella isolates, and some common serovars are associated with infections of human and livestock, including Albany (27.8 %), Newport (14.8 %), Bareilly (13.0 %), Derby (11.1 %), and Typhimurium (7.4 %). Various environmental factors may also affect the presence and proportion of different serovars in the receiving waters. In contrast, serovars with narrower range of hosts, e.g., Dublin, were rarely detected. The Salmonella isolates were subjected to eight antibiotics for drug resistance, and 51.9 % of the samples were resistant to at least one tested antibiotics. Tetracycline and sulfadiazine were the two most ineffective antibiotics against the Salmonella isolates, and the results were indicative of long-term antibiotics abuse as fodder supplements in animal husbandry. The more commonly detected serovars such as Albany, Derby, and Typhimurium were also more likely to be resistant to multiple antibiotics. Finally, a significant correlation was observed between resistance to chloramphenicol and the resistance gene cmlA, suggesting that the resistance genotypes could persist in the environment even long after prohibition of the drug use. The high prevalence of antibiotic-resistant Salmonella spp. infers elevated infection risks that must be further examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarestrup FM, Seyfarth AM, Emborg HD, Pedersen K, Hendriksen RS, Bager F (2001) Effect of abolishment of the use of antimicrobial agents for growth promotion on occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in fecal enterococci from food animals in Denmark. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:2054–2059
Boerlin P, Wissing A, Aarestrup FM, Frey J, Nicolet J (2001) Antimicrobial growth promoter ban and resistance to macrolides and vancomycin in enterococci from pigs. J Clin Microbiol 39:4193–4195
Bureau of Animal and Plant Health Inspection and Quarantine CoA, Taiwan (2010) http://www.baphiq.gov.tw/homeweb5.php. Accessed 30 Dec 2013
Carlson SA, Bolton LF, Briggs CE, Hurd HS, Sharma VK, Fedorka-Cray PJ et al (1999) Detection of multiresistant Salmonella typhimurium DT104 using multiplex and fluorogenic PCR. Mol Cell Probes 13:213–222
CDC (2013) http://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/general/. Accessed 30 Dec 2013
CDC T (2013) http://www.cdc.gov.tw. Accessed 30 Dec 2013
Chiu CH, Ou JT (1996) Rapid identification of Salmonella serovars in feces by specific detection of virulence genes, invA and spvC, by an enrichment broth culture-multiplex PCR combination assay. J Clin Microbiol 34:2619–22
Chiu CH, Su LH, Chu C (2004) Salmonella enterica serotype Choleraesuis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical disease, and treatment. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:311–22
Collignon P (2012) Antibiotic resistance in human Salmonella isolates are related to animal strains. Proc Biol Sci 279:2922–3, author reply 2924-5
Conner CP, Heithoff DM, Julio SM, Sinsheimer RL, Mahan MJ (1998) Differential patterns of acquired virulence genes distinguish Salmonella strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:4641–4645
Daghrir R, Drogui P (2013) Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: a review. Environ Chem Lett 11:209–227
Daum LT, Barnes WJ, McAvin JC, Neidert MS, Cooper LA, Huff WB et al (2002) Real-time PCR detection of salmonella in suspect foods from a gastroenteritis outbreak in kerr county, Texas. J Clin Microbiol 40:3050–2
Davies PR, Turkson PK, Funk JA, Nichols MA, Ladely SR, Fedorka-Cray PJ (2000) Comparison of methods for isolating Salmonella bacteria from faeces of naturally infected pigs. J App Microbiol 89:169–177
Denis M, Houard E, Fablet A, Rouxel S, Salvat G (2013) Distribution of serotypes and genotypes of Salmonella enterica species in French pig production. Vet Rec 173:370
Fang FC, Fierer J (1991) Human infection with Salmonella dublin. Medicine (Baltimore) 70:198–207
Frazier DL, Aucoin DP, Riviere JE (1988) Gentamicin pharmacokinetics and nephrotoxicity in naturally acquired and experimentally induced disease in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 192:57–63
Guerra B, Soto SM, Arguelles JM, Mendoza MC (2001) Multidrug resistance is mediated by large plasmids carrying a class 1 integron in the emergent Salmonella enterica serotype [4,5,12:i:-]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:1305–1308
Guerri ML, Aladuena A, Echeita A, Rotger R (2004) Detection of integrons and antibiotic-resistance genes in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, isolates with resistance to ampicillin and variable susceptibility to amoxicillin-clavulanate. Int J Antimicrob Agents 24:327–333
Haley BJ, Cole DJ, Lipp EK (2009) Distribution, diversity, and seasonality of waterborne Salmonellae in a rural watershed. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1248–1255
Hardnett FP, Hoekstra RM, Kennedy M, Charles L, Angulo FJ, FoodN EIP (2004) Epidemiologic issues in study design and data analysis related to FoodNet activities. Clin Infect Dis 38:S121–S126
Helms M, Vastrup P, Gerner-Smidt P, Molbak K (2002) Excess mortality associated with antimicrobial drug-resistant Salmonella typhimurium. Emer Infect Dis 8:490–5
Hruska K, Franek M (2012) Sulfonamides in the environment: a review and a case report. Vet Med 57:1–35
Ito T, Katayama Y, Asada K, Mori N, Tsutsumimoto K, Tiensasitorn C et al (2001) Structural comparison of three types of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec integrated in the chromosome in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:1323–1336
Jayarao BM, Biro G, Kovacs S, Domjan H, Fabian A (1989) Prevalence of Salmonella serotypes in pigs and evaluation of a rapid, presumptive test for detection of Salmonella in pig faeces. Acta Vet Hung 37:39–44
Kassem II, Esseili MA, Sigler V (2008) Occurrence of mecA in nonstaphylococcal pathogens in surface waters. J Clin Microbiol 46:3868–3869
Krauland MG, Marsh JW, Paterson DL, Harrison LH (2009) Integron-mediated multidrug resistance in a global collection of nontyphoidal Salmonella enterica isolates. Emerg Infect Dis 15:388–396
Lauderdale TL, Shiau YR, Wang HY, Lai JF, Huang IW, Chen PC et al (2007) Effect of banning vancomycin analogue avoparcin on vancomycin-resistant enterococci in chicken farms in Taiwan. Environ Microbiol 9:819–823
Lo YP, Wan MT, Chen MM, Su HY, Lauderdale TL, Chou CC (2012) Molecular characterization and clonal genetic diversity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus of pig origin in Taiwan. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 35:513–521
McDonald LC, Chen MT, Lauderdale TL, Ho M (2001) The use of antibiotics critical to human medicine in food-producing animals in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 34:97–102
Medus C, Smith KE, Bender JB, Besser JM, Hedberg CW (2006) Salmonella outbreaks in restaurants in Minnesota, 1995 through 2003: evaluation of the role of infected foodworkers. J Food Prot 69:1870–1878
Morse EV, Duncan MA (1975) Canine salmonellosis: prevalence, epizootiology, signs, and public health significance. J Am Vet Med Assoc 167:817–20
Ng LK, Martin I, Alfa M, Mulvey M (2001) Multiplex PCR for the detection of tetracycline resistant genes. Mol Cell Probes 15:209–215
Ozdemir K, Acar S (2014) Plasmid profile and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis of salmonella enterica isolates from humans in turkey. Plos One 9:95976
Payne MA, Baynes RE, Sundlof SF, Craigmill A, Webb AI, Riviere JE (1999) Drugs prohibited from extralabel use in food animals. J Am Vet Med Assoc 215:28–32
Ramsden RT, Wilson P, Gibson WP (1980) Immediate effects of intravenous tobramycin and gentamicin on human cochlear function. J Laryngol Otol 94:521–31
Ribot EM, Fair MA, Gautom R, Cameron DN, Hunter SB, Swaminathan B, Barrett TJ (2006) Standardization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for the subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Shigella for PulseNet. Foodborne Pathog Dis 3:59–67
Roberts MC (2005) Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 245:195–203
Rosengren LB, Waldner CL, Reid-Smith RJ (2009) Associations between antimicrobial resistance phenotypes, antimicrobial resistance genes, and virulence genes of fecal Escherichia coli isolates from healthy grow-finish pigs. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1373–1380
Schwartz T, Kohnen W, Jansen B, Obst U (2003) Detection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and their resistance genes in wastewater, surface water, and drinking water biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:325–335
Smith GW, Gehring R, Craigmill AL, Webb AI, Riviere JE (2005) Extralabel intramammary use of drugs in dairy cattle. J Am Vet Med Assoc 226:1994–1996
Solari CA, Mandarino JR, Panizzutti MH, Farias RH (2003) A new serovar and a new serological variant belonging to Salmonella enterica subspecies diarizonae. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 98:501–2
Suar M, Jantsch J, Hapfelmeier S, Kremer M, Stallmach T, Barrow PA et al (2006) Virulence of broad- and narrow-host-range Salmonella enterica serovars in the streptomycin-pretreated mouse model. Infect Immun 74:632–644
Tolba S, Egan S, Kallifidas D, Wellington EMH (2002) Distribution of streptomycin resistance and biosynthesis genes in streptomycetes recovered from different soil sites. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42:269–276
Wegener HC, Aarestrup FM, Jensen LB, Hammerum AM, Bager F (1999) Use of antimicrobial growth promoters in food animals and Enterococcus faecium resistance to therapeutic antimicrobial drugs in Europe. Emerg Infect Dis 5:329–335
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research grant from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST 103-2116-M-194-014 and 103-2622-E-194-007-CC3), and the Tungs’ Taichung MetroHarbor Hospital, Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Wen-Tsai Ji, Jung-Sheng Chen, and Tsui-Kang Hsu have equal contributions to the first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, CY., Hsu, BM., Ji, WT. et al. Antibiotic resistance pattern and gene expression of non-typhoid Salmonella in riversheds. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 7843–7850 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4033-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-4033-y