Abstract
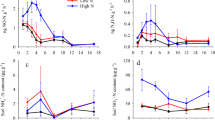
Field management is expected to influence nitrous oxide (N2O) production from arable cropping systems through effects on soil physics and biology. Measurements of N2O flux were carried out on a weekly basis from April 2008 to August 2009 for a spring sown barley crop at Oak Park Research Centre, Carlow, Ireland. The soil was a free draining sandy loam typical of the majority of cereal growing land in Ireland. The aims of this study were to investigate the suitability of combining reduced tillage and a mustard cover crop (RT–CC) to mitigate nitrous oxide emissions from arable soils and to validate the DeNitrification–DeComposition (DNDC) model version (v. 9.2) for estimating N2O emissions. In addition, the model was used to simulate N2O emissions for two sets of future climate scenarios (period 2021–2060). Field results showed that although the daily emissions were significantly higher for RT–CC on two occasions (p < 0.05), no significant effect (p > 0.05) on the cumulative N2O flux, compared with the CT treatment, was found. DNDC was validated using N2O data collected from this study in combination with previously collected data and shown to be suitable for estimating N2O emissions (r 2 = 0.70), water-filled pore space (WFPS) (r 2 = 0.58) and soil temperature (r 2 = 0.87) from this field. The relative deviations of the simulated to the measured N2O values with the 140 kg N ha−1 fertiliser application rate were −36 % for RT–CC and −19 % for CT. Root mean square error values were 0.014 and 0.007 kg N2O–N ha−1 day−1, respectively, indicating a reasonable fit. Future cumulative N2O fluxes and total denitrification were predicted to increase under the RT–CC management for all future climate projections, whilst predictions were inconsistent under the CT. Our study suggests that the use of RT–CC as an alternative farm management system for spring barley, if the sole objective is to reduce N2O emissions, may not be successful.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla, M., Wattenbach, M., Smith, P., Ambus, P., Jones, M., & Williams, M. (2009). Application of the DNDC model to predict emissions of N2O from Irish agriculture. Geoderma, 151, 327–337.
Abdalla, M., Jones, M., Ambus, P., & Williams, M. (2010a). Emissions of nitrous oxide from Irish arable soils: effects of tillage and reduced N input. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 86, 53–65.
Abdalla, M., Jones, M., & Williams, M. (2010b). Simulation of N2O fluxes from Irish arable soils: effect of climate change and management. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 46, 247–260.
Abdalla, M., Kumar, S., Jones, M., Burke, J., & Williams, M. (2011). Testing DNDC model for simulating soil respiration and assessing the effects of climate change on the CO2 gas flux from Irish agriculture. Global and Planetary Change, 78, 106–115.
Addiscott, T. M. (1983). Kinetics and temperature relationships of mineralization and nitrification in Rothamsted soils with differing histories. Soil Science, 34, 343–353.
Andrade, D. S., Colozzi-Filho, A., & Giller, K. E. (2003). The soil microbial community and soil tillage. In A. E. Titi (Ed.), Soil tillage in agroecosystems (pp. 51–81). Boca Raton: CRC.
Antonopoulos, A. Z. (1999). Comparison of different models to simulate soil temperature and moisture-effects on nitrogen mineralization in the soil. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 162, 667–675.
Aulakh, M., Rennie, D., & Paul, E. (1984). The influence of plant residues on denitrification rates in conventional and zero-tilled soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 48, 790–794.
Baggs, E. M., Watson, C. A., & Rees, R. M. (2000). The fate of nitrogen from incorporated cover crop and green manure residues. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 56, 153–163.
Baggs, E. M., Stevenson, M., Pihlatie, M., Regar, A., Cook, H., & Cadisch, G. (2003). Nitrous oxide emissions following application of residues and fertilizer under zero and conventional tillage. Plant and Soil, 254, 361–370.
Baggs, E. M., & Blum, H. (2004). CH4 oxidation and emissions of CH4 and N2O from Lolium perenne swards under elevated atmospheric CO2. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 713–723.
Ball, B. C., Scott, A., & Parker, J. P. (1999). Field N2O, CO2 and CH4 fluxes in relation to tillage, compaction and soil quality in Scotland. Soil and Tillage Research, 53, 29–39.
Barthes, B., Azontonde, A., Blanchart, E., Girardin, C., Villenave, C., Oliver, R., et al. (2006). Effect of a legume cover crop on carbon storage and erosion in an ultisol under maize cultivation in southern Benin. Chapter 10. Soil erosion and carbon dynamics (pp. 143-155). Boca Raton: CRC.
Bavin, T. K., Griffis, T. J., Baker, J. M., & Venterea, R. T. (2009). Impact of reduced tillage and cover cropping on the greenhouse gas budget of a maize/soybean rotation ecosystem. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 134, 234–242.
Beheydt, D., Boeckx, P., Ahmed, H., & Van Cleemput, O. (2008). N2O emission from conventional and minimum-tilled soils. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 44, 863–873.
Bell, M. J., Jones, E., Smith, J., Smith, P., Yeluripati, J., Augustin, J., et al. (2012). Simulation of soil nitrogen, nitrous oxide emissions and mitigation scenarios at 3 European cropland sites using the ECOSSE model. Nutrients Cycling in Agroecosystems, 92, 161–181.
Bouwman, A. F. (1990). Exchange of greenhouse gas between terrestrial ecosystems and atmosphere. In A. F. Bouwman (Ed.), Soil and the greenhouse effects (pp. 61–127). Chichester: Wiley.
Bowden, W. B., & Bormann, F. H. (1986). Transport and loss of nitrous oxide in soil water after forest clear cutting. Science, 233, 867–869.
Bramley, R. G. V., & White, R. E. (1990). The variability of nitrifying activity in field soils. Plant and Soil, 126, 203–208.
Bundy, L. G., & Meisinger, J. J. (1994). Nitrogen availability indices. In R. W. Weaver (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Microbiological and biochemical properties (pp. 951–983). Madison: Soil Science Society of America.
Cai, Z., Swamoto, T., Li, C., Kang, G., Boonjawat, J., Mosier, A., et al. (2003). Field validation of the DNDC-model for greenhouse gas emissions in East Asian cropping systems. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 7, 1107.
Chapman, P. J., Williams, B. L., & Hawkins, A. (2001). Influence of temperature and vegetation cover on soluble inorganic and organic nitrogen in a spodosol. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 1113–1121.
Christopher, S. F., & Lal, R. (2007). Nitrogen management affects carbon sequestration in North American cropland soils. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 26, 45–64.
Chatskikh, D., & Olesen, J. E. (2007). Soil tillage enhanced CO2 and N2O emissions from loamy sand soil under spring barley. Soil and Tillage Research, 97, 5–18.
Choudhary, M. A., Akramkhanov, A., & Saggar, S. (2002). Nitrous oxide emissions from a New Zealand cropped soil: tillage effects, spatial and seasonal variability. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 93, 33–43.
Clayton, H., McTaggert, I. P., Parker, J., Swan, L., & Smith, K. A. (1997). Nitrous oxide emissions from fertilized grassland: a 2 years study of the effect of N fertilizer form and environmental conditions. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 25, 252–260.
Community Climate Change Consortium For Ireland (C4I) (2008). Ireland in a warmer world. Scientific Predictions of the Irish Climate in the Twenty-first century. Final Report. Access at: http://www.c4i.ie/docs/IrelandinaWarmerWorld.pdf
Compton, J. E., & Boone, R. D. (2000). Long-term impacts of agriculture on soil carbon and nitrogen in New England forests. Ecological Society of America, 81, 2314–2330.
Corre, M. D., Van Kessel, C., & Pennock, D. J. (1996). Landscape and seasonal patterns of nitrous oxide emissions in a semiarid region. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 60, 1806–1815.
CSO (2011). Irish Central Statistical Office. Access at: www.cso.ie.
Dalias, P., Anderson, J. M., Bottner, P., & Coûteaux, M. M. (2002). Temperature responses of net nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in conifer forest soils incubated under standard laboratory conditions. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34, 691–701.
Davidson, E. A., Keller, M., Erickson, H. E., Verchot, L. V., & Veldkamp, E. (2000). Testing a conceptual model of soil emissions of nitrous oxide and nitric oxides. Bioscience, 50, 667–680.
Denman, K. L., Brasseur, G., Chidthaisong, A., Ciais, P., Cox, P. M., Dickinson, R. E., et al. (2007). Couplings between changes in the climate system and biogeochemistry. In S. Solomon, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K. B. Averyt, M. Tignor, & H. L. Miller (Eds.), Climate Change (2007): The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
DeVries, W., Kros, J., Kuikman, P. J., Velthof, G. L., Voogd, J. C. H., Wieggers, H. J. J., et al. (2005). Use of measurements and models to improve the national IPCC based assessments of soil emissions of nitrous oxide. Environmental Sciences, 2, 217–233.
Dobbie, K. E., & Smith K. A. (2001). The effects of temperature, water filled pore space and land use on N2O emissions from imperfectly drained gleysol. European Journal of Soil Science, 52, 667–673.
Dobbie, K. E., McTaggart, I. P., & Smith, K. A. (1999). Nitrous oxide emissions from intensive agricultural system: variations between crops and seasons, key driving variable, and mean emission factors. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104, 26891–26899.
Doms, G., & Schatller, U. (2002). A description of the non-hydrostatic regional model LM. Part 1: Dynamics and numerics (p. 144). Offenback: Deutscher Wetterdienst. www.cosmo-model.org.
Doran, J. W., Elliott, E. T., & Paustian, K. (1998). Soil microbial activity, nitrogen cycling, and long-term changes in organic carbon pools as related to fallow tillage management. Soil and Tillage Research, 49, 3–18.
EC (2011). Environment Canada. Access at: http://www.ec.gc.ca/ccmac-cccma/default.asp?lang=En&n=1299529F-1
EEA (2001). European Environment Agency, 2001. YIR99AG05 Area with Organic Farming as Percent of Total Agricultural Area 18, 1985–1999. Access at: http://themes.eea.eu.int/Sectors_and_activities/agriculture/indicators/organic/ag1905_1915.1985.1901.pdf. Accessed 1986 July 2005).
EPA (2011). Irish Environmental protection Agency. Access at: www.epa.ie
Estavillo, J. M., Merino, P., Pinto, M., Yamulki, S., Gebauer, G., Sapek, A., et al. (2002). Short term effect of ploughing a permanent pasture on N2O production from nitrification and denitrification. Plant and Soil, 239, 253–265.
Feng, Y., Motta, A. C., Reeves, D. W., Burmester, C. H., van Santen, E., & Osborne, J. A. (2003). Soil microbial communities under conventional-till and no-till continuous cotton systems. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35, 1693–1703.
Flechard, C., Ambus, P., Skiba, U., Rees, R. M., Hensen, A., Van den Pol, A., et al. (2007). Effects of climate and management intensity on nitrous oxide emissions in grassland systems across Europe. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 121, 135–152.
Follett, R. F. (2001). Soil management concepts and carbon sequestration in cropland soils. Soil and Tillage Research, 61, 77–92.
Forster, P., Ramaswamy, V., Artaxo, P., Berntsen, T., Betts, R., Fahey, D. W., et al. (2007). Changes in Atmospheric Constituents and in Radiative Forcing. In S. Solomon, D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K. B. Averyt, M. Tignor, & H. L. Miller (Eds.), Climate change (2007): The physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Frolking, S. E., Mosier, A. R., Ojima, D. S., Li, C., Parton, W. J., Potter, C. S., et al. (1998). Comparison of N2O emissions from soils at three temperate agricultural sites: simulations of year-round measurements by four models. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 52, 77–105.
Giltrap, D. L., Li, C., & Saggar, S. (2010). DNDC: a process-based model of greenhouse gas fluxes from agricultural soils. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 136, 292–300.
Grandy, A. S., Loecke, T. D., & Parr, S. (2006). Long-term trends in nitrous oxide emissions, soil nitrogen, and crop yields of till and no-till cropping systems. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 1487–1495.
Gregorich, E. G., Rochette, P., Hopkins, D. W., McKim, U. F., & St-Georges, P. (2006). Tillage-induced environmental conditions in soil and substrate limitation determine biogenic gas production. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 38, 2614–2628.
Hart, S. C. (2006). Potential impacts of climate change on nitrogen transformations and greenhouse gas fluxes in forests: a soil transfer study. Global Change Biology, 12, 1032–1046.
Hastings, A. F., Wattenbach, M., Eugster, W., Li, C., Buchmann, N., & Smith, P. (2010). Uncertainty propagation in soil greenhouse gas emission models: an experiment using the DNDC model and at the Oensingen cropland site. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 136, 97–110.
Hellebrand, H. J., Kern, J., & Scholz, V. (2003). Long-term studies on greenhouse gas fluxes during cultivation of energy crops on sandy soils. Atmospheric Environment, 37, 1635–1644.
Hsieh, C. I., Leahy, P., Kiely, G., & Li, C. (2005). The effect of future climate perturbations on N2O emissions from fertilised humid grassland. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosytems, 73, 15–23.
Hutchinson, G. L., & Livingston, G. P. (1993). Uses of chamber systems to measure trace gas fluxes. In L. A. Harper (Ed.), Agricultural ecosystem effects on trace gases and global climate change (pp. 63–78). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Ineson, P., Benham, D. G., Poskitt, J., Harrison, A. F., Taylor, K., & Woods, C. (1998). Effects of climate change on nitrogen dynamics in upland soils. 2. A soil warming study. Global Change Biology, 4, 153–161.
IPCC. (2000). Special Report on Emission Scenarios. In N. Nakicenovic & S. Swart (Eds.), A Special Report of Working Group III of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (p. 599). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
IPCC. (2007). Changes in atmospheric constituents and in radiative forcing. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
John, J., & Draper, N. R. (1980). An alternative family of transformations. Applied Statistics, 29, 190–197.
Jones, C. D., Hughes, J. K., Bellouin, N., Hardiman, S. C., Jones, G. S., Knight, J., et al. (2011). The HadGEM2-ES implementation of CMIP5 centennial simulations. Geoscientific Model Development, 4, 543–570.
Kesik, M., Bruggemann, N., Forkel, R., Kiese, R., Knoche, R., Li, C., et al. (2006). Future scenarios of N2O emissions from European forest soils. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111, G02018. doi:10.1029/2005JG000115, 2006.
Khalil, M. A. K., Rasmussen, R. A., & Shearer, M. J. (2002). Atmospheric nitrous oxide: patterns of global change during recent decades and centuries. Chemosphere, 47, 807–821.
Kirschbaum, M. U. F. (1995). The temperature dependence of soil organic matter decomposition, and the effect of global warming on soil organic C storage. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 27, 753–760.
Kim, D., Michael, M., & Kiely, G. (2010). Effect of increased N use dry periods on N2O emission from fertilized grassland. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 3, 397–410.
Li, C., Frolking, S., & Frolking, T. A. (1992a). A model of nitrous oxide evolution from soil driven by rainfall events: 1. Model structure and sensitivity. Journal of Geophysical Research, 97, 9759–9776.
Li, C., Frolking, S., & Frolking, T. A. (1992b). A model of nitrous oxide evolution from soil driven by rainfall events: 2. Model applications. Journal of Geophysical Research, 97, 9777–9783.
Li, C., Narayanan, V., & Harriss, R. (1996). Model estimate of N2O emissions from agricultural lands in the United States. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 10, 297–306.
Li, C. S. (2000). Modeling trace gas emissions from agricultural ecosystems. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 58, 259–276.
Li, C., Zhuang, Y., Cao, M., Crill, P., Dai, Z., Frolking, S., et al. (2001). Comparing a process-based agro-ecosystem model to the IPCC methodology for developing a national inventory of N2O emissions from arable lands in China. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 60, 159–175.
Li, C., Frolking, S., & Butterbach-Bahl, K. (2005). Carbon sequestration in arable soils is likely to increase nitrous oxide emissions, offsetting reductions in radiative forcing. Climate Change, 72, 321–338.
Liebig, M. A., Morgan, J. A., Reeder, J. D., Ellert, B. H., Gollany, H. T., & Schuman, G. E. (2005). Greenhouse gas contributions and mitigation potential of agricultural practices in northwestern USA and western Canada. Soil and Tillage Research, 83, 25–52.
Linn, D. M., & Doran, J. W. (1984). Effect of water-filled pore space on carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide production in tilled and non-tilled soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 48, 1267–1272.
Liu, X. J., Mosier, A. R., Halvorson, A. D., & Zhang, F. S. (2006). Impact of nitrogen placement on NO, N2O, CH4 and CO2 fluxes from non-tilled soil compared with conventional-tilled soil. Plant and Soil, 280, 177–188.
Liu, X. J., Mosier, A. R., Halvorson, A. D., Reule, C. A., & Zhang, F. S. (2007). Dinitrogen and N2O emissions in arable soils: effect of tillage, N source and soil moisture. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39, 2362–2370.
Ludwig, B., Jager, N., Priesack, E., & Flessa, H. (2011). Application of DNDC model to predict N2O emissions from sandy arable soils with differing fertilization in a long-term experiment. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 174, 350–358.
Lükewille, A., & Wright, R. F. (1997). Experimentally increased soil temperature causes release of nitrogen at a boreal forest catchment in southern Norway. Global Change Biology, 3, 13–21.
McSwiney, C. P., & Robertson, G. P. (2005). Non-linear response of N2O flux to incremental fertilizer addition in a continuous maize (Zea mays L.) cropping system. Global Change Biology, 11, 1712–1719.
Meisinger, J.J., Hargrove, W.L., Mikkelsen, R.L., Williams, J.R., Benson, V.W. (1991). Effects of cover crops on groundwater quality. In W.L. Hargrove (Ed.), Cover crops for clean water (pp. 57–68). Proceedings of an International Conference April 9–11, 1991, Jackson, TN, Soil and Water Conservation Society, Ankeny, IA.
Mogge, B., Kaiser, E. A., & Munch, J. C. (1999). Nitrous oxide emissions and denitrification N-losses from agricultural soils in the Bornhoved Lake region: influence of organic fertilizers and land-use. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 31, 1245–1252.
Mosier, A.R. & Klemedtsson, L. (1994). Measuring denitrification in the field. In R.W. Weaver, S. Angle, P. Bottomley, D. Bezdicek, S. Smith, A. Tabatabai and A. Wollum (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Microbiological and biochemical properties (pp. 1047-1065). Soil Science Society of America Journal, Madison.
Mosier, A. R., Halvorson, A. D., Peterson, G. A., Robertson, G. P., & Sherrod, L. (2005). Measurement of net global warming potential in three agroecosystems. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 72, 67–76.
Moss, R., Babiker, M., Brinkman, S., Calvo, E., Carter, T., Edmonds, J., et al. (2008). Towards new scenarios for analysis of emissions, climate change, impacts, and response strategies (p. 132). Geneva: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
Nolan, P. (2009). Simulating climate change and its effects on the wind energy resource of Ireland. PhD thesis: Access at: http://mathsci.ucd.ie/met/staff/PaulNolan/PhD_Thesis_Paul_Nolan.pdf.
Novoa, R. S. A., & Tejeda, H. R. (2006). Evaluation of the N2O emissions from N in plant residues as affected by environmental and management factors. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 75, 29–46.
Oorts, K., Bossuyt, H., Labreuche, J., Merckx, R., & Nicolardot, B. (2007). Carbon and nitrogen stocks in relation to organic matter fractions, aggregation and pore size distribution in no-tillage and conventional tillage in northern France. European Journal of Soil Science, 58, 248–259.
Oorts, K., Merckx, R., Grehan, E., Labreuche, J., & Nicolardot, B. (2007). Determinants of annual fluxes of CO2 and N2O in long-term no-tillage and conventional tillage systems in northern France. Soil and Tillage Research, 95, 133–148.
Parkin, T. B., & Kaspar, T. C. (2006). Nitrous oxide emissions from corn-soybean systems in the Midwest. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 1496–1506.
Parkin, T. B., Kaspar, T. C., & Singer, J. W. (2006). Cover crop effects on the fate of N following soil application of swine manure. Plant and Soil, 289, 141–152.
Robertson, G. P., & Groffman, P. M. (2007). Nitrogen Transformations. In E. A. Paul (Ed.), Soil microbiology, ecology, and biochemistry (pp. 341–364). Don Mills: Academic Press Canada.
Rosecrance, R. C., McCarty, G. W., Shelton, D. R., & Teasdale, J. R. (2000). Denitrification and N mineralization from hairy vetch (Vicia villosa Roth) and rye (Secale cereale L.) cover crop monocultures and bicultures. Plant and Soil, 227, 283–290.
Rustad, L. E., Campbell, J. L., Marion, G. M., Norby, R. J., Mitchell, M. J., Hartley, A. E., et al. (2001). A meta-analysis of the response of soil respiration, net nitrogen mineralization, and aboveground plant growth to experimental ecosystem warming. Oecologia, 126, 543–562.
Saggar, S., Giltrap, D. L., Li, C., & Tate, K. R. (2007). Measured and modeled estimates of nitrous oxide emission and methane consumption from a sheep-grazed pasture. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 122, 357–365.
Sarkodie-Addo, J., Lee, H. C., & Baggs, E. M. (2003). Nitrous oxide emissions after application of inorganic fertilizer and incorporation of green manure residues. Soil Use and Management, 19, 331–339.
Simek, M., Elhottova, D., Klimes, F., & Hopkins, D. W. (2004). Emissions of N2O and CO2, denitrification measurements and soil properties in red clover and ryegrass stands. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 36, 9–21.
Six, J., Ogle, S. M., Breidt, F. J., Conant, R. T., Mosier, A. R., & Paustian, K. (2004). The potential to mitigate global warming with no-tillage management is only realized when practiced in the long term. Global Change Biology, 10, 155–160.
Skiba, U., Smith, K. A., & Flowler, D. (1993). Nitrification and denitrification of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide in sandy loam soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 25, 1527–1536.
Smith, K. A., Clayton, H., & McTaggart, I. P. (1995). The measurement of nitrous oxide emissions from soil by using chambers. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, 351, 327–337.
Smith, K. (1997). The potential for feedback effects induced by global warming on emissions of nitrous oxide by soils. Global Change Biology, 3, 327–338.
Smith, K. A., Ball, T., Conen, F., Dobbie, K. E., Massheder, J., & Rey, A. (2003). Exchange of greenhouse gases between soil and atmosphere: interactions of soil physical factors and biological processes. European Journal of Soil Science, 54, 779–791.
Smith, W. N., Grant, B. B., Desjardins, R. L., Worth, D., Li, C., Boles, S. H., et al. (2010). A tool to link agricultural activity data with the DNDC model to estimate GHG emissions factor in Canada. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 136, 301–309.
Soane, B. D., Ball, B. C., Arvidsson, J., Basch, G., Moreno, F., & Roger-Estrade, J. (2012). No-till in northern, western and south-western Europe: a review of problems and opportunities for crop production and the environment. Soil and Tillage Research, 118, 66–87.
Spink, J., Street, P., Sylvester-Bradley, R., & Berry, P. (2009). The potential to increase productivity of wheat and oilseed rape in the UK. 2009. Report to the Government Chief Scientific Adviser, January 2009. London: Department for Business Innovation and Skills.
Stanford, G., & Epstein, E. (1974). Nitrogen mineralization-water relations in soils. Soil Science Society of America Proceedings, 38, 103–107.
Stange, F., Butterbach-Bahl, K., Papen, H., Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S., Li, C., & Aber, J. (2000). A process oriented model of N2O and NO emissions from forest soils: sensitivity analysis and validation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105, 4385–4398.
Steppeler, J., Doms, G., Schattler, U., Bitzer, H. W., Gassmann, A., Damrath, U., et al. (2003). Meso-gamma scale forecasts using the non-hydrostatic model LM. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 82, 75–96.
Stolk, P.C., Hendricks, R.F.A., Jacobs, C.M.J., Moors, E.J. (2009). Simulations of nitrous oxide peak emissions from a Dutch peat soil with SWAP-AMINO. In: Proceedings of 5th international symposium on non-CO2 greenhouse gases (NCGG-5), science, reduction policy and implementation, Wageningen, 30 June–3July, 2009.
Sundermeier, A. (2009). The Capability of Cover Crops to Absorb Soil Nutrients [Abstract]. Soil and Water Conservation Society 64th International Annual Conference. Dearborn, MI: 50. www.swcs.org/en/conferences.
Teagasc (2011). Irish Agriculture and Food Development Authority. Access at: www.teagasc.ie.
Tiedje, J. M. (1988). Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium. In A. J. B. Zehner (Ed.), Biology of anaerobic microorganisms (pp. 179–244). New York: Wiley.
Uppala, S. M., Allberg, K., Simmons, P. W., Andrae, A. J., Da Costa, U., Bechtold, V., et al. (2005). The ERA-40 re-analysis. The Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 131, 2961–3012.
Waksman, S. A., & Gerretsen, F. C. (1931). Influence of temperature and moisture upon the nature and extent of decomposition of plant residues by micro-organisms. Ecology, 12, 33–60.
Wagner-Riddle, C., & Thurtell, G. W. (1998). Nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural fields during winter and spring thaw as affected by management practices. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 52, 151–163.
Wang, Y., Xue, M., Zheng, X., Ji, B., Du, R., & Wang, Y. (2005). Effects of environmental factors on N2O emission from and CH4 uptake by the typical grasslands in the Inner Mongolia. Chemosphere, 58, 205–215.
Webb, J., Harrison, R., & Ellis, S. (2000). Nitrogen fluxes in three arable soils in the UK. European Journal of Agronomy, 13, 207–223.
Weier, K. L., Macrae, I. C., & Myers, R. J. K. (1993). Denitrification in clay soil under pasture and annual crop: losses from 15 N-labelled nitrate in the subsoil in the field using C2H2 inhibition. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 25, 999–1004.
Wennman, P., & Katterer, T. (2006). Effects of moisture and temperature on carbon and nitrogen mineralisation in mine tailing mixed with sewage sludge. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 1135–1141.
Wrage, N., Velthof, G. L., van Beusichem, M. L., & Oenema, O. (2001). Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 33, 1723–1732.
Wright, A. L., Hons, F. M., & Matocha, J. J. E. (2005). Tillage impacts on microbial biomass and soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics of corn and cotton rotations. Applied Soil Ecology, 29, 85–92.
Xiong, Z. Q., Xing, G. X., Tsuruta, H., Shen, G. Y., Shi, S. L., & Du, L. J. (2002). Measurement of nitrous oxide emissions from two rice-based cropping systems in China. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 64, 125–133.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by a Teagasc Walsh Fellowship and Nitro-Europe IP (EUFP 6). PS is a Royal Society–Wolfson Research Merit Award holder. Our thanks go to the field staff of the Oak Park Research Centre in maintaining and managing the site, and to technical staff of the Botany Department, Trinity College Dublin in providing help in soil analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdalla, M., Rueangritsarakul, K., Jones, M. et al. How Effective is Reduced Tillage–Cover Crop Management in Reducing N2O Fluxes from Arable Crop Soils?. Water Air Soil Pollut 223, 5155–5174 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1268-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1268-4