Abstract
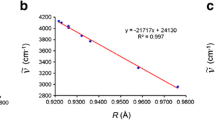
The 17O-NMR spin-lattice relaxation times (T 1) of water molecules in aqueous solutions of n-alkylsulfonate (C1 to C6) and arylsulfonic anions were determined as a function of concentration at 298 K. Values of the dynamic hydration number, \((\mathrm{S}^{-}) = n_{\mathrm{h}}^{ -} (\tau_{\mathrm{c}}^{-} /\tau_{\mathrm{c}}^{0} - 1)\), were determined from the concentration dependence of T 1. The ratios (\(\tau_{\mathrm{c}}^{ -}/\tau_{\mathrm{c}}^{0}\)) of the rotational correlation times (\(\tau_{\mathrm{c}}^{ -} \)) of the water molecules around each sulfonate anion in the aqueous solutions to the rotational correlation time of pure water (\(\tau_{\mathrm{c}}^{0}\)) were obtained from the n DHN(S−) and the hydration number (\(n_{\mathrm{h}}^{ -} \)) results, which was calculated from the water accessible surface area (ASA) of the solute molecule. The \(\tau_{\mathrm{c}}^{ -}/\tau_{\mathrm{c}}^{0}\) values for alkylsulfonate anions increase with increasing ASA in the homologous-series range of C1 to C4, but then become approximately constant. This result shows that the water structures of hydrophobic hydration near large size alkyl groups are less ordered. The rotational motions of water molecules around an aromatic group are faster than those around an n-alkyl group with the same ASA. That is, the number of water–water hydrogen bonds in the hydration water of aromatic groups is smaller in comparison with the hydration water of an n-alkyl group having the same ASA. Hydrophobic hydration is strongly disturbed by a sulfonate group, which acts as a water structure breaker. The disturbance effect decreases in the following order: \(\mbox{--} \mathrm{SO}_{3}^{-} > \mbox{--} \mathrm{NH}_{3}^{ +} > \mathrm{OH}> \mathrm{NH}_{2}\). The partial molar volumes and viscosity B V coefficients for alkylsulfonate anions are linearly dependent on their n DHN(S−) values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uedaira, H., Uedaira, H.: Role of hydration of polyhydroxy compounds in biological systems. Cell. Mol. Biol. 47, 823–830 (2001)
Kornblatt, J.A., Kornblatt, M.J.: Water as its applies to the function of enzymes. Int. Rev. Cyt. 215, 49–73 (2002)
Pal, S.K., Zewail, A.H.: Dynamics of water in biological recognition. Chem. Rev. 104, 2099–2123 (2004)
Dill, K.A., Truskett, T.M., Vlachy, V., Hribar-Lee, B.: Modeling water, the hydrophobic effect, and ion solvation. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 34, 173–199 (2005)
Collins, K.D., Neilson, G.W., Enderby, J.E.: Ions in water: characterizing the forces that control chemical processes and biological structure. Biophys. Chem. 128, 95–104 (2007)
Rand, R.P.: The lipid–water interface: revelations by osmotic stress. Int. Rev. Cyt. 215, 33–48 (2002)
Makhatadze, G.I., Privalov, P.L.: Hydration effects in protein unfolding. Biophys. Chem. 51, 291–309 (1994)
Graziano, G., Lee, B.: Hydration of aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Phys. Chem. B105, 10367–10372 (2001)
Graziano, G.: Aliphatics vs. aromatics hydration thermodynamics. Biophys. Chem. 110, 249–258 (2004)
Privalov, P.L., Makhatadze, G.I.: Heat capacity of proteins. II. Partial molar heat capacity of the unfolded polypeptide chain of proteins: protein unfolding effects. J. Mol. Biol. 213, 385–391 (1990)
Cabani, S., Mollica, V., Lepori, L., Lobo, S.T.: Volume changes in the proton ionization of amines in water. 2. Amino alcohols, amino ethers, and diamines. J. Phys. Chem. 81, 987–993 (1977)
Chalikian, T.V.A., Sarvazyan, P., Breslauer, K.J.: Partial molar volumes, expansibilities, and compressibilities of α,ω-aminocarboxylic acids in aqueous solutions between 18 and 55 °C. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 13017–13026 (1993)
Chalikian, T.V., Gindikin, V.S., Breslauer, K.J.: Hydration of diglycyl tripeptides with non-polar side chains: a volumetric study. Biophys. Chem. 75, 57–71 (1998)
Murphy, K.P.: Hydration and convergence temperature on the use and interpretation of correlation plots. Biophys. Chem. 51, 311–326 (1994)
Makhatadze, G.I., Privalov, P.L.: Energetics of protein structure. Adv. Protein Chem. 47, 307–425 (1995)
Karplus, P.A.: Hydrophobicity regained. Protein Sci. 6, 1302–1307 (1997)
Gallicchio, E., Kubo, M.M., Levy, R.M.: Enthalpy-entropy and cavity decomposition of alkane hydration free energies: numerical results and implications for theories of hydrophobic solvation. J. Phys. Chem. B104, 6271–6285 (2000)
Blokzijl, W., Emgberts, J.B.F.N.: Hydrophobic effects: opinions and facts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 32, 1545–1579 (1993)
Kjellander, R., Marcelja, S.: Perturbation of hydrogen bonding in water near polar surfaces. Chem. Phys. Lett. 120, 393–396 (1985)
Cheng, Y.K., Rossky, P.J.: Surface topography dependence of biomolecular hydrophobic hydration. Nature 392, 696–698 (1998)
Lum, K., Chandler, D., Weeks, J.D.: Hydrophobicity at small and large length scales. J. Phys. Chem. B103, 4570–4577 (1999)
Rajamani, S., Truskett, T.M., Garde, S.: Hydrophobic hydration from small to large lengthscales: understanding and manipulating the crossover. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 9475–9482 (2005)
Okouchi, S., Tsuchida, K., Yoshida, S., Ishihara, Y., Ikeda, S., Uedaira, H.: Dynamics of the hydration of amino alcohols and diamines. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 78, 424–429 (2005)
Okouchi, S., Moto, T., Ishihara, Y., Numajiri, H., Uedaira, H.: Hydration of amines, diamines, polyamines and amides studied by NMR. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 92, 1853–1857 (1996)
Ishihara, Y., Okouchi, S., Uedaira, H.: Dynamics of hydration of alcohols and diols in aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 93, 3337–3342 (1997)
Hertz, H.G.: Microdynamic behaviour of liquids as studied by NMR relaxation times. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 3, 159–230 (1967)
Hertz, H.G., Maurer, R., Killie, S.: An NMR study of dynamics in aqueous strong acid solutions. Part I. The B′ coefficients. Z. Phys. Chem. 172, 157–183 (1991)
Uedaira, H., Uedaira, H.: Nuclear magnetic relaxation of 2H and 23Na in aqueous solutions of sodium sulfonate. Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 107, 1265–1269 (1986)
Lazaridis, T., Paulaitis, M.E.: Simulation studies of the hydration entropy of simple, hydrophobic solutes. J. Phys. Chem. 98, 635–642 (1994)
Tamaki, K., Ohara, Y., Kurachi, H., Akiyama, M., Odaki, H.: Viscosity B coefficients for some homologous series of organic electrolytes in aqueous solutions. The effect of ionic groups. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 47, 384–388 (1974)
Russo, D., Hura, G., Head-Gordon, T.: Hydration dynamics near a model protein surface. Biophys. J. 86, 1852–1862 (2004)
Jorgensen, W.L., Gao, J., Ravimohan, C.: Monte Carlo simulations of alkanes in water: hydration numbers and the hydrophobic effect. J. Phys. Chem. 89, 3470–3473 (1985)
Zielenkiewicz, W., Poznanski, J.: Partial molar volumes of hydrophobic compounds—insight into the solvation shell? Part I. J. Solution Chem. 27, 245–254 (1998)
Uedaira, H., Ishimura, M., Tsuda, S., Uedaira, H.: Hydration of oligosaccharides. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 63, 3376–3379 (1990)
Ishimura, M., Uedaira, H.: Natural-abundance oxygen-17 magnetic relaxation in aqueous solutions of apolar amino acid and glycine peptide. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 63, 1–5 (1990)
Abragam, A.: The Principles of Nuclear Magnetism. Oxford University Press, London (1961)
Bagno, A., Lovato, G., Scorrano, G., Wijnen, J.W.: Solvation of nonelectrolytes in water probed by 17O NMR relaxation of the solvent. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 4601–4607 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okouchi, S., Thanatuksorn, P., Ikeda, S. et al. Dynamics of Hydration of Alkylsulfonate Anions in Aqueous Solutions. J Solution Chem 40, 775–785 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-011-9687-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-011-9687-1