Abstract
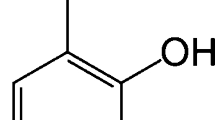
Ethylhexyl triazone (EHT) is a sunscreen agent that is widely used in skin care product formulations, whose physicochemical properties have not been previously studied in detail. For this reason, solubility data were measured for EHT in ethanol (EtOH) + ethyl acetate (AcOEt) mixtures at five temperatures. By using the van’t Hoff and Gibbs equations, the thermodynamic functions: Gibbs energy, enthalpy, and entropy of solution, and of mixing, were evaluated from these solubilities. The solubility is greatest in mixtures with 0.10 and 0.20 mass fraction EtOH, but decrease as the EtOH mass fraction increases in the solvent mixtures. By means of an enthalpy-entropy compensation analysis, a nonlinear \(\Delta H_{\mathrm{soln}}^{0}\) versus \(\Delta G_{\mathrm{soln}}^{0}\) compensation plot was obtained having both negative and positive slopes as the solvent composition was varied. Accordingly to these results, it follows that the driving function for solubility of EHT is the entropy for solutions rich in EtOH or AcOEt, whereas in mixtures of medium composition, the driving function is the enthalpy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuchinda, C., Lim, H.W., Osterwalder, U., Rougier, A.: Novel emerging sunscreen technologies. Dermatol. Clin. 24, 105–117 (2006)
Palm, M.D., O’Donoghue, M.N.: Update on photoprotection. Dermatol. Ther. 20, 360–376 (2007)
Jiménez, F., Martínez, F.: A strategy for systematic selection of cosolvent vehicles in the design of homogeneous liquid pharmaceutical dosage forms. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Quím. Farm. 24, 19–23 (1995)
Tewes, F., Boury, F., Benoit, J.P.: In: Benita, S. (ed.) Microencapsulation: Methods and Industrial Applications, 2nd edn. Taylor & Francis, New York (2006), pp. 1–53
Bustamante, P., Ochoa, R., Reillo, A., Escalera, J.B.: Chameleonic effect of sulfanilamide and sulfamethazine in solvent mixtures: solubility curves with two maxima. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 42, 1129–1133 (1994)
Escalera, J.B., Bustamante, P., Martin, A.: Predicting the solubility of drugs in solvent mixtures: multiple solubility maxima and the chameleonic effect. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 46, 172–176 (1994)
Bustamante, P., Escalera, B.: Enthalpy and entropy contributions to the solubility of sulfamethoxypyridazine in solvent mixtures showing two solubility maxima. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47, 550–555 (1995)
Romero, S., Reillo, A., Escalera, B., Bustamante, P.: The behaviour of paracetamol in mixtures of aprotic and amphiprotic–aprotic solvents: relationship of solubility curves to specific and nonspecific interactions. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 44, 1061–1066 (1996)
Romero, S., Escalera, B., Bustamante, P.: Solubility behavior of polymorphs I and II of mefenamic acid in solvent mixtures. Int. J. Pharm. 178, 193–202 (1999)
Jouyban, A., Romero, S., Chan, H.K., Clark, B.J., Bustamante, P.: A cosolvency model to predict solubility of drugs at several temperatures from a limited number of solubility measurements. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 50, 594–599 (2002)
Bustamante, P., Navarro, J., Romero, S., Escalera, B.: Thermodynamic origin of the solubility profile of drugs showing one or two maxima against the polarity of aqueous and nonaqueous mixtures: niflumic acid and caffeine. J. Pharm. Sci. 91, 874–883 (2002)
Peña, M.A., Reillo, A., Escalera, B., Bustamante, P.: Solubility parameter of drugs for predicting the solubility profile type within a wide polarity range in solvent mixtures. Int. J. Pharm. 321, 155–161 (2006)
Jouyban, A., Acree, Jr. W.E.: Prediction of drug solubility in ethanol–ethyl acetate mixtures at various temperatures using the Jouyban–Acree model. J. Drug Del. Sci. Technol. 17, 159–160 (2007)
Ruidiaz, M.A., Martínez, F.: Extended Hildebrand solubility approach in the estimation of indomethacin solubility in ethyl acetate + ethanol mixtures. Rev. Colomb. Quím. 38, 235–247 (2009)
Ruidiaz, M.A., Vargas, E.F., Martínez, F.: Study of some volumetric properties of the pharmaceutical model solvent system ethanol + ethyl acetate at several temperatures. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 29, 306–312 (2010)
Resa, J.M., González, C., Goenaga, J.M., Iglesias, M.: Temperature dependence of excess molar volumes of ethanol + water + ethyl acetate. J. Solution Chem. 33, 169–198 (2004)
Belda, R., Herraez, J.V., Diez, O.: Rheological study and thermodynamic analysis of the binary system (water/ethanol): influence of concentration. Phys. Chem. Liq. 42, 467–476 (2004)
Jiménez, J.A., Martínez, F.: Temperature dependence of solubility of acetaminophen in propylene glycol + ethanol mixtures. J. Solution Chem. 35, 335–352 (2006)
Kristl, A., Vesnaver, G.: Thermodynamic investigation of the effect of octanol–water mutual miscibility on the partitioning and solubility of some guanine derivatives. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 91, 995–998 (1995)
Barton, A.: Handbook of Solubility Parameters and Other Cohesion Parameters, 2nd edn. CRC Press, New York (1991), pp. 157–193
Krug, R.R., Hunter, W.G., Grieger, R.A.: Enthalpy-entropy compensation. 2. Separation of the chemical from the statistical effects. J. Phys. Chem. 80, 2341–2351 (1976)
Bustamante, P., Romero, S., Peña, A., Escalera, B., Reillo, A.: Nonlinear enthalpy-entropy compensation for the solubility of drugs in solvent mixtures: paracetamol, acetanilide and nalidixic acid in dioxane–water. J. Pharm. Sci. 87, 1590–1596 (1998)
Bevington, P.R.: Data Reduction and Error Analysis for the Physical Sciences. McGraw-Hill, New York (1969)
Perlovich, G.L., Kurkov, S.V., Kinchin, A.N., Bauer-Brandl, A.: Thermodynamics of solutions III: comparison of the solvation of (+)-naproxen with other NSAIDs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 57, 411–420 (2004)
Bustamante, P., Romero, S., Reillo, A.: Thermodynamics of paracetamol in amphiprotic and amphiprotic-aprotic solvent mixtures. Pharm. Sci. 1, 505–507 (1995)
Leffler, J.E., Grunwald, E.: Rates and Equilibria of Organic Reactions. Wiley, New York (1963)
Tomlinson, E.: Enthalpy-entropy compensation analysis of pharmaceutical, biochemical and biological systems. Int. J. Pharm. 13, 115–144 (1983)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, S.J., Cristancho, D.M., Neita, P.C. et al. Solution Thermodynamics of Ethylhexyl Triazone in Some Ethanol + Ethyl Acetate Mixtures. J Solution Chem 39, 1122–1133 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-010-9575-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-010-9575-0