Abstract
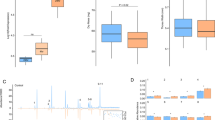
Apis mellifera syriaca is the native honeybee subspecies of Jordan and much of the Levant region. It expresses behavioral adaptations to a regional climate with very high temperatures, nectar dearth in summer, attacks of the Oriental wasp and is resistant to Varroa mites. The A. m. syriaca control reference sample (CRS) in this study was originally collected and stored since 2001 from “Wadi Ben Hammad”, a remote valley in the southern region of Jordan. Morphometric and mitochondrial DNA markers of these honeybees had shown highest similarity to reference A. m. syriaca samples collected in 1952 by Brother Adam of samples collected from the Middle East. Samples 1–5 were collected from the National Center for Agricultural Research and Extension breeding apiary which was established for the conservation of A. m. syriaca. Our objective was to determine the success of an A. m. syriaca honey bee conservation program using genomic information from an array-based comparative genomic hybridization platform to evaluate genetic similarities to a historic reference collection (CRS). Our results had shown insignificant genomic differences between the current population in the conservation program and the CRS indicated that program is successfully conserving A. m. syriaca. Functional genomic variations were identified which are useful for conservation monitoring and may be useful for breeding programs designed to improve locally adapted strains of A. m. syriaca.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arechavaleta-Velasco M, Alcala-Escamilla K, Robles-Rios C, Tsuruda J, Hunt G (2012) Fine-scale linkage mapping reveals a small set of candidate genes influencing honey bee grooming behavior in response to Varroa mites. PLoS ONE 7(11):e47269
Blum R (1956) The bees in the Near East. In: Proceedings of the International Beekeepers Congress, vol 16. Apimondia, Wien, p 28
Bodenheimer S, Ben-Nerya A (1937) One-year studies on the biology of the honey-bee in Palestine. Ann Appl Biol 24(2):385–403
Boecking O, Spivak M (1999) Behavioral defenses of honeybees against Varroa jacobsoni Oud. Apidologie 30(2–3):141–158
Ftayeh A, Meixner M, Fuchs S (1994) Morphometrical investigation in Syrian honeybees. Apidologie 25:396–401
Haddad N (2015) Mitochondrial genome of the Levant region honeybee, Apis mellifera syriaca (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Mitochondrial DNA 30:1–2. doi:10.3109/19401736.2014.1003846
Haddad N, Fuchs S (2004) Honeybee agrobiodiversity: a project in conservation of Apis mellifera syriaca in Jordan. Uludag J 2(3):116–120
Haddad N, Fuchs S, Haddaden J, Kopelke JP (2005) Recording of Sphecophaga vesparum Curtis, a natural enemy of the Vespa orientalis in the northern part of Jordan. Middle East J Zool 35(9):114–116
Haddad N, Evans J, Pettis J, Migdali H (2007) Genetic structure of varroa mite populations in A. mellifera syriaca. Adv Environ Biol 1(1):1–3
Haddad N, Esser J, Neumann P (2008) Association of Cryptophagus hexagonalis (Coleoptera: Cryptophagidae) with honey bee colonies (Apis mellifera). J Apic Res Bee World 47(3):190–191
Haddad N, Meixner M, Fuchs S, Migdadi H, Sheppard W (2009) Mitochondrial DNA variation in honeybees from Jordan. J Apic Res World 48(1):19–22
Haddad N, Batainh A, Migdadi O, Deepti S, Venkatesh K, Sriram P, Alhamuri Z (2015) Next generation sequencing of Apis mellifera syriaca identifies genes for Varroa resistance and beneficial bee keeping traits. Insect Sci. doi:10.1111/1744-7917.12205
Kalman C (1973) Our formerly very aggressive bee. In: Proceedings of the international beekeepers congress, vol 24. Apimondia, Bukarest, pp 306–307
Kence M, Oskay D, Giray T, Kence A (2013) Honeybee colonies from different races show variation in defenses against the varroa mite in a ‘common garden’. Entomol Exp Appl 149(1):36–43. doi:10.1111/eea.12109
Locke DP, Segraves R, Carbone L, Archidiacono N, Albertson DG, Pinkel D, Eichler EE (2003) Large-scale variation among human and great ape genomes determined by array comparative genomic hybridization. Genome Res 13(3):347–357
Navajas M, Migeon A, Alaux C, Martin-Magniette ML, Robinson GE, Evans JD, Cros-Arteil S, Crauser D, Le Conte Y (2008) Differential gene expression of the honeybee Apis mellifera associated with Varroa destructor infection. BMC Genom 9:301
Panova M, Johansson T, Canbäck B, Bentzer J, Rosenblad MA, Johannesson K, Tunlid A, André C (2014) Species and gene divergence in Littorina snails detected by array comparative genomic hybridization. BMC Genom 15:687
Parker R, Guarna MM, Melathopoulos A, Moon KM, White R, Huxter E, Pernal S, Foster L (2012) Correlation of proteome-wide changes with social immunity behaviors provides insight into resistance to the parasitic mite, Varroa destructor, in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Genome Biol 13:R81
Ruttner F (1988) Biogeography and taxonomy of honeybees. Springer, Berlin, pp 284–295
Ruttner F (1992) Naturgeschichte der Honigbienen. Ehrenwirth, München, p 357
Spotter A, Gupta P, Nurnberg G, Reinsch N, Beinefeld K (2012) Development of a 44 K SNP assay focussing on the analysis of a varroa-specific defence behaviour in honey bees (Apis mellifera carnica). Mol Ecol Res 12:323–332
Tsuruda JM, Harris JW, Bourgeois L, Danka RG, Hunt GJ (2012) High-resolution linkage analyses to identify genes that influence varroa sensitive hygiene behavior in honeybees. PLoS ONE 7(11):e48276
Wallberg A, Han F, Wellhagen G, Dahle B, Kawata M, Haddad N, Simões Z, Allsopp M, Kandemir I, De la Rúa P, Pirk C, Webster M (2014) A worldwide survey of genome sequence variation provides insight into the evolutionary history of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nat Genet 46:1081–1088. doi:10.1038/ng.3077
Zakour MK, Ehrhardt K, Bienefeld K (2012) First estimate of genetic parameters for the Syrian honeybee Apis mellifera syriaca. INRA, DIB and Springer, Versailles, New York
Acknowledgements
This research paper is part of the project entitled “Evaluation and Development of Apis mellifera syriaca with Useful keeping Traits for the Middle East Region.” And the project entitled “Impact of the Varroa destructor infestation and its viral load on honeybee colonies in the Middle East and North Africa” funded by USAID grants numbers: TA-MOU-09-M29-075 and TA-MOU-11-M32-035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary table 1
Complete list of significant genome wide alterations (XLSX 68 kb)
Supplementary table 2
List of genes involved in genome wide alterations (XLSX 55 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haddad, N.J., Batainh, A., Saini, D. et al. Evaluation of Apis mellifera syriaca Levant region honeybee conservation using comparative genome hybridization. Genetica 144, 279–287 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-016-9897-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-016-9897-y