Abstract
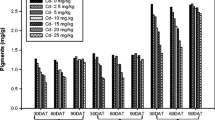
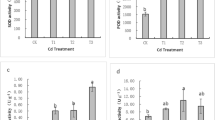
In a preliminary study, we found that the cadmium (Cd) concentrations in shoots of the winter farmland weeds Cardamine hirsuta Linn. and Gnaphalium affine D. Don exceeded the critical value of a Cd-hyperaccumulator (100 mg kg−1), indicating that these two farmland weeds might be Cd-hyperaccumulators. In this study, we grew these species in soil containing various concentrations of Cd to further evaluate their Cd accumulation characteristics. The biomasses of C. hirsuta and G. affine decreased with increasing Cd concentrations in the soil, while the root/shoot ratio and the Cd concentrations in shoot tissues increased. The Cd concentrations in shoots of C. hirsuta and G. affine reached 121.96 and 143.91 mg kg−1, respectively, at the soil Cd concentration of 50 mg kg−1. Both of these concentrations exceeded the critical value of a Cd-hyperaccumulator (100 mg kg−1). The shoot bioconcentration factors of C. hirsuta and G. affine were greater than 1. The translocation factor of C. hirsuta was less than 1 and that of G. affine was greater than 1. These findings indicated that C. hirsuta is a Cd-accumulator and G. affine is Cd-hyperaccumulator. Both plants are distributed widely in the field, and they could be used to remediate Cd-contaminated farmland soil in winter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, A. J. M., & Brooks, R. R. (1989). Terrestrial higher plants which hyperaccumulate metallic elements: a review of their distribution, ecology and phytochemistry. Biorecovery, 1, 81–126.
Bao, S. D. (2000). Soil agrochemical analysis. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, China.
Blaylock, M. J., Salt, D. E., Dushenkov, S., Zakharova, O., Gussman, C., Kapulnik, Y., et al. (1997). Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environmental Science & Technology, 31(3), 860–865.
Brooks, R. R. (1998). Plants that hyperaccumulate heavy metals: Their role in phytoremediation, microbiology, archaeology, mineral exploration and phytomining. Oxford: CAB International.
Brooks, R. R., Lee, J., Reeves, R. D., & Jaffre, T. (1977). Detection of nickeliferous rocks by analysis of herbarium specimens of indicator plants. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 7, 49–57.
Chang, Q. (2013). “Cadmium rice” as a warning to mankind. China Food, 36(11), 56–56 [in Chinese with English summary].
Frey, B., Keller, C., & Zierold, K. (2000). Distribution of Zn in functionally different leaf epidermal cells of the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant, Cell and Environment, 23(7), 675–687.
Ghosh, M., & Singh, S. P. (2005). A comparative study of cadmium phytoextraction by accumulator and weed species. Environmental Pollution, 133, 365–371.
Jiang, H. B. (2011). Contamination of agricultural habitats, preliminary legal regulation. Social Scientist, 26(7), 107–110. [in Chinese with English summary].
Lin, R., Chen, Y. L., Shi, Z., Chen, F. H., Zhang, Z. Q., Hu, Q. M., et al. (1979). Composite. In: X. X. Hu, C. S. Qian, & H. Y. Chen (Eds.), Flora republicae popularis sinicae, 75(2) (pp. 225-226). Beijing: Science Press of China, China.
Liu, Z. L., He, X. Y., Chen, W., Yuan, F. H., Yan, K., & Tao, D. L. (2009). Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in a potential hyperaccumulator-Lonicera japonica Thunb. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169, 170–175.
Lukačová Kuliková, Z., & Lux, A. (2010). Silicon influence on maize, Zea mays L., hybrids exposed to cadmium treatment. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 85(3), 243–250.
Maestri, E., Marmiroli, M., Visioli, G., & Marmiroli, N. (2010). Metal tolerance and hyperaccumulation: costs and trade-offs between traits and environment. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 68(1), 1–13.
McGrath, S. P., Zhao, F. J., & Lombi, E. (2002). Phytoremediation of metals, metalloids, and radionuclides. Advances in Agronomy, 75, 1–56.
Mertens, J., Luyssaert, S., & Verheyen, K. (2005). Use and abuse of trace metal concentrations in plants tissue for biomonitoring and phytoextraction. Environmental Pollution, 138, 1–4.
Nriagu, J. O., & Pacyna, J. M. (1988). Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace-metals. Nature, 333, 134–139.
Reeves, R. D., & Baker, A. J. M. (2000). Metal accumulating plants. In I. Raskin & B. D. Ensley (Eds.), Phytoremediation of toxic metals: Using plant to clean up the environment. New York: Wiley.
Wang, Y., Yan, A., Dai, J., Wang, N. N., & Wu, D. (2012). Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in Chlorophytum comosum: a popular ornamental plant and potential Cd hyperaccumulator. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 929–937.
Wei, S. H., Zhou, Q. X., & Liu, R. (2005). Utilization of weed resource in the remediation of soils contaminated by heavy metals. Journal of Natural Resources, 20(3), 432–440 [in Chinese with English summary].
Wu, L. H., Li, H., Luo, Y. M., & Christie, P. (2004). Nutrients can enhance phytoremediation by Indian mustard. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 26, 331–335.
Zhang, S. R., Chen, M. Y., Li, T., Xu, X. X., & Deng, L. J. (2010). A newly found cadmium accumulator-Malva sinensis Cavan. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 173, 705–709.
Zhang, X. F., Xia, H. P., Li, Z. A., Zhuang, P., & Gao, B. (2011). Identification of a new potential Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum photeinocarpum by soil seed bank-metal concentration gradient method. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 189, 414–419.
Zhang, S. R., Lin, H. C., Deng, L. J., Gong, G. S., Jia, Y. X., Xu, X. X., et al. (2013). Cadmium tolerance and accumulation characteristics of Siegesbeckia orientalis L. Ecological Engineering, 51, 133–139.
Zhao, L. X. (2004). Study on the bioaccumulation character of weeds for heavy metals in contaminated soil. Environmental Protection Science, 30(5), 43–45 [in Chinese with English summary].
Zhao, Y. D., Pan, Y. Z., Liu, B. Y., Yang, H., Hou, Y., Zhang, J. F., et al. (2012). Pilea cadierei Gagnep. et Guill’s growth and accumulation under single and combined pollution of Cd and Pb. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 31(1), 48–53 [in Chinese with English summary].
Zhou, T. Y., Guo, R. L., Lan, Y. Z., Lu, L. L., Guan, K. J., & An, Z. X. (1987). Cruciferae. In X. X. Hu, C. S. Qian, & H. Y. Chen (Eds.), Flora republicae popularis sinicae, 33 (pp. 213–215). Beijing: Science Press of China, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Shi, J., Liu, Q. et al. Cadmium accumulation characteristics of the winter farmland weeds Cardamine hirsuta Linn. and Gnaphalium affine D. Don. Environ Monit Assess 186, 4051–4056 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3679-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3679-8