Abstract
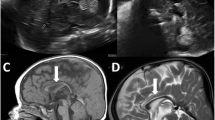
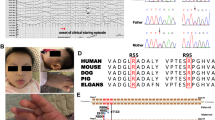
Recessive mutations in genes of the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor synthesis pathway have been demonstrated as causative of GPI deficiency disorders associated with intellectual disability, seizures, and diverse congenital anomalies. We performed whole exome sequencing in a patient with progressive encephalopathies and multiple dysmorphism with hypophosphatasia and identified novel compound heterozygous mutations, c.250G>T (p. Glu84*) and c.1342C>T (p. Arg488Trp), in PIGT encoding a subunit of the GPI transamidase complex. The surface expression of GPI-anchored proteins (GPI-APs) on patient granulocytes was lower than that of healthy controls. Transfection of the Arg488Trp mutant PIGT construct, but not the Glu84* mutant, into PIGT-deficient cells partially restored the expression of GPI-APs DAF and CD59. These results indicate that PIGT mutations caused neurological impairment and multiple congenital anomalies in this patient.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kinoshita T, Fujita M, Maeda Y (2008) Biosynthesis, remodelling and functions of mammalian GPI-anchored proteins: recent progress. J Biochem 144(3):287–294. doi:10.1093/jb/mvn090
Krawitz PM, Schweiger MR, Rodelsperger C, Marcelis C, Kolsch U, Meisel C, Stephani F, Kinoshita T, Murakami Y, Bauer S, Isau M, Fischer A, Dahl A, Kerick M, Hecht J, Kohler S, Jager M, Grunhagen J, de Condor BJ, Doelken S, Brunner HG, Meinecke P, Passarge E, Thompson MD, Cole DE, Horn D, Roscioli T, Mundlos S, Robinson PN (2010) Identity-by-descent filtering of exome sequence data identifies PIGV mutations in hyperphosphatasia mental retardation syndrome. Nat Genet 42(10):827–829. doi:10.1038/ng.653
Krawitz PM, Murakami Y, Hecht J, Kruger U, Holder SE, Mortier GR, Delle Chiaie B, De Baere E, Thompson MD, Roscioli T, Kielbasa S, Kinoshita T, Mundlos S, Robinson PN, Horn D (2012) Mutations in PIGO, a member of the GPI-anchor-synthesis pathway, cause hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 91(1):146–151. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.05.004
Hansen L, Tawamie H, Murakami Y, Mang Y, ur Rehman S, Buchert R, Schaffer S, Muhammad S, Bak M, Nothen MM, Bennett EP, Maeda Y, Aigner M, Reis A, Kinoshita T, Tommerup N, Baig SM, Abou Jamra R (2013) Hypomorphic mutations in PGAP2, encoding a GPI-anchor-remodeling protein, cause autosomal-recessive intellectual disability. Am J Hum Genet 92(4):575–583. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.03.008
Howard MF, Murakami Y, Pagnamenta AT, Daumer-Haas C, Fischer B, Hecht J, Keays DA, Knight SJ, Kolsch U, Kruger U, Leiz S, Maeda Y, Mitchell D, Mundlos S, Phillips JA 3rd, Robinson PN, Kini U, Taylor JC, Horn D, Kinoshita T, Krawitz PM (2014) Mutations in PGAP3 impair GPI-anchor maturation, causing a subtype of hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet 94(2):278–287. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.12.012
Chiyonobu T, Inoue N, Morimoto M, Kinoshita T, Murakami Y (2013) Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor deficiency caused by mutations in PIGW is associated with West syndrome and hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation syndrome. J Med Genet. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-102156
Krawitz PM, Murakami Y, Riess A, Hietala M, Kruger U, Zhu N, Kinoshita T, Mundlos S, Hecht J, Robinson PN, Horn D (2013) PGAP2 mutations, affecting the GPI-anchor-synthesis pathway, cause hyperphosphatasia with mental retardation syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 92(4):584–589. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.03.011
Almeida AM, Murakami Y, Layton DM, Hillmen P, Sellick GS, Maeda Y, Richards S, Patterson S, Kotsianidis I, Mollica L, Crawford DH, Baker A, Ferguson M, Roberts I, Houlston R, Kinoshita T, Karadimitris A (2006) Hypomorphic promoter mutation in PIGM causes inherited glycosylphosphatidylinositol deficiency. Nat Med 12(7):846–851. doi:10.1038/nm1410
Ng BG, Hackmann K, Jones MA, Eroshkin AM, He P, Wiliams R, Bhide S, Cantagrel V, Gleeson JG, Paller AS, Schnur RE, Tinschert S, Zunich J, Hegde MR, Freeze HH (2012) Mutations in the glycosylphosphatidylinositol gene PIGL cause CHIME syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 90(4):685–688. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.010
Johnston JJ, Gropman AL, Sapp JC, Teer JK, Martin JM, Liu CF, Yuan X, Ye Z, Cheng L, Brodsky RA, Biesecker LG (2012) The phenotype of a germline mutation in PIGA: the gene somatically mutated in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Am J Hum Genet 90(2):295–300. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.031
Krawitz PM, Hochsmann B, Murakami Y, Teubner B, Kruger U, Klopocki E, Neitzel H, Hoellein A, Schneider C, Parkhomchuk D, Hecht J, Robinson PN, Mundlos S, Kinoshita T, Schrezenmeier H (2013) A case of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria caused by a germline mutation and a somatic mutation in PIGT. Blood 122(7):1312–1315. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-01-481499
Kvarnung M, Nilsson D, Lindstrand A, Korenke GC, Chiang SC, Blennow E, Bergmann M, Stodberg T, Makitie O, Anderlid BM, Bryceson YT, Nordenskjold M, Nordgren A (2013) A novel intellectual disability syndrome caused by GPI anchor deficiency due to homozygous mutations in PIGT. J Med Genet 50(8):521–528. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2013-101654
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43(5):491–498. doi:10.1038/ng.806
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H (2010) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38(16):e164. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq603
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7(4):248–249. doi:10.1038/nmeth0410-248
Schwarz JM, Rodelsperger C, Schuelke M, Seelow D (2010) MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat Methods 7(8):575–576. doi:10.1038/nmeth0810-575
Ohishi K, Inoue N, Kinoshita T (2001) PIG-S and PIG-T, essential for GPI anchor attachment to proteins, form a complex with GAA1 and GPI8. EMBO J 20(15):4088–4098. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.15.4088
Ashida H, Hong Y, Murakami Y, Shishioh N, Sugimoto N, Kim YU, Maeda Y, Kinoshita T (2005) Mammalian PIG-X and yeast Pbn1p are the essential components of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-mannosyltransferase I. Mol Biol Cell 16(3):1439–1448. doi:10.1091/mbc.E04-09-0802
Genomes Project C, Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Gibbs RA, Hurles ME, McVean GA (2010) A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 467(7319):1061–1073. doi:10.1038/nature09534
Genomes Project C, Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker RE, Kang HM, Marth GT, McVean GA (2012) An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 491(7422):56–65. doi:10.1038/nature11632
Murakami Y, Kanzawa N, Saito K, Krawitz PM, Mundlos S, Robinson PN, Karadimitris A, Maeda Y, Kinoshita T (2012) Mechanism for release of alkaline phosphatase caused by glycosylphosphatidylinositol deficiency in patients with hyperphosphatasia mental retardation syndrome. J Biol Chem 287(9):6318–6325. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.331090
Mornet E (2007) Hypophosphatasia. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2:40. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-40
Acknowledgments
We thank the patient’s family for participating in this work. We also thank Nobuko Watanabe for her technical assistance. This study was supported by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan, a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A), (B), and (C) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Takeda Science Foundation, the fund for Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas Program in the Project for Developing Innovation Systems, the Strategic Research Program for Brain Sciences, and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (Transcription Cycle) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakashima, M., Kashii, H., Murakami, Y. et al. Novel compound heterozygous PIGT mutations caused multiple congenital anomalies-hypotonia-seizures syndrome 3. Neurogenetics 15, 193–200 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-014-0408-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10048-014-0408-y