Abstract
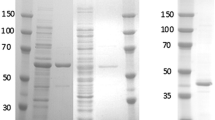
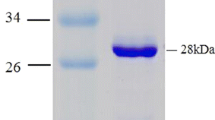
The NAD-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) gene from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei has been cloned. The analysis of the nucleotide sequence revealed an open reading frame of 1323 bp that encodes a NAD-GDH. The amino acid sequence displayed high homology with those from other sources, especially the highly conserved residues involved in 2-oxoglutarate binding. The expression of this gene in Escherichia coli, the refolding and further characterization, yielded a fully active NAD-GDH with the same features than those found for the wild-type enzyme. This halophilic NAD-GDH showed a highly dependence on salts for both stability and activity, being essential for the refolding of the recombinant enzyme.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker PJ, Briton KL, Engel PC, Farrants GW, Lilley KS, Rice DW, Stillman TJ (1992) Subunit assembly and active site location in the structure of glutamate dehydrogenase. Proteins 12:75–86
Bonete MJ, Camacho ML, Cadenas E (1986) Purification and some properties of NAD-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase from Halobacterium halobium. Int J Biochem 18:785–789
Bonete MJ, Camacho ML, Cadenas E (1987) A new glutamate dehydrogenase from Halobacterium halobium with different coenzyme specificity. Int J Biochem 19:1149–1155
Bonete MJ, Pire C, Llorca FI, Camacho ML (1996) Glucose dehydrogenase from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: enzyme purification, characterization and N-terminal sequence. FEBS Lett 383:227–229
Bonete MJ, Pérez-Pomares F, Díaz S, Ferrer J, Oren A (2003) Occurrence of two different glutamate dehydrogenase activities in the halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber. FEMS Microbiol Lett 226:181–186
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bright JR, Byrom D, Danson MJ, Hough DW, Towner P (1993) Cloning sequencing and expression of the gene encoding glucose dehydrogenase from the thermophilic archaeon Thermoplasma acidophilum. Eur J Biochem 211:549–554
Britton KL, Stillman TJ, Yip KSP, Forterre P, Engel PC, Rice DW (1998) Insights into the molecular basis of salt tolerance from the study of glutamate dehydrogenase from Halobacterium salinarum . J Biol Chem 273:9023–9030
Camacho ML, Brown RA, Bonete MJ, Danson MJ, Hough DW (1995) Isocitrate dehydrogenase from Haloferax volcanii and Sulfolobus solfataricus: enzyme purification, characterisation and N-terminal sequence. FEMS Microbiol Lett 134:85–90
Connaris H, Chaudhuri JB, Danson MJ, Hough DW (1999) Expression, reactivation, and purification of enzymes from Haloferax volcanii in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioengin 64:38–45
Danson MJ, Hough DW (1997) The structural basis of halophilicity. Comp Biochem Physiol 117A:307–312
De Bernardez E (2001) Protein refolding for industrial processes. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12:202–207
Dyall-Smith M, Doolittle WF (1994) Construction of composite transposons for halophilic Archaea. Can J Microbiol 40:922–929
Dym O, Mevarech M, Sussman JL (1995) Structural features that stabilize halophilic malate dehydrogenase from archaebacterium. Science 267:1344–1346
Ferrer J, Pérez-Pomares F, Bonete MJ (1996) NADP-glutamate dehydrogenase from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: enzyme purification, N-terminal sequence and stability. FEMS Microbiol Lett 141:59–63
Hayden BM, Bonete MJ, Brown PE, Moir AJG, Engel P (2002) Glutamate dehydrogenase of Halobacterium salinarum: evidence that the gene sequence currently assigned to the NADP+ -dependent enzyme is in fact that of the NAD+ -dependent glutamate dehydrogenase. FEMS Microbiol Lett 211:37–41
Jolley KA, Rapaport E, Hough DW, Danson MJ, Woods WG, Dyall-Smith M (1996) Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase from the halophilic Archaeon Haloferax volcanii: homologous overexpression of the cloned gene. J Bacteriol 178:3044–3048
Knapp S, De Vos WM, Rice Dy, Ladenstein R (1997) Crystal structure of glutamate dehydrogenase from hypertermophilic eubacterium Thermotoga marítima at 3.0 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 267:916–932
Kushner DJ (1985) The Halobacteriaceae. In: Woese CR, Wolfe RS (eds) The bacteria, vol III. Academic Press, NY, pp 171–214
Lilley KS, Engel PC (1992) The essential active-site lysines of clostridial glutamate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem 207:533–540
Madern D, Camacho M, Rodriguez-Arnedo A, Bonete MJ, Zaccai G (2004) Salt dependent studies of NADP dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase form the halophilic archaeon Haloferax volcanii. Extremophiles 8:377–384
Martínez-Espinosa RM, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Bonete MJ (2001) Assimilatory nitrate reductase from the haloarchaeon Haloferax mediterranei: purification and characterization. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204:381–385
Martínez-Espinosa RM, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Donaire A, Bonete MJ (2003) NMR studies of a ferredoxin from Haloferax mediterranei and its physiological role in nitrate assimilatory pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1623:47–51
Palmer JR, Daniels CJ (1995) In vivo definition of an archaeal promoter. J Bacteriol 177:1844–1849
Pérez-Pomares F, Ferrer J, Camacho M, Pire C, Llorca F, Bonete MJ (1999) Amino acid residues implied in the catalytic mechanism of NAD-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase from Halobacterium salinarum Biochim Biophys Acta 1426:513–525
Pérez-Pomares F, Bautista V, Ferrer J, Pire C, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Bonete MJ (2003) α-Amylase activity from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. Extremophiles 7: 299–306
Pire C, Esclapez J, Ferrer J, Bonete MJ (2001) Heterologous overexpression of glucose dehydrogenase from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei, an enzyme of the medium chain dehydrogenase family. FEMS Microbiol Lett 200:221–227
Rice DW, Yip KSP, Stillman TJ, Britton KL, Fuentes A, Connerton I, Pasquo A, Scandurra R, Engel PC (1996). Insights into the molecular basis of thermal stability from the structure determination of Pyrococcus furiosus glutamate dehydrogenase. FEMS Microbiol Rev 18:105–117
Rodríguez-Valera F, Juez G, Kushner DJ (1983) Halobacterium mediterranei spec. nov., a new carbohydrate-utilizing extreme halophile. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:369–381
Ruiz JL, Ferrer J, Camacho M, Bonete MJ (1998) NADP-specific glutamate dehydrogenase from Thermus Thermophilus H8: purification and enzymatic properties. FEMS Microbiol Lett 159:15–22
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain- terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5476
Serrano JA, Camacho M, Bonete MJ (1998) Operation of glyoxylate cycle in halophilic archaea: presence of malate synthase and isocitrate lyase in Haloferax volcanii. FEBS Lett 434:13–16
Smith EL, Austen BM, Blumenthal KM, Nyc JF (1975) Glutamate dehydrogenase. In: Boyer PD (ed) The enzymes, vol 11, 3rd edn. Academic Press, NY, pp 293–367
Studier FW, Rosenberg AH, Dunn JJ, Dubendorf JW (1990) Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Meth Enzymol 185:60–89
Teller JF, Smith RJ, McPherson MJ, Engel PC, Guest JR (1992) The glutamate dehydrogenase gene of Clostridium symbiosum: cloning by polymerase chain reaction, sequence analysis and over-expression in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 206:151–159
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Veronese FM, Nyc JF, Degani Y, Brown DM, Smith EL (1974) Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-specific glutamate dehydrogenase from Neurospora. J Biol Chem 249:7922–7928
Wang S, Feng Y, Zhang Z, Zheng B, Li N, Cao S, Matsui I, Kosugi Y (2003) Heat effect on the structure and activity of the recombinant glutamate dehydrogenase from a hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii. Arch Biochem Biophys 411:56–62
Werber MM, Sussman JL, Eisenberg H (1986) Molecular basis for the special properties of proteins and enzymes from Halobacterium marimortui. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39:129–135
Wierenga RK, De Maeyer MCH, Hol WGJ (1985) Interaction of pyrophosphate moieties with α-helix in dinucleotide binding proteins. Biochemistry 24:1346–1357
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Castillo from Proquimur Company for allowing us the nanoLC/MS in collaboration of Agilent Technologies Company in Germany. DNA sequencing was carried out in “Unidad de Biología Molecular y Análisis Genético” of Servicios Técnicos de Investigación (Universidad de Alicante). Financial support is gratefully acknowledged from MCYT (BIO2002-03179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz, S., Pérez-Pomares, F., Pire, C. et al. Gene cloning, heterologous overexpression and optimized refolding of the NAD-glutamate dehydrogenase from Haloferax mediterranei. Extremophiles 10, 105–115 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0478-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-005-0478-8