Abstract
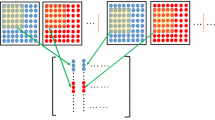
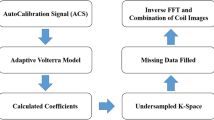
The image quality of iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction (SPIRiT) algorithm highly depends on the accuracy of linear coefficients which can be easily influenced by k-space noise. In this study, an improved calibration framework for SPIRiT is presented to reduce noise-induced errors and to adaptively generate optimal linear weighting coefficients. Specifically, the auto-calibration signals (ACS) are first mapped to a high-dimensional feature space through a polynomial mapping, and the optimal coefficients are adaptively obtained in this new feature space with discrepancy-based Tikhonov regularization and then truncated for SPIRiT reconstruction. Phantom and in vivo brain reconstruction were, respectively, performed and this calibration framework was mainly evaluated in Cartesian k-space-based SPIRiT reconstruction. In both phantom and in vivo reconstructions, noise-induced errors can be reduced by polynomial mapping and optimal regularization parameter, which improves the accuracy of linear coefficients. Both qualitative and quantitative results demonstrated that the proposed calibration framework resulted in better image quality without loss of resolution compared with the conventional calibration at different acceleration factors. The proposed calibration framework can effectively improve SPIRiT image quality.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.K. Sodickson, W.J. Manning, Magn. Reson. Med. 38, 591–603 (1997)
K.P. Pruessmann, M. Weiger, M.B. Scheidegger, P. Boesiger, Magn. Reson. Med. 42, 952–962 (1999)
K. Pruessmann, M. Weiger, P. Bornert, P. Boesiger, Magn. Reson. Med. 46, 638–651 (2001)
L. Chen, Y. Chang, L. Wang, X. Yang, Comput. Meas. Control. 23, 4177–4179 (2015)
A.A. Samsonov, E.G. Kholmovski, D.L. Parker, C.R. Johnson, Magn. Reson. Med. 52, 1397–1406 (2004)
M.A. Griswold, P.M. Jakob, R.M. Heidemann, M. Nittka, V. Jellus, J. Wang, B. Kiefer, A. Haase, Magn. Reson. Med. 47, 1202–1210 (2002)
Z. Wang, J. Wang, J.A. Detre, Magn. Reson. Med. 54, 738–742 (2005)
R. Nana, X. Hu, Magn. Reson. Imaging 28, 119–128 (2010)
F.H. Lin, K.K. Kwong, J.W. Belliveau, L.L. Wald, Magn. Reson. Med. 51, 559–567 (2004)
W. Liu, X. Tang, Y. Ma, J. Gao, Magn. Reson. Med. 69, 1109–1114 (2013)
H. Wang, D. Liang, K.F. King, G. Nagarsekar, Y. Chang, L. Ying, Magn. Reson. Med. 67, 1042–1053 (2012)
B. Sharif, Y. Bresler, in: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Chicago, 2011, p. 52–56
Y. Chang, D. Liang, L. Ying, Magn. Reson. Med. 68, 730–740 (2012)
D. Wang, S. Bao, Chin. J. Med. Imaging Technol. 27, 1688–1693 (2011)
L. Chen, Y. Chang, L. Wang, L. Wang, Y. Xu, G. Zhang, X. Yang, Chin. J. Med. Phys. 32, 617–621 (2015)
M. Lustig, J.M. Pauly, Magn. Reson. Med. 64, 457–471 (2010)
P. Qu, C. Wang, G.X. Shen, J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 24, 248–255 (2006)
X. Shi, X. Ma, W. Wu, F. Huang, C. Yuan, H. Guo, Magn. Reson. Med. 73, 1775–1785 (2015)
M. Murphy, M. Alley, J. Demmel, K. Keutzer, S. Vasanawala, M. Lustig, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 31, 1250–1262 (2012)
K.H. Jin, D. Lee, J.C. Ye, IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging. 2, 480–495 (2016)
C. Liao, Y. Chen, X. Cao, S. Chen, H. He, M. Mani, M. Jacob, V. Magnotta, J. Zhong, Magn. Reson. Med. 77, 1359–1366 (2017)
M. Lustig, D. Donoho, J.M. Pauly, Magn. Reson. Med. 58, 1182–1195 (2007)
J. Zhang, J. Shi, H. Guang, S. Zuo, F. Liu, J. Bai, J. Luo, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 63, 1107–1115 (2016)
D.J. Holland, D.M. Malioutov, A. Blake, A.J. Sederman, L.F. Gladden, J. Magn. Reson. 203, 236–246 (2010)
Y. Chen, X. Ye, F. Huang, Inverse Problems Imaging 4, 223–240 (2017)
R. Otazo, E. Candès, D.K. Sodickson, Magn. Reson. Med. 73, 1125–1136 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Instrument Developing Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. YZ201445) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11505281; 11675254).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z., Zhu, J., Chang, Y. et al. An Improved Calibration Framework for Iterative Self-Consistent Parallel Imaging Reconstruction (SPIRiT). Appl Magn Reson 50, 103–120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-018-1036-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-018-1036-8