Abstract
Background
Minimally invasive treatment may be an alternative to breast-conserving surgery.
Methods
A structured PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, and Web of Science search was performed. Endpoints studied were feasibility, completeness of ablation, timing of the sentinel node biopsy (SNB), imaging modalities, and treatment-related complications.
Results
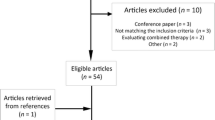
A total of 24 articles were retrieved, and the level of evidence varied (2B-4). Mainly phase II studies with a treat-and-resect protocol were analyzed. Up to 100% completeness of ablation was reported for radiofrequency ablation (RFA), cryosurgery, and focused ultrasound (FUS). The oncologic results need further evaluation. Dynamic contrast enhanced MRI seems to be the best method for monitoring treatment response (77% sensitivity, 100% specificity). Ultrasound is suitable for guiding probes into the tumor. There is no consensus on the timing of the SNB.
Conclusions
All studies on minimally invasive ablative modalities published so far show that these techniques are feasible and safe. At this stage only T1 tumors should be ablated in a clinical trial setting; it is unclear which of the modalities is most suitable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. (2007) Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 57(1):43–66
Elmore JG, Armstrong K, Lehman CD, et al. (2005) Screening for breast cancer. JAMA 293(10):1245–1256
Arriagada R, Le MG, Guinebretiere JM, et al. (2003) Late local recurrences in a randomised trial comparing conservative treatment with total mastectomy in early breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol 14(11):1617–1622
Bajaj AK, Kon PS, Oberg KC, et al. (2004) Aesthetic outcomes in patients undergoing breast conservation therapy for the treatment of localized breast cancer. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(6):1442–1449
Bakker XR, Roumen RM (2002) Bleeding after excision of breast lumps. Eur J Surg 168(7):401–403
Dian D, Schwenn K, Mylonas I, et al. (2007) Aesthetic result among breast cancer patients undergoing autologous breast reconstruction versus breast conserving therapy. Arch Gynecol Obstet 275(6):445–450
El Tamer MB, Ward BM, Schifftner T, et al. (2007) Morbidity and mortality following breast cancer surgery in women: national benchmarks for standards of care. Ann Surg 245(5):665–671
Furey PC, Macgillivray DC, Castiglione CL, et al. (1994) Wound complications in patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy after mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for breast cancer. J Surg Oncol 55(3):194–197
Burak WE Jr, Agnese DM, Povoski SP, et al. (2003) Radiofrequency ablation of invasive breast carcinoma followed by delayed surgical excision. Cancer 98(7):1369–1376
Dowlatshahi K, Francescatti DS, Bloom KJ (2002) Laser therapy for small breast cancers. Am J Surg 184(4):359–363
Gardner RA, Vargas HI, Block JB, et al. (2002) Focused microwave phased array thermotherapy for primary breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 9(4):326–332
Pfleiderer SO, Marx C, Camara O, et al. (2005) Ultrasound-guided, percutaneous cryotherapy of small (< or = 15 mm) breast cancers. Invest Radiol 40(7):472–477
Wu F, Wang ZB, Cao YD, et al. (2003) A randomised clinical trial of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for the treatment of patients with localised breast cancer. Br J Cancer 89(12):2227–2233
Oura S, Tamaki T, Hirai I, et al. (2007) Radiofrequency ablation therapy in patients with breast cancers two centimeters or less in size. Breast Cancer 14(1):48–54
Mazur P (1970) Cryobiology: the freezing of biological systems. Science 168(934):939–949
Heisterkamp J, van Hillegersberg R, IJzermans JN (1999) Critical temperature and heating time for coagulation damage: implications for interstitial laser coagulation (ILC) of tumors. Lasers Surg Med 25(3):257–262
Heisterkamp J, van Hillegersberg R, Zondervan PE, et al. (2001) Metabolic activity and DNA integrity in human hepatic metastases after interstitial laser coagulation (ILC). Lasers Surg Med 28(1):80–86
Izzo F, Thomas R, Delrio P, et al. (2001) Radiofrequency ablation in patients with primary breast carcinoma: a pilot study in 26 patients. Cancer 92(8):2036–2044
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, Mayo-Smith WW (2005) Microwave ablation: principles and applications. Radiographics 25(Suppl 1):S69–S83
Halpern EJ (2005) Science to practice: High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation: will image-guided therapy replace conventional surgery? Radiology 235(2):345–346
Morin J, Traore A, Dionne G, et al. (2004) Magnetic resonance-guided percutaneous cryosurgery of breast carcinoma: technique and early clinical results. Can J Surg 47(5):347–351
Roubidoux MA, Sabel MS, Bailey JE, et al. (2004) Small (<2.0-cm) breast cancers: mammographic and US findings at US-guided cryoablation–initial experience. Radiology 233(3):857–867
Sabel MS, Kaufman CS, Whitworth P, et al. (2004) Cryoablation of early-stage breast cancer: work-in-progress report of a multi-institutional trial. Ann Surg Oncol 11(5):542–549
Fornage BD, Sneige N, Ross MI, et al. (2004) Small (<or = 2-cm) breast cancer treated with US-guided radiofrequency ablation: feasibility study. Radiology 231(1):215–224
Hayashi AH, Silver SF, van der Westhuizen NG, et al. (2003) Treatment of invasive breast carcinoma with ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation. Am J Surg 185(5):429–435
Jeffrey SS, Birdwell RL, Ikeda DM, et al. (1999) Radiofrequency ablation of breast cancer: first report of an emerging technology. Arch Surg 134(10):1064–1068
Marcy PY, Magne N, Castadot P, et al. (2007) Ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation in elderly breast cancer patients: preliminary institutional experience. Br J Radiol 80(952):267-273
Susini T, Nori J, Olivieri S, et al. (2007) Radiofrequency ablation for minimally invasive treatment of breast carcinoma. A pilot study in elderly inoperable patients. Gynecol Oncol 104(2):304-310
Akimov AB, Seregin VE, Rusanov KV, et al. (1998) Nd:YAG interstitial laser thermotherapy in the treatment of breast cancer. Lasers Surg Med 22(5):257–267
Bloom KJ, Dowlat K, Assad L (2001) Pathologic changes after interstitial laser therapy of infiltrating breast carcinoma. Am J Surg 182(4):384–388
Harries SA, Amin Z, Smith ME, et al. (1994) Interstitial laser photocoagulation as a treatment for breast cancer. Br J Surg 81(11):1617–1619
Mumtaz H, Hall-Craggs MA, Wotherspoon A, et al. (1996) Laser therapy for breast cancer: MR imaging and histopathologic correlation. Radiology 200(3):651–658
Furusawa H, Namba K, Thomsen S, et al. (2006) Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound surgery of breast cancer: reliability and effectiveness. J Am Coll Surg 203(1):54–63
Gianfelice D, Khiat A, Amara M, et al. (2003) MR imaging-guided focused ultrasound surgery of breast cancer: correlation of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI with histopathologic findings. Breast Cancer Res Treat 82(2):93–101
Zippel DB, Papa MZ (2005) The use of MR imaging-guided focused ultrasound in breast cancer patients; a preliminary phase one study and review. Breast Cancer 12(1):32–38
Vargas HI, Dooley WC, Gardner RA, et al. (2003) Success of sentinel lymph node mapping after breast cancer ablation with focused microwave phased array thermotherapy. Am J Surg 186(4):330–332
Vargas HI, Dooley WC, Gardner RA, et al. (2004) Focused microwave phased array thermotherapy for ablation of early-stage breast cancer: results of thermal dose escalation. Ann Surg Oncol 11(2):139–146
Forsberg F, Goldberg BB, Merritt CR, et al. (2004) Diagnosing breast lesions with contrast-enhanced 3-dimensional power Doppler imaging. J Ultrasound Med 23(2):173–182
Quesson B, de Zwart JA, Moonen CT (2000) Magnetic resonance temperature imaging for guidance of thermotherapy. J Magn Reson Imaging 12(4):525–533
Bageacu S, Kaczmarek D, Lacroix M, et al. (2007) Cryosurgery for resectable and unresectable hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 33(5):590-596
Wu YC, Chen DR, Kuo SJ (2006) Personal experience of ultrasound-guided 14-gauge core biopsy of breast tumor. Eur J Surg Oncol 32(7):715–718
Bergkvist L, Frisell J (2005) Multicentre validation study of sentinel node biopsy for staging in breast cancer. Br J Surg 92(10):1221–1224
Hung WK, Chan CM, Ying M, et al. (2005) Randomized clinical trial comparing blue dye with combined dye and isotope for sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer. Br J Surg 92(12):1494–1497
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Esser, S., van den Bosch, M.A.A.J., van Diest, P.J. et al. Minimally Invasive Ablative Therapies for Invasive Breast Carcinomas: An Overview of Current Literature. World J Surg 31, 2284–2292 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-007-9278-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-007-9278-x