Abstract
Purpose
Two-helix scaffold proteins (~ 5 kDa) against human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 (HER2) have been discovered in our previous work. In this research we aimed to develop an 18F-labeled two-helix scaffold protein for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of HER2-positive tumors.
Methods
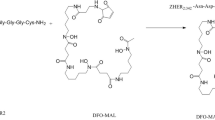
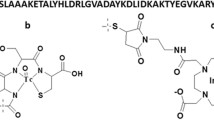
An aminooxy-functionalized two-helix peptide (AO-MUT-DS) with high HER2 binding affinity was synthesized through conventional solid phase peptide synthesis. The purified linear peptide was cyclized by I2 oxidation to form a disulfide bridge. The cyclic peptide was then conjugated with a radiofluorination synthon, 4-18F-fluorobenzyl aldehyde (18F-FBA), through the aminooxy functional group at the peptide N terminus (30% yield, non-decay corrected). The binding affinities of the peptides were analyzed by Biacore analysis. Cell uptake assay of the resulting PET probe, 18F-FBO-MUT-DS, was performed at 37°C. 18F-FBO-MUT-DS with high specific activity (20–32 MBq/nmol, 88–140 μCi/μg, end of synthesis) was injected into mice xenograft model bearing SKOV3 tumor. MicroPET and biodistribution and metabolic stability studies were then conducted.
Results
Cell uptake assays showed high and specific cell uptake (~12% applied activity at 1 h) by incubation of 18F-FBO-MUT-DS with HER2 high-expressing SKOV3 ovarian cancer cells. The affinities (KD) of AO-MUT-DS and FBO-MUT-DS as tested by Biacore analysis were 2 and 1 nM, respectively. In vivo small animal PET demonstrated fast tumor targeting, high tumor accumulation, and good tumor to normal tissue contrast of 18F-FBO-MUT-DS. Biodistribution studies further revealed that the probe had excellent tumor uptake (6.9%ID/g at 1 h post-injection) and was cleared through both liver and kidneys. Co-injection of the probe with 500 μg of HER2 Affibody protein reduced the tumor uptake (6.9 vs 1.8%ID/g, p < 0.05).
Conclusion
F-FBO-MUT-DS displays excellent HER2 targeting ability and tumor PET imaging quality. The two-helix scaffold proteins are suitable for development of 18F-based PET probes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HER2:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor type 2
- FBO:
-
Fluorobenzyl oxime
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- p.i.:
-
Post-injection
References
Getmanova EV, Chen Y, Bloom L, Gokemeijer J, Shamah S, Warikoo V, et al. Antagonists to human and mouse vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 generated by directed protein evolution in vitro. Chem Biol 2006;13:549–56.
Jonsson A, Wållberg H, Herne N, Ståhl S, Frejd FY. Generation of tumour-necrosis-factor-alpha-specific affibody molecules capable of blocking receptor binding in vitro. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 2009;54:93–103.
Kimura RH, Levin AM, Cochran FV, Cochran JR. Engineered cystine knot peptides that bind alphavbeta3, alphavbeta5, and alpha5beta1 integrins with low-nanomolar affinity. Proteins 2009;77:359–69.
Orlova A, Magnusson M, Eriksson TL, Nilsson M, Larsson B, Höidén-Guthenberg I, et al. Tumor imaging using a picomolar affinity HER2 binding affibody molecule. Cancer Res 2006;66:4339–48.
Silverman AP, Levin AM, Lahti JL, Cochran JR. Engineered cystine-knot peptides that bind alpha(v)beta(3) integrin with antibody-like affinities. J Mol Biol 2009;385:1064–75.
Gill DS, Damle NK. Biopharmaceutical drug discovery using novel protein scaffolds. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2006;17:653–8.
Orlova A, Tolmachev V, Pehrson R, Lindborg M, Tran T, Sandström M, et al. Synthetic affibody molecules: a novel class of affinity ligands for molecular imaging of HER2-expressing malignant tumors. Cancer Res 2007;67:2178–86.
Meric-Bernstam F, Hung MC. Advances in targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 signaling for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:6326–30.
Leader B, Baca QJ, Golan DE. Protein therapeutics: a summary and pharmacological classification. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008;7:21–39.
Artemov D, Mori N, Ravi R, Bhujwalla ZM. Magnetic resonance molecular imaging of the HER-2/neu receptor. Cancer Res 2003;63:2723–7.
Hilger I, Leistner Y, Berndt A, Fritsche C, Haas KM, Kosmehl H, et al. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging of HER-2 protein over-expression in tumour cells. Eur Radiol 2004;14:1124–9.
Engfeldt T, Orlova A, Tran T, Bruskin A, Widström C, Karlström AE, et al. Imaging of HER2-expressing tumours using a synthetic Affibody molecule containing the 99mTc-chelating mercaptoacetyl-glycyl-glycyl-glycyl (MAG3) sequence. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:722–33.
Nilsson FY, Tolmachev V. Affibody molecules: new protein domains for molecular imaging and targeted tumor therapy. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel 2007;10:167–75.
Steffen AC, Orlova A, Wikman M, Nilsson FY, Ståhl S, Adams GP, et al. Affibody-mediated tumour targeting of HER-2 expressing xenografts in mice. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;33:631–8.
Cheng Z, De Jesus OP, Kramer DJ, De A, Webster JM, Gheysens O, et al. 64Cu-labeled affibody molecules for imaging of HER2 expressing tumors. Mol Imaging Biol 2009;12:316–24.
Eigenbrot C, Ultsch M, Dubnovitsky A, Abrahmsén L, Härd T. Structural basis for high-affinity HER2 receptor binding by an engineered protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010;107:15039–44.
Webster JM, Zhang R, Gambhir SS, Cheng Z, Syud FA. Engineered two-helix small proteins for molecular recognition. Chembiochem 2009;10:1293–6.
Ren G, Zhang R, Liu Z, Webster JM, Miao Z, Gambhir SS, et al. A 2-helix small protein labeled with 68Ga for PET imaging of HER2 expression. J Nucl Med 2009;50:1492–9.
Cheng Z, De Jesus OP, Namavari M, De A, Levi J, Webster JM, et al. Small-animal PET imaging of human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2 expression with site-specific 18F-labeled protein scaffold molecules. J Nucl Med 2008;49:804–13.
Namavari M, Padilla De Jesus O, Cheng Z, De A, Kovacs E, Levi J, et al. Direct site-specific radiolabeling of an Affibody protein with 4-[18F]fluorobenzaldehyde via oxime chemistry. Mol Imaging Biol 2008;10:177–81.
Miao Z, Ren G, Liu H, Jiang L, Cheng Z. Small-animal PET imaging of human epidermal growth factor receptor positive tumor with a 64Cu labeled affibody protein. Bioconjug Chem 2010;21:947–54.
Jiang L, Kimura RH, Miao Z, Silverman AP, Ren G, Liu H, et al. Evaluation of a (64)Cu-labeled cystine-knot peptide based on agouti-related protein for PET of tumors expressing alphavbeta3 integrin. J Nucl Med 2010;51:251–8.
Perik PJ, Lub-De Hooge MN, Gietema JA, van der Graaf WT, de Korte MA, Jonkman S, et al. Indium-111-labeled trastuzumab scintigraphy in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2006;24:2276–82.
Tai W, Mahato R, Cheng K. The role of HER2 in cancer therapy and targeted drug delivery. J Control Release 2010;146:264–75.
Gill HS, Tinianow JN, Ogasawara A, Flores JE, Vanderbilt AN, Raab H, et al. A modular platform for the rapid site-specific radiolabeling of proteins with 18F exemplified by quantitative positron emission tomography of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. J Med Chem 2009;52:5816–25.
Kramer-Marek G, Kiesewetter DO, Martiniova L, Jagoda E, Lee SB, Capala J. [18F]FBEM-Z(HER2:342)-Affibody molecule-a new molecular tracer for in vivo monitoring of HER2 expression by positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:1008–18.
Baum RP, Prasad V, Müller D, Schuchardt C, Orlova A, Wennborg A, et al. Molecular imaging of HER2-expressing malignant tumors in breast cancer patients using synthetic 111In- or 68Ga-labeled affibody molecules. J Nucl Med 2010;51:892–7.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by the California Breast Cancer Research Program 14IB-0091 and an SNM Pilot Research Grant (ZC). We also thank the Radiochemistry Facility at MIPS for their help on 18F production.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, Z., Ren, G., Jiang, L. et al. A novel 18F-labeled two-helix scaffold protein for PET imaging of HER2-positive tumor. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38, 1977–1984 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1879-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1879-9