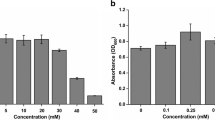
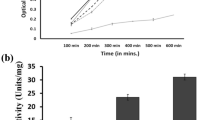
Abstract
Arsenic is a naturally occurring ubiquitous highly toxic metalloid. In this study, we have identified ars gene cluster in Pannonibacter indicus strain HT23T (DSM 23407T), responsible for reduction of toxic pentavalent arsenate. The ars gene cluster is comprised of four non-overlapping open reading frames (ORFs) encoding a transcriptional regulator (ArsR), a low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatases (LMW-PTPase) with hypothetical function, an arsenite efflux pump (Acr3), and an arsenate reductase (ArsC). Heterologous expression of arsenic inducible ars gene cluster conferred arsenic resistance to Escherichia coli ∆ars mutant strain AW3110. The recombinant ArsC was purified and assayed. Site-directed mutagenesis was employed to ascertain the role of specific amino acids in ArsC catalysis. Pro94X (X = Ala, Arg, Cys, and His) amino acid substitutions led to enzyme inactivation. Circular dichroism spectra analysis suggested Pro94 as an essential amino acid for enzyme catalytic activity as it is indispensable for optimum protein folding in P. indicus Grx-coupled ArsC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaltonen EK, Silow M (2008) Trans-membrane topology of the Acr3 family arsenite transporter from Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1778:963–973
Achour AR, Bauda P, Billard P (2007) Diversity of arsenite transporter genes from arsenic-resistant soil bacteria. Res Microbiol 158:128–137
Achour-Rokbani A, Cordi A, Poupin P, Bauda P, Billard P (2010) Characterization of the ars gene cluster from extremely arsenic-resistant Microbacterium sp. strain A33. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:948–955
Bandyopadhyay S, Schumann P, Das SK (2013) Pannonibacter indica sp. nov., a highly arsenate-tolerant bacterium isolated from a hot spring in India. Arch Microbiol 195:1–8
Bandyopadhyay S, Schumann P, Das SK (2015) List of new names and new combinations previously effectively, but not validly, published—validation list no. 150. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:797–798
Biebl H, Pukall R, Lunsdorf H, Schulz S, Allgaier M, Tindall BJ, Wagner-Dobler I (2007) Description of Labrenzia alexandrii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel alphaproteobacterium containing bacteriochlorophyll a, and a proposal for reclassification of Stappia aggregata as Labrenzia aggregata comb. nov., of Stappia marina as Labrenzia marina comb. nov. and of Stappia alba as Labrenzia alba comb. nov., and emended descriptions of the genera Pannonibacter, Stappia and Roseibium, and of the species Roseibium denhamense and Roseibium hamelinense. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1095–1107
Borsodi AK, Micsinai A, Kovács G, Tóth E, Schumann P, Kovács AL, Böddi B, Márialigeti K (2003) Pannonibacter phragmitetus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel alkalitolerant bacterium isolated from decomposing Reed rhizomes in a Hungarian soda lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:555–561
Carlin A, Shi W, Dey S, Rosen BP (1995) The ars operon of Escherichia coli confers arsenical and antimonial resistance. J Bacteriol 177:981–986
Ciria R, Abreu-Goodger C, Morett E, Merino E (2004) GeConT: gene context analysis. Bioinformatics 20:2307–2308
Claros MG, von Heijne G (1994) TopPred II: an improved software for membrane protein structure predictions. Comput Appl Biosci 10:685–686
Gladysheva TB, Oden KL, Rosen BP (1994) Properties of the arsenate reductase of plasmid R773. Biochemistry 33:7288–7293
Hirokawa T, Boon-Chieng S, Mitaku S (1998) SOSUI: classification and secondary structure prediction system for membrane proteins. Bioinformatics 14:378–379
Jensen KF (1993) The Escherichia coli K-12 “wild types” W3110 and MG1655 have an rph frameshift mutation that leads to pyrimidine starvation due to low pyrE expression levels. J Bacteriol 175:3401–3407
Li R, Haile JD, Kennelly PJ (2003) An arsenate reductase from Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 exhibits a novel combination of catalytic characteristics. J Bacteriol 185:6780–6789
Li X, Krumholz LR (2007) Regulation of arsenate resistance in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans G20 by an arsRBCC operon and an arsC gene. J Bacteriol 189:3705–3711
Liu J, Gladysheva TB, Lee L, Rosen BP (1995) Identification of an essential cysteinyl residue in the ArsC arsenate reductase of plasmid R773. Biochemistry 34:13472–13476
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lopez-Maury L, Florencio FJ, Reyes JC (2003) Arsenic sensing and resistance system in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. J Bacteriol 185:5363–5371
Mansour NM, Sawhney M, Tamang DG, Vogl C, Saier MH Jr (2007) The bile/arsenite/riboflavin transporter (BART) superfamily. FEBS J 274:612–629
Meng YL, Liu Z, Rosen BP (2004) As(III) and Sb(III) uptake by GlpF and efflux by ArsB in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 279:18334–18341
Messens J, Silver S (2006) Arsenate reduction: thiol cascade chemistry with convergent evolution. J Mol Biol 362:1–17
Ordóñez E, Letek M, Valbuena N, Gil JA, Mateos LM (2005) Analysis of genes involved in arsenic resistance in Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6206–6215
Poklar N, Lah J, Salobir M, Macˇek P, Vesnaver G (1997) pH and temperature-induced molten globule-like denatured states of equinatoxin II: a study by UV-melting, DSC, far- and near-UV CD spectroscopy, and ANS fluorescence. Biochemistry 36:14345–14352
Rosen BP (1999) Families of arsenic transporters. Trends Microbiol 7:207–212
Sato T, Kobayashi Y (1998) The ars operon in the skin element of Bacillus subtilis confers resistance to arsenate and arsenite. J Bacteriol 180:1655–1661
Shi W, Wu J, Rosen BP (1994) Identification of a putative metal binding site in a new family of metalloregulatory proteins. J Biol Chem 269:19826–19829
Silver S (1996) Bacterial resistances to toxic metal ions—a review. Gene 179:9–19
Sonnhammer EL, von Heijne G, Krogh A (1998) A hidden Markov model for predicting transmembrane helices in protein sequences. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 6:175–182
Tusnady GE, Simon I (1998) Principles governing amino acid composition of integral membrane proteins: application to topology prediction. J Mol Biol 283:489–506
Wang L, Jeon B, Sahin O, Zhang Q (2009) Identification of an arsenic resistance and arsenic-sensing system in Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5064–5073
Zegers I, Martins JC, Willem R, Wyns L, Messens J (2001) Arsenate reductase from S. aureus plasmid pI258 is a phosphatase drafted for redox duty. Nat Struct Biol 8:843–847
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Department of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology, Bhubaneswar, for the CD spectroscopic analysis. This work was supported in part by the funding received from Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (D.O. No. BT/PR9712/NBD/52/91/2007) to SKD. The author SB acknowledges the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India, for providing the research fellowship. We like to thank Dr. BK Mohanty (University of Georgia, USA) for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 400 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bandyopadhyay, S., Das, S.K. Functional analysis of ars gene cluster of Pannonibacter indicus strain HT23T (DSM 23407T) and identification of a proline residue essential for arsenate reductase activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 3235–3244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7390-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7390-2