Abstract
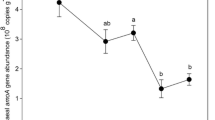
The genetic diversity and distribution of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea (AOA) in nine seasonally frozen soils sampled around the city of Harbin, China, is analyzed based on archaeal amoA gene. Soil samples are divided into four groups by its properties: fertilized/unfertilized mesic (well-balanced supply of moisture) soils and fertilized/unfertilized hydric (abundant of moisture) soils. Clone libraries based on AOA amoA gene polymerase chain reaction products are constructed, and the phylogenetic analysis at 5 % cutoff level shows that AOA members mainly belong to the soil/sediment lineage which includes four clusters, and very few archaeal amoA gene sequences fall into the marine lineage. The four groups of soils have different archaeal amoA gene assemblage, and the available nitrogen and organic carbon are significantly correlated with diversity indexes. The result shows that long-term artificial amendment such as fertilization and agriculture cultivation has an important impact on AOA community shift in terrestrial environment. Moisture may drive the shape of different AOA communities by changing the aerobic environment into anaerobic. Soil composition is another noticeable factor effect AOA community, which can help the shape of a special AOA community with only two species.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beman JM, Francis CA (2006) Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in the sediments of a hypernutrified subtropical estuary: Bahia del Tobari, Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7767–7777
Blair GJ, Lefroy RDB, Lisle L (1995) Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust J Agr Res 46:1459–1466
Caffrey JM, Bano N, Kalanetra K, Hollibaugh JT (2007) Ammonia oxidation and ammonia-oxidizing Bacteria and Archaea from estuaries with differing histories of hypoxia. ISME J 1:660–662
Cao H, Li M, Dang H, Gu JD (2011a) Responses of aerobic and anaerobic ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing microorganisms to anthropogenic pollution in coastal marine environments. Method Enzymol 496:35–62
Cao H, Hong Y, Li M, Gu JD (2011b) Phylogenetic diversity and ecological pattern of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in the surface sediments of the western Pacific. Microb Ecol 62(4):813–823
Cao H, Li M, Hong Y, Gu JD (2011c) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in sediments from the coastal Pearl River estuary to the South China Sea. Anton Leeuw 100(4):545–556
Cao H, Li M, Hong Y, Gu JD (2011d) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in polluted mangrove sediment. Syst Appl Microbiol 34(7):513–523
Cao HL, Hong YG, Li M, Gu JD (2012) Lower abundance of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria detected in the subsurface sediments of the northern South China Sea. Geomicrobiol J 29(4):332–339
Chen XP, Zhu YG, Xia Y, Shen JP, He JZ (2008) Ammonia-oxidizing Archaea: important players in paddy rhizosphere soil? Environ Microbiol 10:1978–1987
Erguder TH, Boon N, Wittebolle L, Marzorati M, Verstraete W (2009) Environmental factors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33(5):855–869
Francis CA, O'Mullan GD, Ward BB (2003) Diversity of ammonia monooxygenase (amoA) genes across environmental gradients in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Geobiology 1(2):129–140
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. PNAS 102:14683–14688
Hatzenpichler R, Lebedeva EV, Spieck E, Stoecker K, Richter A, Daims H, Wagner M (2008) A moderately thermophilic ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeote from a hot spring. PNAS 105:2134–2139
He J, Shen J, Zhang L, Zhu Y, Zheng Y, Xu M, Di HJ (2007) Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing Archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. Environ Microbiol 9:2364–2374
Hughes JB, Hellmann JJ, Ricketts TH, Bohannan BJ (2001) Counting the uncountable: statistical approaches to estimating microbial diversity. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4399–4406
Könneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546
Lam P, Jensen MM, Lavik G, McGinnis DF, Muller B, Schubert CJ, Amann R, Thamdrup B, Kuypers MM (2007) Linking crenarchaeal and bacterial nitrification to anammox in the Black Sea. PNAS 104:7104–7109
Laurent E, Guillaume L, Stefan S (2005) Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online 1:47–50, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2658868. Published online 2007 February 23
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schuster SC, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Li H, Mu ZB, Jiang Y, Gu JD (2011a) Production processes affected prokaryotic amoA gene abundance and distribution in high-temperature petroleum reservoirs. Geomicrobiol J 28(8):692–704
Li M, Cao H, Hong Y, Gu JD (2011b) Spatial distribution and abundances of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in mangrove sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(4):1243–1254
Martin AP (2002) Phylogenetic approaches for describing and comparing the diversity of microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3673–3682
Mincer TJ, Church MJ, Taylor LT, Preston C, Karl DM, DeLong EF (2007) Quantitative distribution of presumptive archaeal and bacterial nitrifiers in Monterey Bay and the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Environ Microbiol 9:1162–1175
Mulvaney RL, Khan SA, Stevens WB, Mulvaney CS (1997) Improved diffusion methods for determination of inorganic nitrogen in soil extracts and water. Biol Fertil Soils 24:413–420
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. PNAS 76:5269–5273
Park HD, Wells GF, Bae H, Criddle CS, Francis CA (2006) Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in wastewater treatment plant bioreactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5643–5647
Raymond M, Rousset F (1995) An exact test for population differentiation. Evolution 49:1280–1283
Reynolds J, Weir BS, Cockerham CC (1983) Estimation for the coancestry coefficent: basis for a short-term genetic distance. Genetics 105:767–779
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(23):7537–7541
Schouten S, van der Meer MT, Hopmans EC, Rijpstra WI, Reysenbach AL, Ward DM, Sinninghe Damsté JS (2007) Archaeal and bacterial glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraether lipids in hot springs of Yellowstone National Park. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:6181–6191
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zhang JB, He JZ (2008) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing Archaea communities of an alkaline sandy loam. Environ Microbiol 10:1601–1611
Szukics U, Hackl E, Zechmeister-Boltensternb S, Sessitscha A (2012) Rapid and dissimilar response of ammonia oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria to nitrogen and water amendment in two temperate forest soils. Microbiol Res 167(2):103–109
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739
Tourna M, Freitag TE, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2008) Growth, activity and temperature responses of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in soil microcosms. Environ Microbiol 10:1357–1364
Treusch AH, Leininger S, Kletzin A, Schuster SC, Klenk HP, Schleper C (2005) Novel genes for nitrite reductase and Amo-related proteins indicate a role of uncultivated mesophilic crenarchaeota in nitrogen cycling. Environ Microbiol 7:1985–1995
Urakawa H, Tajima Y, Numata Y, Tsuneda S (2008) Low temperature decreases the phylogenetic diversity of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in aquarium biofiltration systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:894–900
Venter JC, Remington K, Heidelberg JF, Halpern AL, Rusch D, Eisen JA, Wu D, Paulsen I, Nelson KE, Nelson W, Fouts DE, Levy S, Knap AH, Lomas MW, Nealson K, White O, Peterson J, Hoffman J, Parsons R, Baden-Tillson H, Pfannkoch C, Rogers YH, Smith HO (2004) Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 304:66–74
Wang SF, Xiao X, Jiang LJ, Peng XT, Zhou HY, Meng J, Wang FP (2009) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in hydrothermal vent chimneys of the Juan de Fuca Ridge. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4216–4220
Wang S, Wang Y, Feng X, Zhai L, Zhu G (2011) Quantitative analyses of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in the sediments of four nitrogen-rich wetlands in China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90(2):779–787
Ward BB (2002) How many species of prokaryotes are there. PNAS 99:10234–10236
Weidler GW, Dornmayr-Pfaffenhuemer M, Gerbl FW, Heinen W, Stan-Lotter H (2007) Communities of Archaea and Bacteria in a subsurface radioactive thermal spring in the Austrian Central Alps, and evidence of ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeota. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:259–270
Wuchter C, Abbas B, Coolen MJ, Herfort L, van Bleijswijk J, Timmers P, Strous M, Teira E, Herndl GJ, Middelburg JJ, Schouten S, Sinninghe Damsté JS (2006) Archaeal nitrification in the ocean. PNAS 103:12317–12322
You J, Das A, Dolan EM, Hu ZQ (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing Archaea involved in nitrogen removal. Water Res 43(7):1801–1809
Zhang T, Barry RG, Knowles K, Heginbottom JA, Brown J (2008) Statistics and characteristics of permafrost and ground-ice distribution in the Northern Hemisphere. Polar Geogr 31(1–2):47–68
Zhang LM, Wang M, Prosser JI, Zheng YM, He JZ (2009a) Altitude ammonia-oxidizing Bacteria and Archaea in soils of Mount Everest. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:52–61
Zhang T, Jin T, Yan Q, Shao M, Wells G, Criddle CP, Fang HH (2009b) Occurrence of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in activated sludges of a laboratory scale reactor and two wastewater treatment plants. J Appl Microbiol 107:970–977
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soils of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(2):316–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 696 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CH., Gao, DW. & Tao, Y. Diversity and distribution of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in the seasonally frozen soils in Northeastern China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 6571–6579 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4448-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4448-7