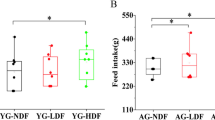
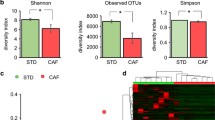
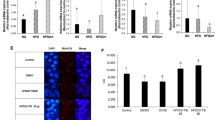
Abstract
Alterations of the gut microbiota induced by diet exert a strong influence on the development of metabolic syndrome. In this study, we prove the hypothesis that the long-term high-fat diet (HFD) may influence gut microbiota directly and/or indirectly by changing the redox state. Lipoic acid (LA), as a universal antioxidant, was used to improve the redox state. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and malondialdehyde (MDA) were analyzed to profile oxidative stress states. PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) was used to describe gut flora structures, while plate count was employed for the quantitative analysis of Escherichia coli, lactobacilli, and enterococcus. The influence of redox state on the vitality of gut-derived bacteria was measured in vitro. ROS and MDA, which significantly decreased in LA mice compared with HFD mice, showed a strong positive association with E. coli and enterococcus (P < 0.05) and a negative association with lactobacilli (P < 0.05). Increased T-AOC in LA mice showed a high positive association with lactobacilli (P < 0.05) and a negative correlation with E. coli and enterococcus. These correlations implied that the dietary effects on the gut microbiota were conferred, at least in part, through an effect on oxidative stress. This study provides evidence that modulation of the redox state by an antioxidant has the potential to improve gut microbiota, which has relevance for metabolic health.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biasucci G, Benenati B, Morelli L, Bessi E, Boehm G (2008) Cesarean delivery may affect the early biodiversity of intestinal bacteria. J Nutr 138(9):1796S–1800S
Bosscher D, Breynaert A, Pieters L (2009) Food-based strategies to modulate the composition of the intestinal microbiota and their associated health effects. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(6):5–11
Brownleea IA, Knighta J, Dettmarb PW, Pearsona JP (2007) Action of reactive oxygen species on colonic mucus secretions. Free Radic Biol Med 43(5):800–808
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Knauf C, Burcelin RG, Tuohy KM, Gibson GR, Delzenne NM (2007) Selective increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia 50(11):2374–2383
Chalmers S, Coats P, McCarron JG (2011) Mitochondrial motility and vascular smooth muscle proliferation. Heart 97(24):e8
Clement K (2011) Bariatric surgery, adipose tissue and gut microbiota. Int J Obesity 35:S7–S15
Cohen MF, Yamasaki H (2003) Involvement of nitric oxide synthase in sucrose-enhanced hydrogen peroxide tolerance of Rhodococcus sp strain APG1, a plant-colonizing bacterium. Nitric Oxide-biol Ch 9(1):1–9
Cui J, Le GW, Yang RL, Shi YH (2009) Lipoic acid attenuates high fat diet-induced chronic oxidative stress and immunosuppression in mice jejunum: a microarray analysis. Cell Immunol 260(1):44–50
Deitch EA, Xu D, Naruhn MB, Deitch DC, Lu Q, Marino AA (1995) Elemental diet and IV-TPN-induced bacterial translocation is associated with loss of intestinal mucosal barrier function against bacteria. Ann Surg 221(3):299–307
Delzenne NM, Neyrinck AM, Bäckhed F, Cani PD (2011) Targeting gut microbiota in obesity: effects of prebiotics and probiotics. Nat Rev Endocrinol 7(11):639–46
Fleissner CK, Huebel N, Abd El-Bary MM, Loh G, Klaus S, Blaut M (2010) Absence of intestinal microbiota does not protect mice from diet-induced obesity. Br J Nutr 104(6):919–929
Gori A, Tincati C, Rizzardini G, Torti C, Quirino T, Haarman M, Ben Amor K, van Schaik J, Vriesema A, Knol J, Marchetti G, Welling G, Clerici M (2008) Early impairment of gut function and gut flora supporting a role for alteration of gastrointestinal mucosa in human immunodeficiency virus pathogenesis. J Clin Microbiol 46(2):757–758
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M (2010) Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140(6):883–899
Hall DM, Buettner GR, Oberley LW, Xu L, Matthes RD, Gisolfi CV (2001) Mechanisms of circulatory and intestinal barrier dysfunction during whole body hyperthermia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280(2):H509–21
Han KS, Balan P, Molist Gasa F, Boland M (2011) Green kiwifruit modulates the colonic microbiota in growing pigs. Lett Appl Microbiol 52(4):379–85
Hildebrandt MA, Hoffmann C, Sherrill-Mix SA, Keilbaugh SA, Hamady M, Chen YY, Knight R, Ahima RS, Bushman F, Wu GD (2009) High-fat diet determines the composition of the murine gut microbiome independently of obesity. Gastroenterology 137(5):1716–1724
Houstis N, Rosen ED, Lander ES (2006) Reactive oxygen species have a causal role in multiple forms of insulin resistance. Nature 440(7086):944–948
Imlay JA (2008) Cellular defenses against superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. Annu Rev Biochem 77:755–776
Ley RE, Bäckhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI (2005) Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(31):11070–5
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444(7122):1009–10
Li M, Wang B, Zhang M, Rantalainen M, Wang S, Zhou H, Zhang Y, Shen J, Pang X, Zhang M, Wei H, Chen Y, Lu H, Zuo J, Su M, Qiu Y, Jia W, Xiao C, Smith LM, Yang S, Holmes E, Tang H, Zhao G, Nicholson JK, Li L, Zhao L (2008) Symbiotic gut microbes modulate human metabolic phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(6):2117–2122
Martínez I, Wallace G, Zhang C, Legge R, Benson AK, Carr TP, Moriyama EN, Walter J (2009) Diet-induced metabolic improvements in a hamster model of hypercholesterolemia are strongly linked to alterations of the gut microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(12):4175–4184
Matsuzawa-Nagata N, Takamura T, Ando H, Nakamura S, Kurita S, Misu H, Ota T, Yokoyama M, Honda M, Miyamoto K, Kaneko S (2008) Increased oxidative stress precedes the onset of high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity. Metabolism 57(8):1071–7
Melstrom KA Jr, Kozlowski R, Hassett DJ, Suzuki H, Bates DM, Gamelli RL, Shankar R (2007) Cytotoxicity of Pseudomonas secreted exotoxins requires OxyR expression. J Srug Res 143(1):50–57
Morris EM, Whaley-Connell AT, Thyfault JP, Britton SL, Koch LG, Wei Y, Ibdah JA, Sowers JR (2009) Low aerobic capacity and high-fat diet contribute to oxidative stress and IRS-1 degradation in the kidney. Am J Nephrol 30(2):112–9
Muccioli GG, Naslain D, Bäckhed F, Reigstad CS, Lambert DM, Delzenne NM, Cani PD (2010) The endocannabinoid system links gut microbiota to adipogenesis. Mol Syst Biol 6:392
Ngo DN, Kim MM, Kim SK (2008) Chitin oligosaccharides inhibit oxidative stress in live cells. Carbohyd Polym 74(2):228–234
Orellana-Gavaldà JM, Herrero L, Malandrino MI, Pañeda A, Sol Rodríguez-Peña M, Petry H, Asins G, Van Deventer S, Hegardt FG, Serra D (2011) Molecular therapy for obesity and diabetes based on a long-term increase in hepatic fatty-acid oxidation. Hepatology 53(3):821–32
Ou SY, Jackson GM, Jiao X, Chen J, Wu JZ, Huang XS (2007) Protection against oxidative stress in diabetic rats by wheat bran feruloyl oligosaccharides. J Agric Food Chem 55(8):3191–3195
Poyton RO, Ball KA, Castello PR (2009) Mitochondrial generation of free radicals and hypoxic signaling. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20(7):332–340
Qian Y, Borowski WJ, Calhoon WD (2011) Intracellular granule formation in response to oxidative stress in Bifidobacterium. Int J Food Microbiol 145(1):320–325
Roberfroid M, Gibson GR, Hoyles L, McCartney AL, Rastall R, Rowland I, Wolvers D, Watzl B, Szajewska H, Stahl B, Guarner F, Respondek F, Whelan K, Coxam V, Davicco MJ, Léotoing L, Wittrant Y, Delzenne NM, Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Meheust A (2010) Prebiotic effects: metabolic and health benefits. Br J Nutr 104(Suppl 2):S1–63
Roy DG, Klaenhammer TR, Hassan HM (1993) Cloning and expression of the manganese superoxide dismutase gene of Escherichia coli in Lactococcus lactis and Lactobacillus gasseri. Mol Gen Genet 239(1–2):33–40
Sarmiento-Rubiano LA, Zúñiga M, Pérez-Martínez G, Yebra MJ (2007) Dietary supplementation with sorbitol results in selective enrichment of lactobacilli in rat intestine. Res Microbiol 158(8–9):694–701
Seib KL, Wu HJ, Srikhanta YN, Edwards JL, Falsetta ML, Hamilton AJ, Maguire TL, Grimmond SM, Apicella MA, McEwan AG, Jennings MP (2007) Characterization of the OxyR regulon of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Mol Microbiol 63(1):54–68
Seksik P, Rigottier-Gois L, Gramet G, Sutren M, Pochart P, Marteau P, Jian R, Doré J (2003) Alterations of the dominant faecal bacterial groups in patients with Crohn's disease of the colon. Gut 52(2):237–242
Sokol H, Seksik P, Rigottier-Gois L, Lay C, Lepage P, Podglajen I, Marteau P, Doré J (2006) Specificities of the fecal microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 12(2):106–111
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444(7122):1027–1031
Turnbaugh PJ, Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Knight R, Gordon JI (2009) The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome:a metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci Transl Med 1(6):6ra14
Wellen KE, Fucho R, Gregor MF, Furuhashi M, Morgan C, Lindstad T, Vaillancourt E, Gorgun CZ, Saatcioglu F, Hotamisligil GS (2007) Coordinated regulation of nutrient and inflammatory responses by STAMP2 is essential for metabolic homeostasis. Cell 129(3):537–548
Xiao Y, Cui J, Shi YH, Sun J, Wang ZP, Le GW (2010) Effects of duodenal redox status on calcium absorption and related genes expression in high-fat diet-fed mice. Nutrition 26(11–12):1188–94
Yang R, Le G, Li A, Zheng J, Shi Y (2006) Effect of antioxidant capacity on blood lipid metabolism and lipoprotein lipase activity of rats fed a high-fat diet. Nutrition 22(11–12):1185–1191
Yoon-Suk K, Kim YJ, Jeon CO, Woojun P (2006) Characterization of naphthalene-degrading Pseudomonas species isolated from pollutant-contaminated sites: oxidative stress during their growth on naphthalene. J Microbio Biotechn 16(11):1819–1825
Yu Y, Du JR, Wang CY, Qian ZM (2008) Protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury by Z-ligustilide in PC12 cells. Exp Brain Res 184(3):307–12
Yuan XP, Wang J, Yao HY (2005) Antioxidant activity of feruloylated oligosaccharides from wheat bran. Food Chem 90(4):759–764
Zhang M, Liu B, Zhang Y, Wei H, Lei Y, Zhao L (2007) Subgroup in patients with ulcerative colitis lactobacilli and Clostridium leptum structural shifts of mucosa-associated. J Clin Microbiol 45(2):496–500
Zhang C, Zhang M, Wang S, Han R, Cao Y, Hua W, Mao Y, Zhang X, Pang X, Wei C, Zhao G, Chen Y, Zhao L (2010) Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. Isme J 4(2):232–241
Zhou JL, Jin GH, Yi YL, Zhang JL, Huang XL (2003) Role of nitric oxide and peroxynitrite anion in lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia–reperfusion in rats. World J Gastroenterol 9(6):1318–22
Zhou W, Wang GJ, Han ZK, Yao W, Zhu WY (2009) Metabolism of flaxseed lignans in the rumen and its impact on ruminal metabolism and flora. Anim Feed Sci Tech 150(1–2):18–26
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30671525), the 12th Five-Year Plan for Science and Technology Development (No. 2012BAD33B05) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. JUSRP111A32).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, Y., Sun, J., Ding, Y. et al. Alterations of the gut microbiota in high-fat diet mice is strongly linked to oxidative stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 1689–1697 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4323-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4323-6