Abstract.
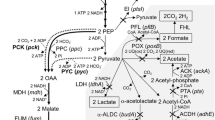
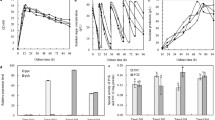
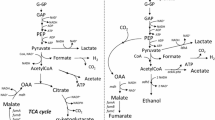
We had previously shown that succinic acid production in a pfl ldhA double mutant strain of Escherichia coli could be enhanced by amplifying the malic enzyme activity. However, recombinant E. coli NZN111 (F– Δpfl::Cam ldhA::Kan) harboring pTrcML, a plasmid containing the E. coli malic enzyme gene, produced a considerable amount of malic acid along with the desired product, succinic acid. To have an insight into the intracellular metabolism, metabolic control analysis was carried out. From the results of a simulation, it was predicted that supplying additional reducing power could enhance succinic acid production. More reduced carbon substrate sorbitol was thus examined for the possibility of matching the potential during succinic acid production. When NZN111 (pTrcML) was cultured in LB medium containing 20 g sorbitol/l under a CO2 atmosphere, 10 g succinic acid/l was produced. The apparent yield of succinic acid was 1.1 g succinic acid/g sorbitol, which is 85% of the maximum theoretical yield. Therefore, it was found that redox balancing was important for the enhanced production of succinic acid in metabolically engineered E. coli.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, .S., Lee, .S. Importance of redox balance on the production of succinic acid by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58, 286–290 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-001-0899-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-001-0899-y